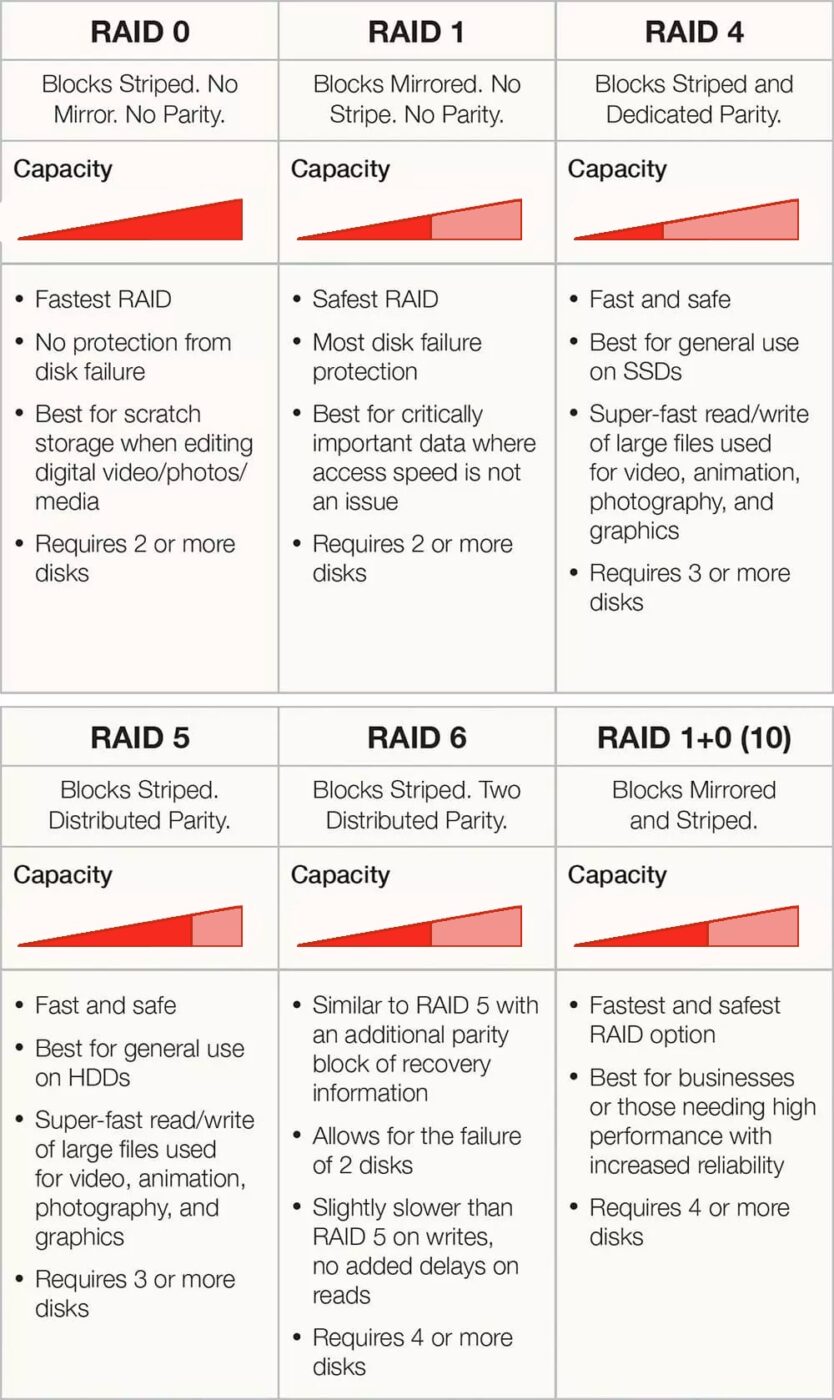
What is the capacity of RAID 0
A RAID 0 setup can be created with disks of differing sizes, but the storage space added to the array by each disk is limited to the size of the smallest disk. For example, if a 120 GB disk is striped together with a 320 GB disk, the size of the array will be 120 GB × 2 = 240 GB.
Is RAID 0 or 1 better
RAID 0 offers the best performance and capacity but no fault tolerance. Conversely, RAID 1 offers fault tolerance but does not offer any capacity of performance benefits. While performance is an important factor, backup admins may prioritize fault tolerance to better protect data.
Does RAID 1 reduce storage capacity
No redundancy or fault tolerance. If one drive in the RAID fails, all data is lost. Storage capacity is effectively cut in half because two copies of all data are stored.
Why is RAID 1 good
RAID 1 is the perfect choice if you require high levels of performance coupled with data redundancy. In a RAID 1 array, two or more hard disk drives are combined to make an array with the capacity of one drive, and the read speed of multiple – along with at least one backup.
Does RAID 1 reduce performance
Writes to a RAID 1 unit is slower compared with RAID 0, but about the same as writing to a single disk. This is because the entire data is written to two disks, but in parallel.
Is RAID 1 more reliable than SSD
RAID 1 systems provide more reliability, where data mirrors a second SSD. In this system, data is stored twice simultaneously by writing on both the data drive and a mirror drive. If a drive fails, it can be recovered from the mirror drive. That said, RAID 1 performs slower and doubles the number of SSDs needed.
What is the downside of RAID 1
RAID 1 has a storage capacity of only half as data is written twice. Additionally, it may not allow for a host swap of the failed drive, which means you'll need to power down the system before replacing the drive.
Is RAID 1 safer than RAID 5
Raid 5 has good failure resistance and better security. The performance is great in Raid 1, but in Raid 5, performance is slow due to disks' redundancy. Data cannot be accessed from a failed drive in Raid 1, whereas data can be accessed from a failed drive in Raid 5.
Why RAID 1 is not good for backup
A RAID is still a single device and because of that, also a single point of failure. A BACKUP needs to be a complete and recoverable copy of your data that resides on a separate hard drive possibly even a RAID.
Will RAID 1 slow down performance
RAID 1 offers slower write speeds but could offer the same read performance as RAID 0 if the RAID controller uses multiplexing to read data from disks. Where data reliability is less of a concern and speed is important.
Is RAID 1 or 10 better
RAID 10 and RAID 01 provide identical capacities and performance, and both architectures have the same amount of storage overhead, prioritizing redundancy over capacity. The difference is that RAID 10 provides better fault tolerance in most cases because it is not limited to two groups.
Which RAID is safest
RAID 10 is ideal for situations where performance and safety are the priorities. RAID 10 has much faster write performance and is safe regardless of disk type used (low cost consumer disks can still be extremely safe, even in large arrays.)
Can RAID 1 be recovered
In the event of a RAID 1 failure resulting in data loss, you can try to run some RAID 1 data recovery software. However, even the best RAID 1 recovery programs cannot fix most problems that cause RAID 1 data loss in the first place.
How safe is RAID 10 really
RAID 10 stores all data in duplicate. As long as one disk of a mirror pair is still running, the information stored is therefore safe – even if a data carrier fails. Data is only lost if all storage media in a subordinate RAID 1 fail due to a defect or another reason.
Should I use RAID 1 or no RAID
RAID 0 offers the best performance and capacity but no fault tolerance. Conversely, RAID 1 offers fault tolerance but does not offer any capacity of performance benefits. While performance is an important factor, backup admins may prioritize fault tolerance to better protect data.
Can you break RAID 1 without losing data
RAID 1 (Mirror) volumes can be deleted without losing data if the RAID 1 volume is: The only volume on the drives.
Will RAID 1 erase data
Will rebuilding the RAID 1 array erase data There are risks of losing data when you are rebuilding RAID 1. The best way is to back up RAID, and you can use EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard to recover RAID data if you have no backup.
Is RAID 1 necessary with SSD
RAID 1 systems provide more reliability, where data mirrors a second SSD. In this system, data is stored twice simultaneously by writing on both the data drive and a mirror drive. If a drive fails, it can be recovered from the mirror drive. That said, RAID 1 performs slower and doubles the number of SSDs needed.
What happens if a RAID 1 drive fails
RAID 1, or mirroring, provides a local full-image backup of your data. Data is mirrored across both drives in the array, meaning if one drive fails, another copy of its data is stored on the other drive.
Is RAID 1 slower than single drive
Drawbacks of RAID 1
Lower performance – RAID 1 is designed to provide consistent data across both drives in the array, which means it's slower than a single drive. Increased cost – Due to the need for two drives, RAID 1 is one of the more expensive configurations available.
Is RAID 1 good for SSD
That said, RAID 1 performs slower and doubles the number of SSDs needed. It is ideal for critical storage and suitable for small servers, where data security is more important than performance.
Does RAID 1 slow down performance
RAID 1 offers slower write speeds but could offer the same read performance as RAID 0 if the RAID controller uses multiplexing to read data from disks. Where data reliability is less of a concern and speed is important.