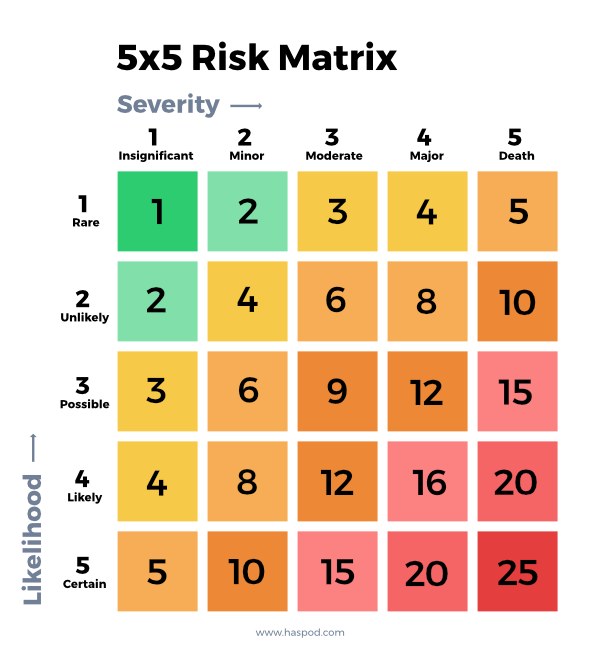
How to calculate risk of return
Remember, to calculate risk/reward, you divide your net profit (the reward) by the price of your maximum risk. Using the XYZ example above, if your stock went up to $29 per share, you would make $4 for each of your 20 shares for a total of $80. You paid $500 for it, so you would divide 80 by 500 which gives you 0.16.
How to calculate risk in Excel
And I get the variance of the market portfolio.
Why do we calculate risk and return
The concept of risk and return in finance is an analysis of the likelihood of challenges involved in investing while measuring the returns from the same investment. The underlying principle is that high-risk investments give better returns to investors and vice-versa.
How do you calculate risk at work
Identify and define what kinds of risks you are concerned about.Make a list of actions that would create greater risk if they happened or would reduce risk if they did not happen.Assign a rank to each action from high-risk to low-risk.Create a scatterplot of risk using your data.
What is the formula for risk percentage
We used the (appropriately transformed) risk formula to get this answer: probability of failure = risk/loss . Plugging in the numbers, we get 100 / 1000 = 0.10 = 10% .
What is the formula for risk in finance
Risk is commonly defined as: Risk = Threat x Vulnerability x Consequence.
How do you measure risk in finance
The five measures include the alpha, beta, R-squared, standard deviation, and Sharpe ratio. Risk measures can be used individually or together to perform a risk assessment. When comparing two potential investments, it is wise to compare like for like to determine which investment holds the most risk.
What is an example of a calculated risk
Meaning of calculated risk in English. a risk that you consider worth taking because the result, if it is successful, will be so good: The director took a calculated risk in giving the film's main role to an unknown actor.
How do you calculate 95% value at risk
We first calculate the mean and standard deviation of the returns. According to the assumption, for 95% confidence level, VaR is calculated as a mean -1.65 * standard deviation. Also, as per the assumption, for 99% confidence level, VaR is calculated as mean -2.33* standard deviation.
What is a 1% risk
One of the most popular risk management techniques is the 1% risk rule. This rule means that you must never risk more than 1% of your account value on a single trade. You can use all your capital or more (via MTF) on a trade but you must take steps to prevent losses of more than 1% in one trade.
How do you calculate risk and odds
For example, when the odds are 1:10, or 0.1, one person will have the event for every 10 who do not, and, using the formula, the risk of the event is 0.1/(1+0.1) = 0.091. In a sample of 100, about 9 individuals will have the event and 91 will not.
What is an example of a calculated risk in business
Here's an example of a calculated risk:
Investing in a Stocks and Shares ISA – Investing in a Stocks and Shares ISA that aims for steady growth could be a calculated risk, providing you have done your research and fully understand the plan.
What does a 5% value at risk mean
Thus, there is a 5% chance that a minimum loss of 15% of the portfolio (i.e. $3000) will occur within the next 1 month. In other words, we are 95% confident that the loss will not exceed $3000 within the next 1 month. 2. Historical VAR- This is probably the easiest way to calculate VAR.
What does a 99% VaR mean
From standard normal tables, we know that the 95% one-tailed VAR corresponds to 1.645 times the standard deviation; the 99% VAR corresponds to 2.326 times sigma; and so on.
What does 2% risk mean
What Is the 2% Rule The 2% rule is an investing strategy where an investor risks no more than 2% of their available capital on any single trade. To implement the 2% rule, the investor first must calculate what 2% of their available trading capital is: this is referred to as the capital at risk (CaR).
Should I risk 1% or 2%
Traders with trading accounts of less than $100,000 commonly use the 1% rule. While 1% offers more safety, once you're consistently profitable, some traders use a 2% risk rule, risking 2% of their account value per trade. 6 A middle ground would be only risking 1.5%, or any other percentage below 2%.
How do you calculate risk ratio vs odds ratio
Group or the odds of experiencing the outcome is reduced by 63 percent among participants in the intervention. Group compared to participants in the control.
Is risk the same as odds
“Risk” refers to the probability of occurrence of an event or outcome. Statistically, risk = chance of the outcome of interest/all possible outcomes. The term “odds” is often used instead of risk. “Odds” refers to the probability of occurrence of an event/probability of the event not occurring.
How is risk measured in a company
Risk—or the probability of a loss—can be measured using statistical methods that are historical predictors of investment risk and volatility. Commonly used risk management techniques include standard deviation, Sharpe ratio, and beta.
What is the 95% value at risk
It is defined as the maximum dollar amount expected to be lost over a given time horizon, at a pre-defined confidence level. For example, if the 95% one-month VAR is $1 million, there is 95% confidence that over the next month the portfolio will not lose more than $1 million.
What does a 5% VaR of $1 million mean
Informally, a loss of $1 million or more on this portfolio is expected on 1 day out of 20 days (because of 5% probability). More formally, p VaR is defined such that the probability of a loss greater than VaR is (at most) (1-p) while the probability of a loss less than VaR is (at least) p.
What does a 95% VaR mean
It is defined as the maximum dollar amount expected to be lost over a given time horizon, at a pre-defined confidence level. For example, if the 95% one-month VAR is $1 million, there is 95% confidence that over the next month the portfolio will not lose more than $1 million.
What are Level 1 2 3 risks
Level 1, the lowest category, encompasses routine operational and compliance risks. Level 2, the middle category, represents strategy risks. Level 3 represents unknown, unknown risks. Level 1 risks arise from errors in routine, standardized and predictable processes that expose the organization to substantial loss.
Is risk ratio the same as odds ratio
The relative risk (also known as risk ratio [RR]) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (e.g., exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (e.g., nonexposed group). The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group.
How do you convert risk ratio to odds
To convert an odds ratio to a risk ratio, you can use "RR = OR / (1 – p + (p x OR)), where p is the risk in the control group" (source: http://www.r-bloggers.com/how-to-convert-odds-ratios-to-relative-risks/).