Will IPv4 go away
There is no definitive timeline for the phasing out of IPv4. However, the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses, coupled with the rapidly increasing adoption of IPv6, suggests that IPv4 will eventually be phased out.
How many more IPv4 addresses are left
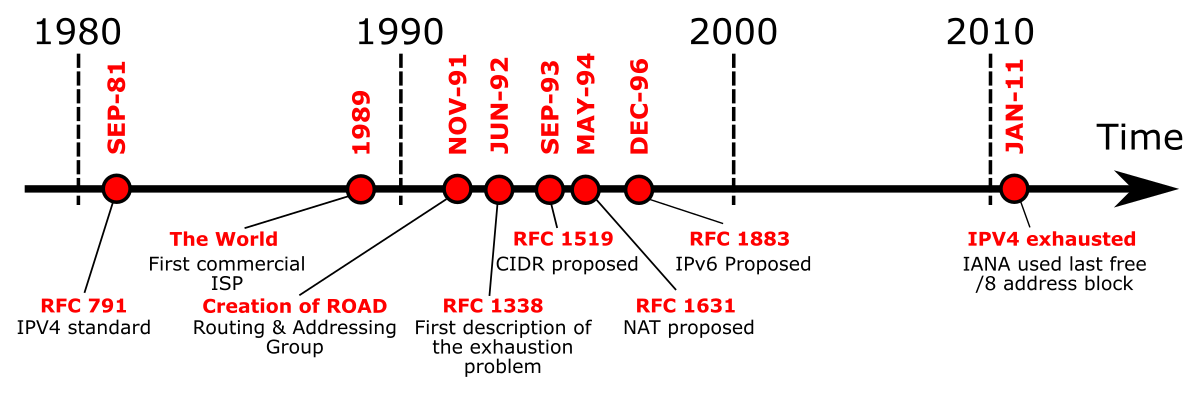
Current Status. The IPv4 address space is a 32 bit field. There are 4,294,967,296 unique values, considered in this context as a sequence of 256 "/8s", where each "/8" corresponds to 16,777,216 unique address values.
Will IPv4 be replaced by IPv6
In conclusion, IPv6 will eventually replace IPv4 completely, but the transition may take a considerable amount of time. The adoption of IPv6 will be driven by the exhaustion of available IPv4 addresses and the need for enhanced features such as improved security and efficient routing.
Will IPv6 ever run out
“the number of IPv6 address possible is 340 undecillion, or 340 followed by 36 zeroes, enough to assign an IP address to every atom on Earth. “ yes Earth not the whole Universe !!!
Is IPv4 still supported
IPv4 will die as a functional protocol by 2040. It will still exist in some "yea, we have that print server that hasn't been touched since the 20's" configurations, but all new network construction will be IPv6 by 2040 (if another protocol hasn't replaced IPv6, and if ethernet is still king).
How many IPv4 addresses are left 2023
There are 4,294,967,296 (Nearly 4.3 billion) IPv4 addresses, 600 million of which are reserved and cannot be used for public routing.
Will IPv6 ever go away
Will IPv6 addresses run out eventually In practical terms, no. There are 2^128 or 340 trillion, trillion, trillion IPv6 addresses, which is more than 100 times the number of atoms on the surface of the Earth. This will be more than sufficient to support trillions of Internet devices for the forseeable future.
Why is there no IPv5
Since IPv5 also used 32-bit addressing, the companies thought that it would again limit the ability to generate IPv5 addresses and hence decided against adopting it as a standard protocol. The abandonment of IPv5 from all these major tech companies discouraged others from using IPv5.
Why is IPv4 not enough
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) has roughly 4 billion IP addresses. This is a problem because there are more than 4 billion Internet-connected computers in the world. This has led to a shortage of IPv4 addresses.
Has IPv4 been exhausted
The free pool of IPv4 addresses managed by regional internet registries (RIR) have been fully allocated. The American Registry of Internet Numbers (ARIN), the regional internet registry (RIR) serving the U.S., Canada, and several Caribbean and North Atlantic islands, was fully depleted in September 2015.
Is IPv4 Limited
Internet Protocol version 4 provides 232 (4,294,967,296) addresses. However, large blocks of IPv4 addresses are reserved for special uses and are unavailable for public allocation.
How many IPv6 are left
There are a total of 4,294,967,296 (2^32) or roughly 4.2 billion ipv6/32s (which is also the number of individual IPv4 addresses). The current IPv4 minimum allocation is a /20 (ipv4/20) of which there are 1,048,576 (2^20). This means that there are only 4,096 times more ipv6/32s than ipv4/20s.
Has the world run out of IPv4 addresses
On the 25th of November 2019, RIPE NCC made the final /22 IPv4 allocation from the last remaining addresses in the available pool and has officially run out of IPv4 addresses.
Will there ever be IPv8
IPv8 has been obsoleted.
Was there ever an IPv1
IPv1-IPv2 These were never really defined, but the protocol numbers were used for TCPv1 and TCPv2. The reason for this overlap is that prior to v3, TCP was being intended as the Layer3 and Layer4 replacement for NCP, so there wasn't yet a separate IP specification.
Why does IPv4 stop at 255
The reason that the highest octet value is 255 is that IP addresses are given in bits, which are the power of 2. The maximum number you can write with bit notation is with 8 1's or 11111111=255.
Why is IPv4 being replaced
The Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is more advanced and has better features compared to IPv4. It has the capability to provide an infinite number of addresses. It is replacing IPv4 to accommodate the growing number of networks worldwide and help solve the IP address exhaustion problem.
Can there be over 4 billion IP addresses with IPv4
What is IPv4 Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is a system of addresses used to identify devices on a network. IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers. This means that there are 232, or just over four billion, possible addresses.
Will IPv6 run out
“the number of IPv6 address possible is 340 undecillion, or 340 followed by 36 zeroes, enough to assign an IP address to every atom on Earth. “ yes Earth not the whole Universe !!!
What is the future of IPv4
In the long term, perhaps within 10-15 years or even longer, the majority of internet connections will use IPv6, rendering IPv4 obsolete. However, due to the variety of factors influencing the adoption of new technologies, the exact time when IPv4 will become a thing of the past remains unclear.
Why did they skip IPv5
Since IPv5 also used 32-bit addressing, the companies thought that it would again limit the ability to generate IPv5 addresses and hence decided against adopting it as a standard protocol. The abandonment of IPv5 from all these major tech companies discouraged others from using IPv5.
Does IPv7 exist
Is there, or will there be, an IPv7, and what new problems will it solve During the period of time when we were trying to figure out what to do about expanding in the address space, there were actually four proposals made. Those were eventually narrowed down to one. So actually, 7, 8, 9, don't exist.
Does IPv5 exist
IPv5 was never accepted as an official internet protocol. This was mainly due to the 32-bit limitation. IPV5 used the same addressing system as IPv4. Each address was made up of four sets of numbers between 0 and 255.
Is 0.0 0.0 a valid IP
0.0 as a reserved, special-purpose address for "this host, this network." Its IPv6 equivalent is expressed as ::/0. Although 0.0. 0.0 is valid address syntax, a client device using it as a source IP address cannot communicate on a network.
Is .255 a usable address
0 or . 255 are not usable… in most cases! The reason for this is because we tend to allocate full Class C type addresses to our networks, making it obviously very simple for us to administer. A standard Class C network consists of 256 addresses (0 to 255 inclusive), of which one is the network address (.