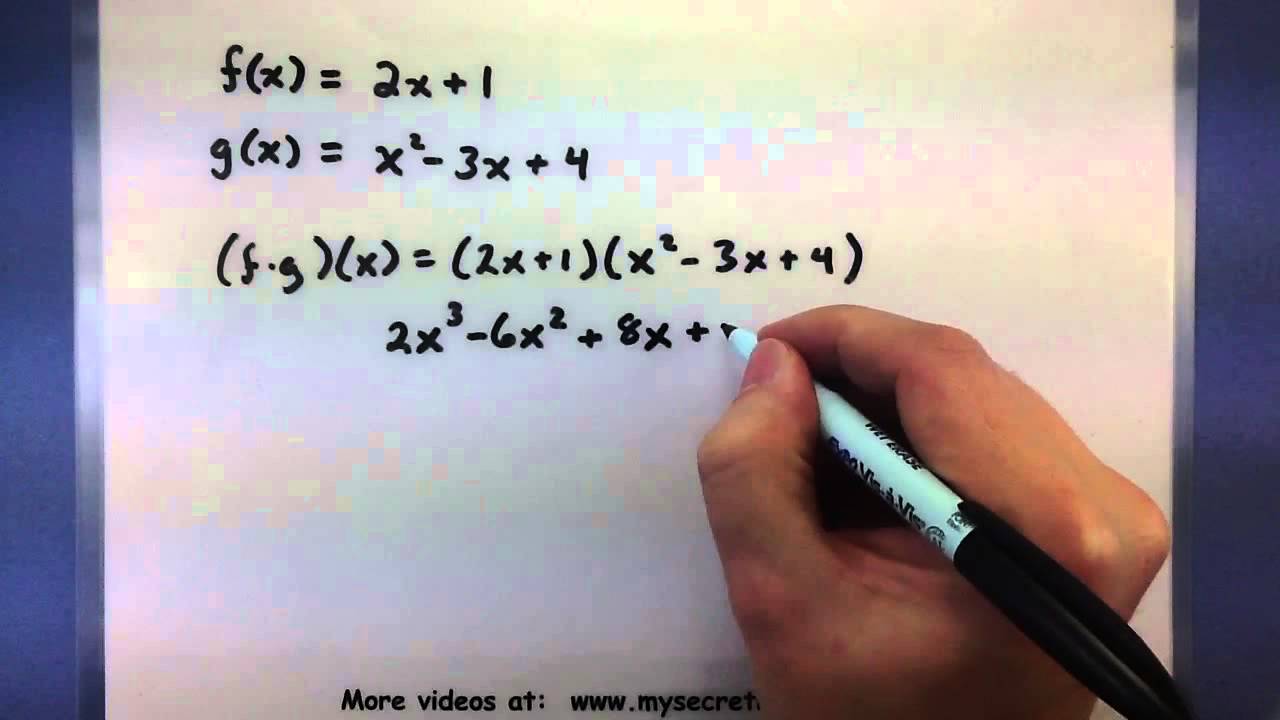What is the distributive law in maths year 4
Distributive Law in Maths states that multiplying a group of large 2 or 3-digit numbers will create the same value as those numbers being partitioned, multiplied and added together. This is the same as (50 x 8) + (2 x 8).
What is the Bodmas rule
According to BODMAS rule, the brackets have to be solved first followed by powers or roots (i.e. of), then Division, Multiplication, Addition, and at the end Subtraction.
What is an example of a distributive law
It is used to solve expressions easily by distributing a number to the numbers given in brackets. For example, if we apply the distributive property of multiplication to solve the expression: 4(2 + 4), we would solve it in the following way: 4(2 + 4) = (4 × 2) + (4 × 4) = 8 + 16 = 24.
Is Bodmas or Pemdas correct
Both BODMAS and PEMDAS are correct and used in different areas of the world. BODMAS is common in the UK while PEMDAS is used in the US.
What is the Bodmas rule for 4 10 15 5 * 4 2 * 2
Hence, the final answer is 72. Therefore, 4(10+15÷5×4-2×2) = 72.
What are 2 examples of distributive property
Examples of distributive property of multiplication over addition and subtraction:Example 1: Solve the expression: 6 × ( 20 + 5 ) using the distributive property of multiplication over addition.Example 2: Solve the expression 2 × ( 2 + 4 ) using the distributive law of multiplication over addition.
What is the distributive law of multiplication
distributive law, also called distributive property, in mathematics, the law relating the operations of multiplication and addition, stated symbolically as a(b + c) = ab + ac; that is, the monomial factor a is distributed, or separately applied, to each term of the binomial factor b + c, resulting in the product ab + …
Is Pemdas sometimes wrong
There is no universally accepted rule as there are several: PEMDAS, BEDMAS, PE(MD)AS. It is not possible to say what is correct and what is incorrect. There are different rules, leading to different results. The expression is not well defined.
Is Bodmas flawed
Unfortunately, in mathematical terms it is wrong! If you look at the rules of BIDMAS/BODMAS you will see that multiplication comes before addition (the two operations we are dealing with) and therefore you should have dealt with the Multiplication BEFORE you dealt with the Addition.
What is 2 4 6 8 10 all the way to 200
What is 2 4 6 8 10 all the way to 200 So in from 2 to 200, there are 100 even numbers. 10100. Thus the sum is 10100.
What is the equation for 2 4 6 8 10
This is an arithmetic sequence since there is a common difference between each term. In this case, adding 2 to the previous term in the sequence gives the next term. In other words, an=a1+d(n−1) a n = a 1 + d ( n – 1 ) . This is the formula of an arithmetic sequence.
Does distributive property work with multiplication
The distributive property of multiplication lets you simplify expressions wherein you multiply a number by a sum or difference. According to this property, the product of a sum or difference of a number is equal to the sum or difference of the products.
What does it mean if 2 forms are equivalent
What are equivalent expressions Equivalent expressions are expressions that work the same even though they look different. If two algebraic expressions are equivalent, then the two expressions have the same value when we plug in the same value(s) for the variable(s).
Does multiplication distribute over multiplication
The distributive laws are among the axioms for rings (like the ring of integers) and fields (like the field of rational numbers). Here multiplication is distributive over addition, but addition is not distributive over multiplication.
What is an example of distributive multiplication
The distributive property of multiplication over addition is used when we multiply a value by the sum of two or more numbers. For example, let us solve the expression: 5(5 + 9). This expression can be solved by multiplying 5 by both the addends. So, 5(5) + 5(9) = 25 + 45 = 70.
What is the hardest math equation
The equation x3+y3+z3=k is known as the sum of cubes problem. While seemingly straightforward, the equation becomes exponentially difficult to solve when framed as a “Diophantine equation” — a problem that stipulates that, for any value of k, the values for x, y, and z must each be whole numbers.
Is Pemdas still correct
Which is correct: BODMAS or PEMDAS Both BODMAS and PEMDAS are correct and used in different areas of the world. BODMAS is common in the UK while PEMDAS is used in the US. BODMAS stands for Brackets, Order, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction.
What is the correct answer to 2 5 * 4 8 4 ⁄ 5
2+5*4-8÷ ⅘ = 12.
What is 1 2 3 4 5 6 all the way to 100
According to arithmetic progression, natural numbers can be written down as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 to 100. Basically, the sum of the first 100 natural numbers is equal to 5050.
What is the rule for 1 3 5 7 9
This is an arithmetic sequence since there is a common difference between each term. In this case, adding 2 to the previous term in the sequence gives the next term.
What is the answer to 8 5 6 2 1 4
8 5/6÷2 1/4 = 10627 = 3 2527 ≅ 3.9259259. Spelled result in words is one hundred six twenty-sevenths (or three and twenty-five twenty-sevenths).
Why can’t you distribute with multiplication
You can't do that because multiply is not one level above divide; they're at the same level. You can distribute only when moving down one level.
What are the rules of distributive property
distributive law, also called distributive property, in mathematics, the law relating the operations of multiplication and addition, stated symbolically as a(b + c) = ab + ac; that is, the monomial factor a is distributed, or separately applied, to each term of the binomial factor b + c, resulting in the product ab + …
Is the expression x3 x3 x3 equivalent to x3 3 3
Is the expression x3•x3•x3 equivalent to x3•3•3 Why or why not Explain your reasoning. It is not because when numbers have an exponent and are multiplied, the exponents are added.
Are two equations equivalent
Two systems of equations are equivalent if they have the same solution(s). This article reviews how to tell if two systems are equivalent. Systems of equations that have the same solution are called equivalent systems.