Can chemicals cause mutations
A mutagen is a chemical or physical agent capable of inducing changes in DNA called mutations. Examples of mutagens include tobacco products, radioactive substances, x-rays, ultraviolet radiation and a wide variety of chemicals.
Which is an example of a genetic mutation
If a parent carries a gene mutation in their egg or sperm, it can pass to their child. These hereditary (or inherited) mutations are in almost every cell of the person's body throughout their life. Hereditary mutations include cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease.
How mutations can be both beneficial and harmful in biology
Some mutations are beneficial and improve fitness. An example is a mutation that confers antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Other mutations are harmful and decrease fitness, such as the mutations that cause genetic disorders or cancers .
What is the role of mutation in evolution
Mutation is the engine of evolution in that it generates the genetic variation on which the evolutionary process depends. To understand the evolutionary process we must therefore characterize the rates and patterns of mutation.
What chemicals cause DNA mutations
The most commonly used chemical mutagens are alkylating agents such as ethylmethane sulfonate and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea that induce point mutations in DNA.
What chemicals can alter your DNA
In-vitro, animal, and human investigations have identified several classes of environmental chemicals that modify epigenetic marks, including metals (cadmium, arsenic, nickel, chromium, methylmercury), peroxisome proliferators (trichloroethylene, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid), air pollutants (particulate …
What can cause DNA to mutate
Mutations result either from errors in DNA replication or from the damaging effects of mutagens, such as chemicals and radiation, which react with DNA and change the structures of individual nucleotides.
What are 4 causes of mutations
Mutations are caused by environmental factors k nown as mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents. Mutations may be spontaneous in nature.
How does UV radiation cause mutations
Ultraviolet (UV) light is a form of radiation that acts as a mutagen, an agent that causes mutations in DNA. Exposure to ultraviolet light causes chemical changes that alter the shape of your DNA, and the process that corrects DNA's shape can also cause changes to the DNA code.
How does UV light cause mutations
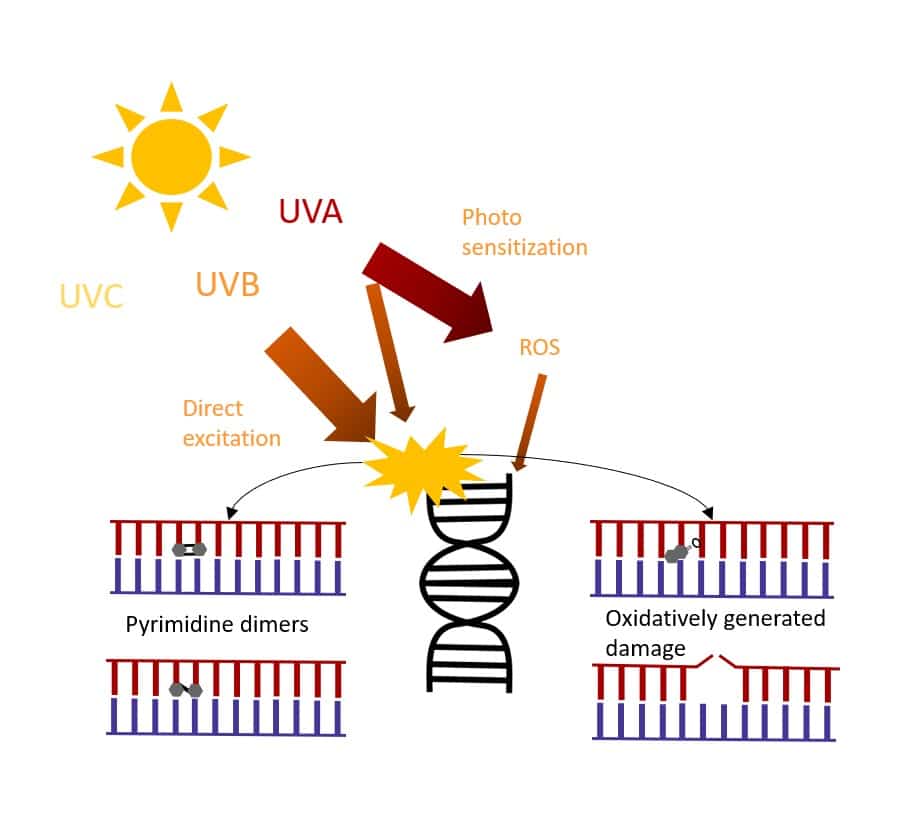
UVA (and also UVB) radiation cause indirect damage to DNA via absorption of photons by non-DNA chromophores. This generates reactive oxygen species like singlet oxygen or hydrogen peroxide that oxidize the DNA bases causing mutations.
What are 3 causes of DNA mutations
A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism. Mutations can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division, exposure to mutagens or a viral infection.
What are 3 common chemical agents that may cause DNA mutations
Mutagens cause changes in the base pairs of DNA. Three different types of mutagens are 5-Bromouracil (5BU or BrU), 2-Aminopurine, and nitrous acid.
What are 3 agents that can cause DNA damage
Exogenous DNA damage, on the other hand, occurs when environmental, physical and chemical agents damage the DNA. Examples include UV and ionizing radiation, alkylating agents, and crosslinking agents.
What are 3 factors that can cause DNA mutations
As previously mentioned, DNA in any cell can be altered by way of a number of factors, including environmental influences, certain chemicals, spontaneous mutations, and errors that occur during the process of replication. Each of these mechanisms is discussed in greater detail in the following sections.
What are the 4 causes of mutations
Mutations are caused by environmental factors k nown as mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents. Mutations may be spontaneous in nature.
What are 3 examples of causes of mutation
Mutations are caused by environmental factors known as mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents.
Does UV damage DNA
One way ultraviolet light can harm cells is by directly damaging DNA. This is something many of us are reminded of every spring and summer – it's the cause of sunburn! As the name suggests, direct DNA damage occurs when a photon of UV light hits DNA.
Does UV radiation cause genetic damage
While UVA and UVB rays differ in how they affect the skin, they both do harm. Unprotected exposure to UVA and UVB damages the DNA in skin cells, producing genetic defects, or mutations, that can lead to skin cancer and premature aging.
What factors increase DNA mutation
Mutations happen spontaneously. The rate of mutation can be increased by environmental factors such as UV radiation , X-rays, gamma rays and certain types of chemicals such as bromine.
What is the most mutagenic effect of UV radiation on DNA
The damage to DNA caused by UV radiation can be direct or indirect. The direct DNA damage consists predominantly of dimerized pyrimidines, and it is this type of damage that is likely the most relevant for skin cancer induction.
What things cause DNA mutations
Mutations result either from errors in DNA replication or from the damaging effects of mutagens, such as chemicals and radiation, which react with DNA and change the structures of individual nucleotides. All cells possess DNA-repair enzymes that attempt to minimize the number of mutations that occur (Section 14.2).
How does UV cause mutations
Ultraviolet (UV) light induces specific mutations in the cellular and skin genome such as UV-signature and triplet mutations, the mechanism of which has been thought to involve translesion DNA synthesis (TLS) over UV-induced DNA base damage.
How does UV light damage DNA
UVA (and also UVB) radiation cause indirect damage to DNA via absorption of photons by non-DNA chromophores. This generates reactive oxygen species like singlet oxygen or hydrogen peroxide that oxidize the DNA bases causing mutations.
What are 4 factors which can cause mutations or changes in genetic materials
Several factors cause genetic conditions, including:Mutation of one gene (monogenic).Mutation of multiple genes (multifactorial inheritance).Mutation of one or more chromosomes.Environmental factors (chemical exposure, UV rays) that change your genetic makeup.
What causes DNA mutations
Mutations result either from errors in DNA replication or from the damaging effects of mutagens, such as chemicals and radiation, which react with DNA and change the structures of individual nucleotides. All cells possess DNA-repair enzymes that attempt to minimize the number of mutations that occur (Section 14.2).