Is space absolute 0
It is only one degree warmer than absolute zero or zero on the Kelvin scale – it is the lowest temperature that's theoretically possible. Outer space has a baseline temperature of 2.7 Kelvin, minus 453.8 degrees Fahrenheit or minus 270.45 degrees Celsius, according to LiveScience.
Why isn’t space absolute zero
Completely empty space would have no temperature since there are no molecules there – it would make no sense to discuss the temperature of nothingness. We wouldn't even call it zero degrees. Technically, there must be matter present to have an associated temperature.
Can you reach absolute zero in space
Even at its very end, no matter how far into the future we go, the Universe will always continue to produce radiation, ensuring that it will never reach absolute zero.
What happens to a human at absolute zero
The Law of Conservation of Energy states that it isn't possible to achieve absolute zero. To answer your question, if the human body were to reach absolute zero somehow, it would stop all motion and become truly lifeless, same as any other object.
Are black holes absolute zero
Black holes are freezing cold on the inside, but incredibly hot just outside. The internal temperature of a black hole with the mass of our Sun is around one-millionth of a degree above absolute zero.
What does absolute 0 look like
The theoretical temperature is determined by extrapolating the ideal gas law; by international agreement, absolute zero is taken as −273.15 degrees on the Celsius scale (International System of Units), which equals −459.67 degrees on the Fahrenheit scale (United States customary units or imperial units).
Why is 0 kelvin impossible
According to the third law of thermodynamics, “ A system has 0 entropy at 0 K if and only if the system is in the pure state.” Since a system can not avoid 100 % interaction with the environment and always exchange energy with the surroundings, it is impossible to achieve 0 K temperature.
Would absolute zero cause a black hole
Again given that you'd expect a black hole to be absolute zero. But it isn't the space time around them emits hawking radiation. And that radiation is surprisingly thermal what's hawking radiation.
How cold is absolute 0
−459.67 °F
absolute zero, temperature at which a thermodynamic system has the lowest energy. It corresponds to −273.15 °C on the Celsius temperature scale and to −459.67 °F on the Fahrenheit temperature scale.
Is there an absolute hot
At one extreme is something called Planck temperature, and is equivalent to 1.417 x 1032 Kelvin (or something like 141 million million million million million degrees). This is what people will often refer to as the 'absolute hot'.
What’s colder than absolute zero
Nothing can be colder than absolute zero (0K)! Negative absolute temperatures (or negative Kelvin temperatures) are hotter than all positive temperatures – even hotter than infinite temperature.
Does absolute zero feel cold
At minus 273.15 degrees it literally can't get any colder.
Could a black hole stop
In pure general relativity, with no other modifications or considerations of other physics, they remain black for eternity. Once one forms, it will just hang out there, being a black hole, forever.
Did Einstein reject black holes
In a paper written in 1939, Albert Einstein attempted to reject the notion of black holes that his theory of general relativity and gravity, published more than two decades earlier, seemed to predict.
Is absolute zero infinite
Absolute zero cannot be reached — unless you have an infinite amount of energy or an infinite amount of time. Scientists in Vienna (Austria) studying the connection between thermodynamics and quantum physics have now found out that there is a third option: Infinite complexity.
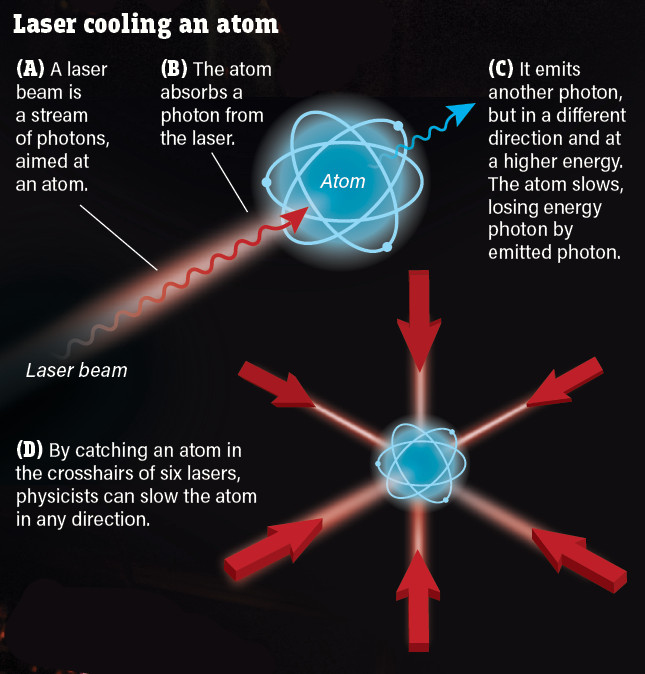
What’s the closest to absolute zero
The exact temperature scientists measured was 38 trillionths of a degree above -273 degrees Celsius — the closest that has ever been measured to absolute zero in a lab. Absolute zero in Kelvin, a temperature thought to be impossible for anything in the universe to reach, is -273.15 degrees Celsius.
Is a black hole infinitely hot
Stellar black holes are very cold: they have a temperature of nearly absolute zero – which is zero Kelvin, or −273.15 degrees Celsius. Supermassive black holes are even colder. But a black hole's event horizon is incredibly hot. The gas being pulled rapidly into a black hole can reach millions of degrees.
Are black holes colder than absolute zero
Black holes are freezing cold on the inside, but incredibly hot just outside. The internal temperature of a black hole with the mass of our Sun is around one-millionth of a degree above absolute zero.
Is absolute zero hotter than the Sun
Negative Temperatures That Are Hotter Than The Sun Scientists have cooled potassium gas to one billionth of a degree below absolute zero. But in the quantum world, that's actually hotter than the Sun. It's hotter, even, than infinity degrees Kelvin.
Can it snow at absolute zero
According to AccuWeather, “Only at absolute zero (equivalent to –273.15°C or –459.67°F) would snow become impossible.”
What is the 142 Nonillion
142 NONILLION degrees Celsius is the ultimate heat level that, according to scientists, represents the absolute heat point in our universe.
What is 142 Nonillion degrees
As such, it seems that the highest possible known temperature is 142 nonillion kelvins (1032 K.). This is the highest temperature that we know of according to the standard model of particle physics, which is the physics that underlies and governs our universe. Beyond this, physics starts to breakdown.
How long is 1 minute in a black hole
Black hole news: Standing on edge of black hole would cause 700 years to pass in 1 minute.
What destroys a black hole
Eventually, in theory, black holes will evaporate through Hawking radiation. But it would take much longer than the entire age of the universe for most black holes we know about to significantly evaporate.
Who proved E mc2 is wrong
ECG Sudarshan and his colleagues suggested that if the said particles were created initially with the help of faster-than-light speed during particle collisions, there will be no need of acceleration or infinite energy.