Is there a condition where you see in 2d
Stereoblindness (also stereo blindness) is the inability to see in 3D using stereopsis, or stereo vision, resulting in an inability to perceive stereoscopic depth by combining and comparing images from the two eyes.
Why am I seeing in 3D
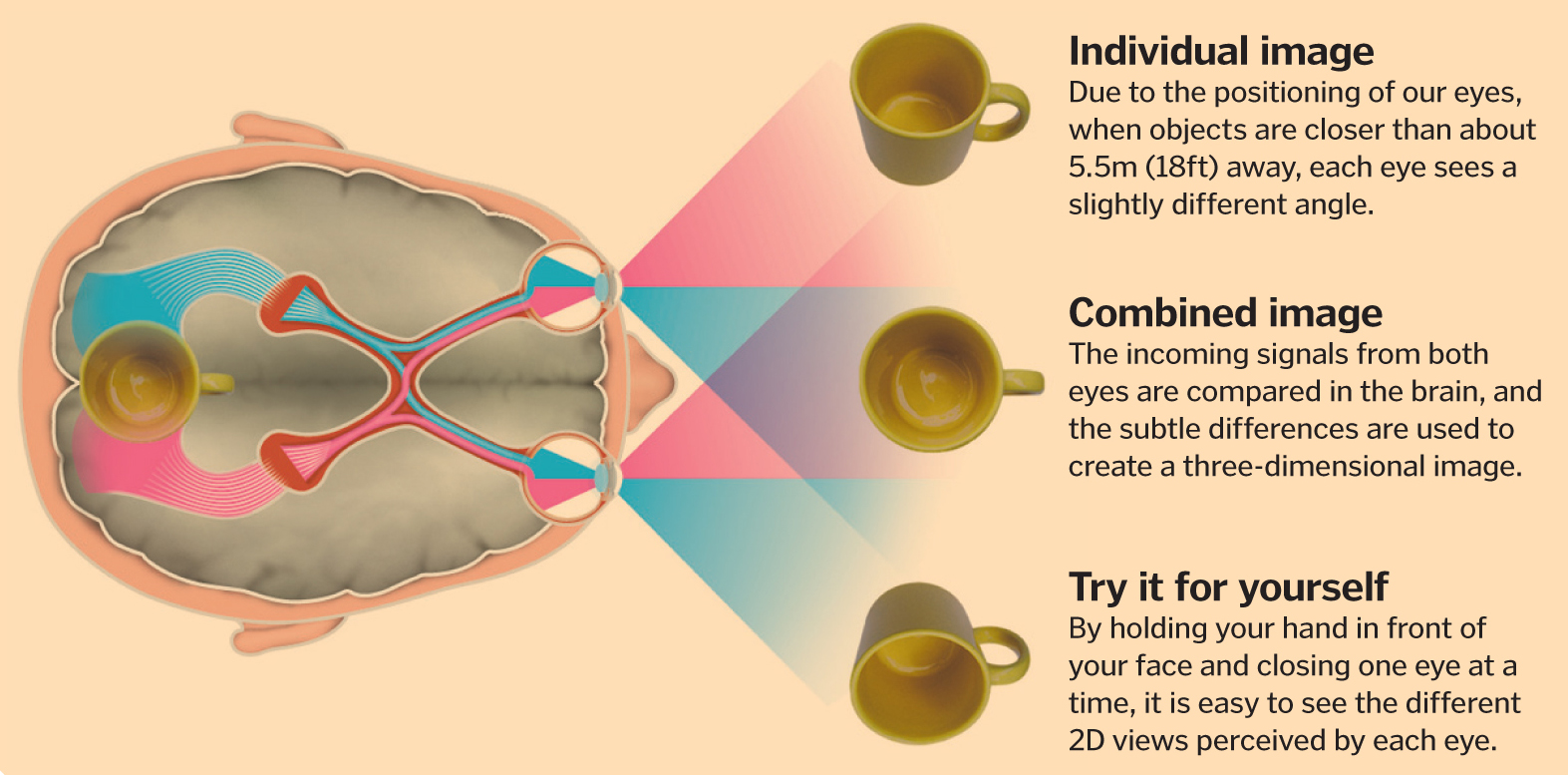
In a natural, real life setting the retina in each eye forms a two-dimensional image of our surroundings. Each eye produces a slightly different image because the eyes are in different locations. Our brain processes these two images and combines them into one 3D visual experience.
How does 3D vision work
3D vision is the direct effect of our brains merging the images from both of our eyes together. Each of our eyes creates a single two-dimensional image, but the brain is able to interpret depth when it merges both two-dimensional images and understands the difference between them.
Is stereo blindness a disability
Some people who suffer from stereo-blindness also have trouble reading and may fall behind in school because of their “disability.” Processing all types of information on TV, on paper, or on the white board in school can, unfortunately, limit a person from finding a job that they like, are good at, or may be a good …
Can you only see 2D with one eye
Humans can perceive depth when viewing with one eye, and even when viewing a two-dimensional picture of a three-dimensional scene. However, viewing a real scene with both eyes produces a more compelling three-dimensional experience of immersive space and tangible solid objects.
Can some people only see in 2D
For the 3% of the population with asymmetrical eyes, the brain cannot fuse the images from the eyes to create a 3D image.
Can a one eyed person see 3D
Humans can perceive depth when viewing with one eye, and even when viewing a two-dimensional picture of a three-dimensional scene. However, viewing a real scene with both eyes produces a more compelling three-dimensional experience of immersive space and tangible solid objects.
Why am I seeing in 2D
We see the world in 2D if we only look with one eye but our brain attempts to give us depth perception clues. The reason more than one eye is needed for 3D or stereoscopic vision is that the 2 eyes are looking at things from a different vantage.
Can you still see in 3D with one eye
Humans can perceive depth when viewing with one eye, and even when viewing a two-dimensional picture of a three-dimensional scene. However, viewing a real scene with both eyes produces a more compelling three-dimensional experience of immersive space and tangible solid objects.
What is 4D vision
4D Vision is an example of an AI problem-solving technique. The cycle of discover, dream, design and deliver helps to set out a strategy for developing solutions to an existing problem; a graphical representation is shown below.
Why can’t my child see 3D
Children need a clear, sharp image in each eye in order for their vision to develop properly. If something upsets that balance, it can lead to reduced vision – known as amblyopia – in one or both eyes and poor 3D vision. If the problem only affects one eye it can easily go unnoticed, resulting in a 'lazy eye'.
Why can’t I see 3D
Not everyone can see in depth, either with 3D movie glasses or even with their daily vision. The most common causes of not having depth perception (or stereopsis) are: 1) Blurry Vision: Refractive errors like myopia, astigmatism, and hyperopia can cause a blurry image to he brain which inhibits depth perception.
Do both eyes see the same image
Each eye looks at an item from a slightly different angle and registers a slightly different image on its retina (the back of the eye). The two images are sent to the brain where the information is processed. In a fraction of a second our brain brings one three-dimensional image to our awareness.
Can you see OK with one eye
Sudden loss of vision in one eye can take longer to adapt to than if the vision loss has happened gradually. However, once someone has adjusted to monocular vision, they find that they can read, watch television and perform many daily activities without any problems.
Do you see in 2D with one eye closed
And it's not entirely accurate to say we see 2D with one eye. If you close one eye, your brain still extrapolates a 3D world form shadows and context clues. If you only have one eye open and move your head, you still get a lot of the same information as if you had two eyes.
What is 2D vision like
While it is impossible for humans to see the world in 2D, we can simulate this experience by covering one eye. This eliminates the binocular cues that are necessary for depth perception, leaving only the monocular cues. The result is a flatter, less detailed view of the world.
Do you see in 2D if you close one eye
And it's not entirely accurate to say we see 2D with one eye. If you close one eye, your brain still extrapolates a 3D world form shadows and context clues. If you only have one eye open and move your head, you still get a lot of the same information as if you had two eyes.
Would we see 4D if we had 3 eyes
You would need six eyes to see in 4-D. The reason for this is that our point of view is one dimension less than our current dimension. Therefore, to see in 4-D, you need to have a spherical view and maybe even spheric tesseract shaped eyes.
Is the human eye 3D or 4D
We are 3D creatures, living in a 3D world but our eyes can show us only two dimensions. The depth that we all think we can see is merely a trick that our brains have learned; a byproduct of evolution putting our eyes on the front of our faces.
Can you see 3D with one eye
Humans can perceive depth when viewing with one eye, and even when viewing a two-dimensional picture of a three-dimensional scene. However, viewing a real scene with both eyes produces a more compelling three-dimensional experience of immersive space and tangible solid objects.
Why can I see 3D with one eye
According to the study, current thinking is that it takes two visual images – one from each eye – to be combined in the visual cortex of the brain to produce our sense of depth that produces the “special” 3D effect. But the St Andrews study suggests that, in fact, both eyes are not necessary for this 3D experience.
Do we use both eyes to see
The human visual system is a complex network including the eye, ocular nerves, and key brain areas that process visual information. Under most circumstances, we use information from both eyes to create a single visual image. This ability to converge information from both eyes is called binocular vision.
Do you see better with both eyes
In all of the experiments, two eyes facilitated performance. The findings suggest that the binocular system is able to detect the matching information, that is, the concordance, in the monocular optic arrays and to use that information to increase visual efficiency.
Can you see 3d with only one eye
Humans can perceive depth when viewing with one eye, and even when viewing a two-dimensional picture of a three-dimensional scene. However, viewing a real scene with both eyes produces a more compelling three-dimensional experience of immersive space and tangible solid objects.
Do you see the same out of both eyes
Unaided Vision is Often Similar
In most cases, you expect similar natural vision between the two eyes. If you wear eyeglasses, the lenses are usually similar in power. It is uncommon for children to have a sizeable difference – or anisometropia – between the two eyes.