How much of Antarctica has been lost
Ice sheet tipping points
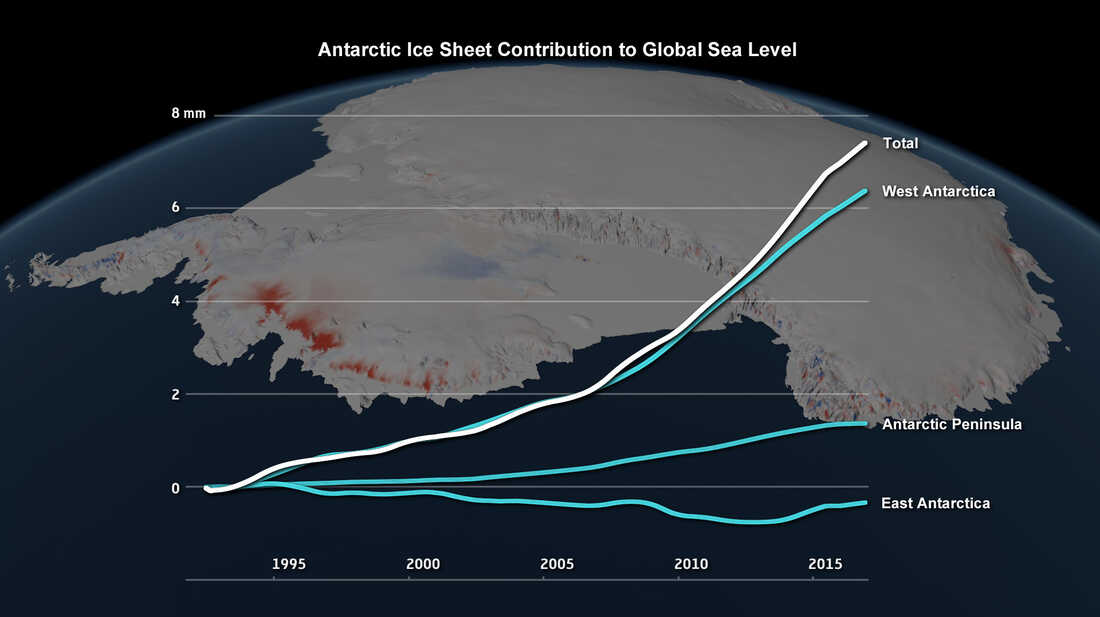
Since the early 1990s, Antarctica has lost roughly three trillion tons of ice. Today, the rate of loss is accelerating as warm ocean water melts and destabilizes the floating ice shelves that hold back West Antarctica's glaciers, causing those glaciers to flow more quickly into the sea.
How much ice has Antarctica lost in the last 25 years
Similarly, when snowfall supply drops, the Embayment can lose mass overall and contribute to sea level rise. The results show that West Antarctica saw a net decline of 3,331 billion tonnes of ice between 1996 and 2021, contributing over nine millimetres to global sea levels.
How many tons of ice has Antarctica lost
Scientists have calculated that the fastest changing Antarctic region – the Amundsen Sea Embayment – has lost more than 3,000 billion tonnes of ice over a 25-year period. If all the lost ice was piled on London, it would stand over 2 km tall – or 7.4 times the height of the Shard.
How much ice is Antarctica losing per year
about 150 billion tons per year
Antarctica is losing ice mass (melting) at an average rate of about 150 billion tons per year, and Greenland is losing about 270 billion tons per year, adding to sea level rise.
How much ice is left
Summary
| Ice mass | Total ice volume | % Global land surface |
|---|---|---|
| WAIS & APIS | 4.5 m SLE | |
| Greenland | 7.36 m SLE | 1.2% |
| Global glaciers and ice caps* | 0.43 m SLE (113,915 to 191,879 Gt) | 0.5% |
| Total | 12.5% |
Is Antarctica fully claimed
Antarctica doesn't belong to anyone. There is no single country that owns Antarctica. Instead, Antarctica is governed by a group of nations in a unique international partnership. The Antarctic Treaty, first signed on December 1, 1959, designates Antarctica as a continent devoted to peace and science.
How thick was the ice only 15 000 years ago
a mile thick
About 15,000 years ago the ice sheet grew to more than a mile thick and covered all but the highest peaks in the area. During its maximum stand the cordilleran ice sheet buried much of the northeastern North Cascade Range.
Is Antarctica still in a ice age
The Late Cenozoic Ice Age, or Antarctic Glaciation, began 33.9 million years ago at the Eocene-Oligocene Boundary and is ongoing. It is Earth's current ice age or icehouse period. Its beginning is marked by the formation of the Antarctic ice sheets.
Is 90% of the ice on Earth in Antarctica
At its thickest point the ice sheet is 4,776 meters deep. It averages 2,160 meters thick, making Antarctica the highest continent. This ice is 90 percent of all the world's ice and 70 percent of all the world's fresh water.
Was Antarctica ever ice free
Antarctica hasn't always been covered with ice – the continent lay over the south pole without freezing over for almost 100 million years. Then, about 34 million years ago, a dramatic shift in climate happened at the boundary between the Eocene and Oligocene epochs.
What if all of Antarctica melted
But our coastlines would be very different. If all the ice covering Antarctica , Greenland, and in mountain glaciers around the world were to melt, sea level would rise about 70 meters (230 feet). The ocean would cover all the coastal cities. And land area would shrink significantly.
Has Antarctica ever been ice free
Antarctica hasn't always been covered with ice – the continent lay over the south pole without freezing over for almost 100 million years. Then, about 34 million years ago, a dramatic shift in climate happened at the boundary between the Eocene and Oligocene epochs.
Where is 90% of Earth’s ice
Antarctic ice sheet
The present Antarctic ice sheet accounts for 90 percent of Earth's total ice volume and 70 percent of its fresh water. It houses enough water to raise global sea level by 200 ft. if completely melted.
Where is 90% of the Earth’s ice currently stored
The vast majority, almost 90 percent, of Earth's ice mass is in Antarctica, while the Greenland ice cap contains 10 percent of the total global ice mass.
What will happen to Antarctica in 2048
The Antarctic treaty expires in 2048. The Antarctic treaty is an agreement that sets aside the continent of Antarctica for peaceful scientific research. It does not permit any military activity on the continent and it also prevents mining and resource exploitation.
Why no one owns Antarctica
Antarctica doesn't belong to anyone. There is no single country that owns Antarctica. Instead, Antarctica is governed by a group of nations in a unique international partnership. The Antarctic Treaty, first signed on December 1, 1959, designates Antarctica as a continent devoted to peace and science.
Was the Earth warmer 12000 years ago than today
While some previous proxy reconstructions suggest that average Holocene temperatures peaked between 6,000 and 10,000 years ago and the planet cooled after this, climate models suggest that global temperatures have actually risen over the past 12,000 years, with the help of factors like rising greenhouse gas emissions …
Was there an ice age 700000 years ago
Summary: Approximately 700,000 years ago, a 'warm ice age' permanently changed the climate cycles on Earth. During this exceptionally warm and moist period, the polar glaciers greatly expanded.
What will Antarctica be like in 50 years
The temperature of Antarctica as a whole is predicted to rise by a small amount over the next 50 years. Any increase in the rate of ice melting is expected to be at least partly offset by increased snowfall as a result of the warming.
Where is 91% of the Earth’s ice
91% Antarctica is home to most of the glacial ice on Earth – a whopping 91%. 3/4 About 75% (3/4) of the Earth's fresh water is stored in glacial ice.
Are we still in ice age
Striking during the time period known as the Pleistocene Epoch, this ice age started about 2.6 million years ago and lasted until roughly 11,000 years ago. Like all the others, the most recent ice age brought a series of glacial advances and retreats. In fact, we are technically still in an ice age.
Is Antarctica ice Drinkable
The Antarctic ice sheet holds about 90 percent of Earth's fresh water in 30 million cubic kilometres of ice. But there's not a drop to drink, unless you pour some serious energy into making it.
What if Antarctica was green
If Antarctica were to be green again and have a climate where plants could grow like they do in the temperate or tropical regions, it would need the ice cover to melt to clear the land Then it would need soil to form, which would take hundreds to thousands of years and then it would need temperatures to increase very …
What will happen to Antarctica in 2050
Scientists warn deep ocean water flows from the Antarctic could decline by 40 percent by 2050, threatening the collapse of circulation crucial for planetary systems.
Is ice 7 on Earth
The pressures ice-VII requires to form can be found on our planet, but they exist only deep in the mantle where the temperature is too warm for this form of ice to be stable.