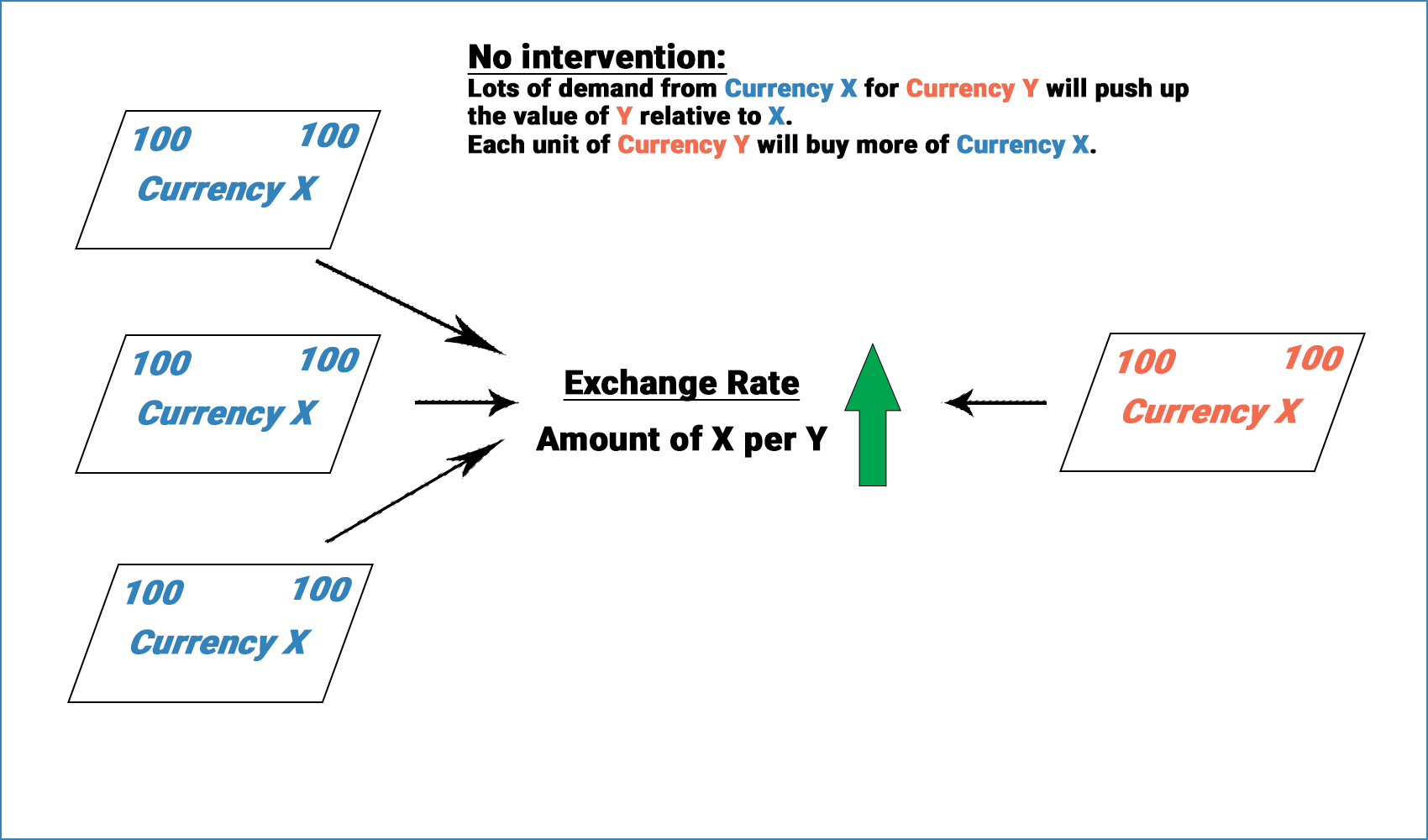
How does currency manipulation work
Simply explained, in order to weaken its currency, a country sells its own currency and buys foreign currency – usually U.S. dollars. Following the laws of supply and demand, the result is that the manipulating country reduces the demand for its own currency while increasing the demand for foreign currencies.
What is the manipulation of exchange rates
Currency manipulation is an effort to tinker with the value of a nation's currency about foreign currency exchange rates to boost exports in international trade or reduce its debt interest burden. Currency devaluation can lead to trade wars and backfire on the country trying to undertake it.
What is currency manipulation in world trade
Currency manipulation refers to the nation's imports as well as exports. In general, it is the weaker currency that makes imports extra expensive, while stimulating the exports via making those cheaper for the overseas customers for purchase. Thus currency manipulation can negatively affect trade affirs.
What are the advantages of currency manipulation
In fact, devaluating a currency can have several advantages:
The quantity of products sold abroad increases as these products become more affordable to a greater number of consumers overseas. As exported products become cheaper, foreign demand for these products increases.
Why does China manipulate its own currency
China manages its currency to control the prices of its exports. It wants to make sure its exports cost less than other products when sold in the United States.
Why do countries manipulate their currency
Currency devaluations can be used by countries to achieve economic policy. Having a weaker currency relative to the rest of the world can help boost exports, shrink trade deficits, and reduce the cost of interest payments on outstanding government debts. There are, however, some negative effects of devaluations.
How China manipulates the exchange rate
A currency peg is a monetary policy that keeps the value of a currency low compared to other countries. The Chinese yuan has had a currency peg since 1994. The effect of the peg and the low currency is that Chinese exports are cheaper and, therefore, more attractive compared to those of other nations.
Why do countries manipulate the value of their currency
The Bottom Line
Currency devaluations can be used by countries to achieve economic policy. Having a weaker currency relative to the rest of the world can help boost exports, shrink trade deficits, and reduce the cost of interest payments on outstanding government debts.
Why do countries use currency manipulation
The Bottom Line. Currency devaluations can be used by countries to achieve economic policy. Having a weaker currency relative to the rest of the world can help boost exports, shrink trade deficits, and reduce the cost of interest payments on outstanding government debts.
Why would a country want to manipulate the value of its currency
By devaluing its currency, a country makes its money cheaper and boosts exports, rendering them more competitive in the global market. Conversely, foreign products become more expensive, so the demand for imports falls. Governments use devaluation to combat a trade imbalance and have exports exceed imports.
How does China manipulate the dollar
The PBOC holds the dollars in its foreign exchange reserves and regularly adjusts these reserves by buying or selling dollars via foreign currency markets in exchange for yuan.
How does China artificially keep currency low
The Chinese yuan has had a currency peg since 1994. This approach keeps the value of the yuan low compared to other countries. The effect on trade is that Chinese exports are cheaper and, therefore, more attractive compared to those of other nations.
How currency manipulation can lead to a currency war
How currency manipulation can lead to a currency war. A currency war can break out after a country deliberately devalues its own currency and prompts another nation to do the same. This is also known as 'competitive devaluation'.
Why is currency manipulation bad
But foreign manipulation of a country's currency weakens its competitiveness and shifts economic activity, including employment, from home to abroad.
Why China is called currency manipulator
The US Treasury department defines currency manipulation as when countries deliberately influence the exchange rate between their currency and the US dollar to gain "unfair competitive advantage in international trade". A weaker yuan makes Chinese exports more competitive, or cheaper to buy with foreign currencies.
How does China control exchange rates
China has a policy of pegging its currency (the yuan) to the U.S. dollar. If the yuan is undervalued against the dollar, there are likely to be both benefits and costs to the U.S. economy. It would mean that imported Chinese goods are cheaper than they would be if the yuan were market determined.
How does China fix its exchange rate
China achieves this by pegging the yuan to the U.S. dollar at a daily reference rate set by the People's Bank of China (PBOC) and allowing the currency to fluctuate within a fixed band (set at 1% as of January 2014) on either side of the reference rate.
How do countries manipulate currencies and how do currency wars start
Lesson Summary. Countries devalue their currencies to increase economic growth. Occasionally, countries engage in competitive devaluation to increase exports and decrease imports. If other countries also engage, it can become a currency war.
Is Vietnam a currency manipulator
The US Treasury today officially labelled Vietnam as a currency manipulator , a process that will trigger “enhanced bilateral engagement with Vietnam” and could eventually be used to justify countervailing duties against Vietnam.
Is Vietnam fixed exchange rate
The VND is on a managed float, similar to a crawling peg, to the US dollar. The SBV sets the price of the local currency each day. The currency can then only be traded within a band either side of the SBV's set rate.
How does China manipulate exchange rate
A currency peg is a monetary policy that keeps the value of a currency low compared to other countries. The Chinese yuan has had a currency peg since 1994. The effect of the peg and the low currency is that Chinese exports are cheaper and, therefore, more attractive compared to those of other nations.
How does China peg its currency to the dollar
The People's Bank of China (PBOC) allows the yuan to trade in a 2% range around a mid-point it fixes against the dollar each day. That mid-point is based on the yuan's movement in the previous session and moves in currencies of China's main trading partners.
Is China’s exchange rate fixed or floating
For most of its early history, the renminbi was pegged to the US dollar. However, under growing pressure from the country's trade partners, the Chinese government decided to move away from the fixed exchange rate regime in 2005. Today, the currency operates under a managed floating exchange rate system.
How do countries fix their exchange rate
A fixed or pegged rate is determined by the government through its central bank. The rate is set against another major world currency (such as the U.S. dollar, euro, or yen). To maintain its exchange rate, the government will buy and sell its own currency against the currency to which it is pegged.
What makes a country a currency manipulator
Countries manipulate the value of their currency by buying and selling in currency markets in order to make their exports cheaper and imports more expensive.