What are the 7 principles of GDPR
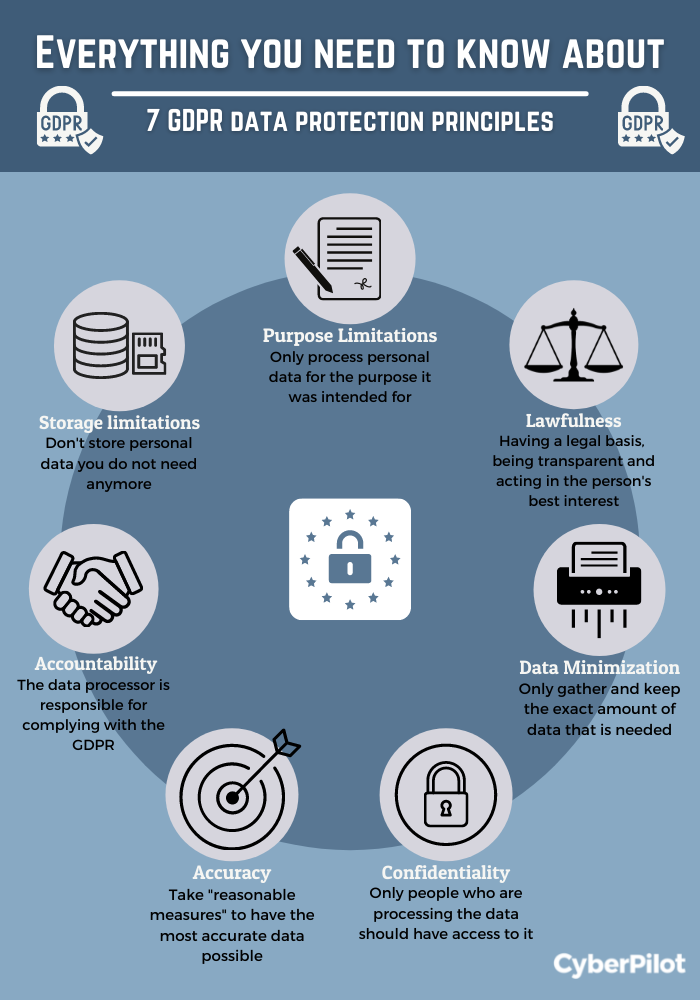
The principles are: Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency; Purpose Limitation; Data Minimisation; Accuracy; Storage Limitations; Integrity and Confidentiality; and Accountability. We take you through an example of creating an online newsletter to illustrate how each principle works.
What are the principles of the data protection Act
The UK GDPR sets out seven key principles:Lawfulness, fairness and transparency.Purpose limitation.Data minimisation.Accuracy.Storage limitation.Integrity and confidentiality (security)Accountability.
Is GDPR incorporated 7 principles True or false
The GDPR sets out seven principles for the lawful processing of personal data. Processing includes the collection, organisation, structuring, storage, alteration, consultation, use, communication, combination, restriction, erasure or destruction of personal data.
What are the 8 rules of data protection under the data protection Act
Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency; ▪ Purpose limitation; ▪ Data minimisation; ▪ Accuracy; ▪ Storage limitation; ▪ Integrity and confidentiality; and ▪ Accountability. These principles are found right at the outset of the GDPR, and inform and permeate all other provisions of that legislation.
What is principle 7 of the data protection Act 1998
7Appropriate technical and organisational measures shall be taken against unauthorised or unlawful processing of personal data and against accidental loss or destruction of, or damage to, personal data.
What is principle 7 of the data protection Act and how can it be avoided
Principle 7 – Accountability
The final GDPR principle is accountability. This requires those processing personal data to take responsibility for their interactions with personal data and their adherence to the other principles.
How many principles are there under data protection law
The Seven Principles
At the heart of both the GDPR and the DPA are principles that are designed to act as the foundations upon which data protection legislation is built, informing the ways in which all organisations should adhere to data protection and compliance issues.
Is GDPR a rule or law
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is legislation that updated and unified data privacy laws across the European Union (EU). GDPR was approved by the European Parliament on April 14, 2016 and went into effect on May 25, 2018. GDPR replaces the EU Data Protection Directive of 1995.
What is principle 7 of the Data Protection Act and how can it be avoided
Principle 7 – Accountability
The final GDPR principle is accountability. This requires those processing personal data to take responsibility for their interactions with personal data and their adherence to the other principles.
Why is the 8 principles for Data Protection Act important
The 8 principles of the Act guided its purpose and the data protection policies of organisations. At its core, the DPA 1998 has eight principles which were used by organisations to design their own data protection policies. Complying with these was essential for organisations to meet their obligations.
What is data protection Directive Article 7
The data subject shall have the right to withdraw his or her consent at any time. The withdrawal of consent shall not affect the lawfulness of processing based on consent before its withdrawal. Prior to giving consent, the data subject shall be informed thereof. It shall be as easy to withdraw as to give consent.
What is the data protection law in the UK
The Data Protection Act 2018 is the UK's implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Everyone responsible for using personal data has to follow strict rules called 'data protection principles'. They must make sure the information is: used fairly, lawfully and transparently.
What is principle 6 of the Data Protection Act
What is the sixth principle about “Appropriate security” includes “protection against unauthorised or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage”.
What is principle 7 of the Data Protection Act 1998
7Appropriate technical and organisational measures shall be taken against unauthorised or unlawful processing of personal data and against accidental loss or destruction of, or damage to, personal data.
Is the UK GDPR a law
Yes. The GDPR is retained in domestic law as the UK GDPR, but the UK has the independence to keep the framework under review. The 'UK GDPR' sits alongside an amended version of the DPA 2018. The key principles, rights and obligations remain the same.
Is GDPR an international law
The statement that an international organization must be “set up by, or on the basis of an agreement between states” allows an organization given a mandate under public international law is considered subject to the requirements and rigors of the GDPR.
How many principles are there in the Data Protection Act 1998
8 principles
The 8 principles of the Act guided its purpose and the data protection policies of organisations. At its core, the DPA 1998 has eight principles which were used by organisations to design their own data protection policies. Complying with these was essential for organisations to meet their obligations.
What is S 7 of the data protection Act 1998
Personal data shall be processed in accordance with the rights of data subjects. 7. Personal data shall be protected by appropriate technical and organisational measures against unauthorised or unlawful processing and against accidental loss, destruction or damage.
What is Principle 7 of the data protection Act and how can it be avoided
Principle 7 – Accountability
The final GDPR principle is accountability. This requires those processing personal data to take responsibility for their interactions with personal data and their adherence to the other principles.
What is the data protection law in Europe
What is the GDPR The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European law that established protections for privacy and security of personal data about individuals in European Economic Area (“EEA”)-based operations and certain non-EEA organizations that process personal data of individuals in the EEA.
When did UK GDPR become law
25 May 2018
New rules relating to how we collect and process personal data – the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – came into effect in the UK on 25 May 2018.
Is GDPR a regulation in EU law
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European law that established protections for privacy and security of personal data about individuals in European Economic Area (“EEA”)-based operations and certain non-EEA organizations that process personal data of individuals in the EEA.
Is GDPR a law in the US
There is no federal data privacy law like GDPR in the United States. There are some national laws that have been put in place to regulate the use of data in certain industries. 1974 – The U.S. Privacy Act which outlines rights and restrictions regarding data held by US government agencies.
How many data protection principles are there in PDPA 2010
7 PRINCIPLES
7 PRINCIPLES OF DATA PROTECTION
Third – Disclosure Principle destination is a subject of personal data in order to identify the purposes for which personal data are to be disclosed.
What is the Data Protection Act 1998 A level
The Data Protection Act 1998
The Act also gives data subjects certain rights, such as the right to request a copy of the data held about them, the right to correct the data held about them and the right to prevent marketing using contact details provided by the data subject.