Is Heartbleed bug fixed
The Heartbleed fix
1g of the OpenSSL library, released on April 8, 2014, and was also included in all subsequent versions of the software. You can fix the Heartbleed vulnerability by upgrading to the latest version of OpenSSL, and can find links to all the latest code on the OpenSSL website.
What is the Heartbleed virus 2014
Heartbleed is a security bug in some outdated versions of the OpenSSL cryptography library, which is a widely used implementation of the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. It was introduced into the software in 2012 and publicly disclosed in April 2014.
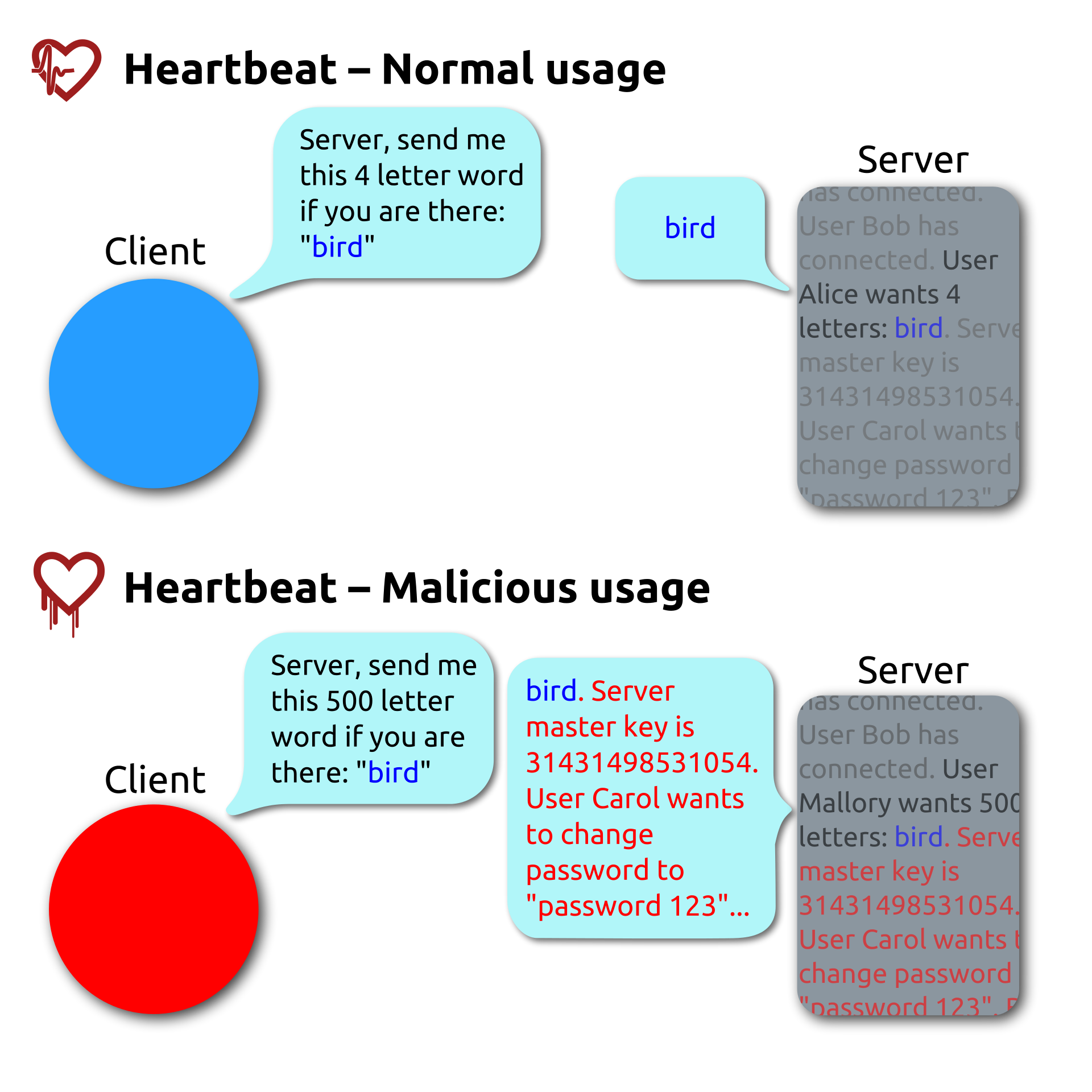
What is the heartbeat bug 2014
The Heartbleed bug is a vulnerability in open source software that was first discovered in 2014. Anyone with an internet connection can exploit this bug to read the memory of vulnerable systems, leaving no evidence of a compromised system.
Why was the heartbleed bug so concerning
Heartbleed vulnerability behavior
The Heartbleed vulnerability weakens the security of the most common Internet communication protocols (SSL and TSL). Websites affected by Heartbleed allow potential attackers to read their memory. That means the encryption keys could be found by savvy cybercriminals.
Is Heartbleed a virus
Heartbleed was a vulnerability in some implementations of OpenSSL, an open source cryptographic library. It was publicly announced by researchers on April 7, 2014 and patched the same month.
Has the Log4j exploit been fixed
Since December, most vendors have published security updates that resolve the Log4j flaw within their applications, and Apache themselves have released fixes and updated versions that remediate the vulnerability. With that being said, thousands of systems are still vulnerable today.
What does CVE 2014 6271 belong to
The Shellshock Vulnerability (CVE-2014-6271) is a serious vulnerability in Bash on Linux. According to RedHat, “A flaw was found in the way Bash (aka bourne-again shell) evaluated certain specially crafted environment variables.
What is heartbeat extension
The HiveMQ Heartbeat Extension allows seamless integration of HiveMQ with load balancers and proxies, by creating an HTTP endpoint that can be used for health checks.
Which type of security flaw is the Heartbleed bug
The Heartbleed Bug is a serious vulnerability in the popular OpenSSL cryptographic software library. This weakness allows stealing the information protected, under normal conditions, by the SSL/TLS encryption used to secure the Internet.
How many systems are still vulnerable to Heartbleed
The Heartbleed flaw still impacts almost 200,000 services connected to the internet. Expert Nick Lewis explains why these services remain unpatched and vulnerable. Shodan released a report stating that almost 200,000 services connected to the internet remain unpatched against the OpenSSL Heartbleed vulnerability.
What companies are affected by Heartbleed bug
The bug, called "Heartbleed", affects web servers running a package called OpenSSL. Among the systems confirmed to be affected are Imgur, OKCupid, Eventbrite, and the FBI's website, all of which run affected versions of OpenSSL.
What is the deadliest software virus
Mydoom
Mydoom. Considered by many to be the most dangerous computer virus in history, the Mydoom virus cost around $38 billion worth of damage in 2004. If you think in terms of today's economy, given inflation, that would amount to about $52 billion.
Can an app get a virus
Android devices are more vulnerable to viruses—rooted or not—since the OS allows access to third-party apps not available in the Play Store. External apps available on websites and other platforms are not always safe; some may contain malicious codes and files. Rooted Android phones are more vulnerable to viruses.
Is Log4j still vulnerable
With 40% of Log4j Downloads Still Vulnerable, Security Retrofitting Needs to Be a Full-Time Job. Vulnerabilities like Log4j remain responsible for security breaches a full year after the discovery of the flaw.
Is Log4j safe to use now
The widespread vulnerability that first appeared in Apache Log4j in 2021 will continue to be exploited, potentially even in worse ways than we've seen to date. The more worrisome aspect of these threats is that there's a good chance they'll continue to be exploited months or years into the future.
What is 7 zip vulnerability CVE
CVE-2022-29072
7-Zip vulnerability or CVE-2022-29072 is an active zero-day vulnerability and is characterized as allowing privilege escalation and command execution for Windows when a file with the .
Who developed CVE 2014 6271
Stéphane Chazelas
On 12 September 2014, Stéphane Chazelas informed Bash's maintainer Chet Ramey of his discovery of the original bug, which he called "Bashdoor". Working with security experts, Mr. Chazelas developed a patch (fix) for the issue, which by then had been assigned the vulnerability identifier CVE- 2014-6271.
When was Heartbleed patched
April 7, 2014
Heartbleed was a vulnerability in some implementations of OpenSSL, an open source cryptographic library. It was publicly announced by researchers on April 7, 2014 and patched the same month.
What is the max safe heartbeat
You can estimate your maximum heart rate based on your age. To estimate your maximum age-related heart rate, subtract your age from 220. For example, for a 50-year-old person, the estimated maximum age-related heart rate would be calculated as 220 – 50 years = 170 beats per minute (bpm).
What companies are affected by heartbleed bug
The bug, called "Heartbleed", affects web servers running a package called OpenSSL. Among the systems confirmed to be affected are Imgur, OKCupid, Eventbrite, and the FBI's website, all of which run affected versions of OpenSSL.
Who found the heartbleed bug
Codenomicon first discovered Heartbleed—originally known by the infinitely less catchy name “CVE-2014-0160”—during a routine test of its software.
Who found the Heartbleed bug
Codenomicon first discovered Heartbleed—originally known by the infinitely less catchy name “CVE-2014-0160”—during a routine test of its software.
How many servers were affected by Heartbleed
Even harder to believe is that three years later, many servers and devices are still affected by the Heartbleed vulnerability. According to a January 2017 report by Shodan, about 200,000 devices and servers are still vulnerable to this OpenSSL vulnerability.
How many web apps are vulnerable to Heartbleed
The Heartbleed flaw still impacts almost 200,000 services connected to the internet. Expert Nick Lewis explains why these services remain unpatched and vulnerable. Shodan released a report stating that almost 200,000 services connected to the internet remain unpatched against the OpenSSL Heartbleed vulnerability.
Does PC virus still exist
No matter which device you use, computer viruses are not a thing of the past. Keep reading to learn more about what a computer virus is and why you should still be concerned about online security in the modern tech age.