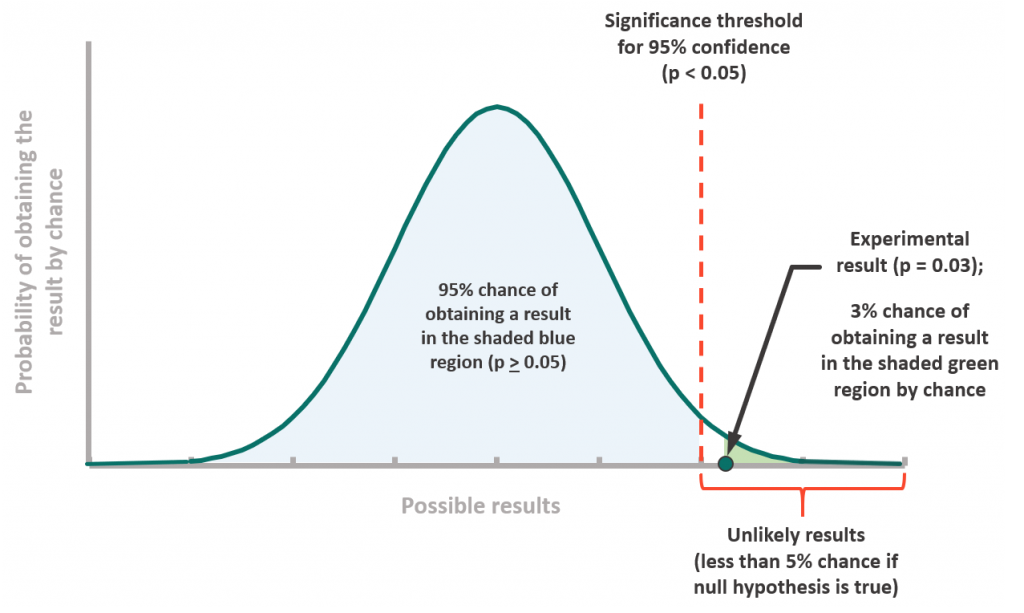
Why is 0.05 the threshold for statistical significance
The threshold for significance and its origin
In the theoretical system proposed by Ronald A. Fisher (1890–1962), the p value had to be considered only as a rough guide of the strength of evidence against the null hypothesis. In other words, the meaning of p < 0.05 was merely that one should repeat the experiment.
Is .01 significant
If the p-value of the hypothesis test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = . 01), then we can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that we have sufficient evidence to say that the alternative hypothesis is true.
Is AP value of 0.1 significant
This leads to the typical guidelines of: p < 0.001 indicating very strong evidence against H0, p < 0.01 strong evidence, p < 0.05 moderate evidence, p < 0.1 weak evidence or a trend, and p ≥ 0.1 indicating insufficient evidence [1], and a strong debate on what this threshold should be.
Is 0.005 statistical significance
If the p-value is under . 01, results are considered statistically significant and if it's below . 005 they are considered highly statistically significant.
Is p-value of 0.05 too high
If the p-value is 0.05 or lower, the result is trumpeted as significant, but if it is higher than 0.05, the result is non-significant and tends to be passed over in silence.
Is 0.5 significant
A P-value less than 0.5 is statistically significant, while a value higher than 0.5 indicates the null hypothesis is true; hence it is not statistically significant.
Is .059 significant
Alternatively, P = . 059 can be considered as “marginally nonsignificant” to qualitatively differentiate it from larger values, say P = . 80, which are clearly nonsignificant. Third, a key distinction is that between clinical and statistical significance.
Is AP value of .015 significant
If your p-value is less than or equal to 0.05 (the significance level), you would conclude that your result is statistically significant.
Is AP value of .050 significant
A P-value less than 0.5 is statistically significant, while a value higher than 0.5 indicates the null hypothesis is true; hence it is not statistically significant.
Is 0.045 statistically significant
Thus, a p-value of 0.045 might be classified as statistically significant while a p-value of 0.055 might not. However, it is important to keep in mind that the limit 0.05 is not black and white. A finding of p=0.055 or p=0.045 is very similar.
Is .055 statistically significant
Usually statistical significance in this context is defined as a pre-set P-value <0.05. A p-value of 0.055 is considered not statistically significant.
What happens if p-value is less than 5%
If your p-value is less than or equal to 0.05 (the significance level), you would conclude that your result is statistically significant. This means the evidence is strong enough to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
What does p is less than 0.05 mean
statistically significant
A p-value less than 0.05 is typically considered to be statistically significant, in which case the null hypothesis should be rejected. A p-value greater than 0.05 means that deviation from the null hypothesis is not statistically significant, and the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Is less than 0.5 statistically significant
A P-value less than 0.05 is deemed to be statistically significant, meaning the null hypothesis should be rejected in such a case. A P-Value greater than 0.05 is not considered to be statistically significant, meaning the null hypothesis should not be rejected.
Is less than .05 significant
What does p-value of 0.05 mean If your p-value is less than or equal to 0.05 (the significance level), you would conclude that your result is statistically significant. This means the evidence is strong enough to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
Is p-value less than 0.05 significant
A statistically significant test result (P ≤ 0.05) means that the test hypothesis is false or should be rejected. A P value greater than 0.05 means that no effect was observed.
Is the result significant at the 5% level
Statistical hypothesis testing is used to determine whether the result of a data set is statistically significant. Generally, a p-value of 5% or lower is considered statistically significant.
Is AP value of .051 significant
But P values of 0.051 and 0.049 should be interpreted similarly despite the fact that the 0.051 is greater than 0.05 and is therefore not "significant" and that the 0.049 is less than 0.05 and thus is "significant." Reporting actual P values avoids this problem of interpretation.
Is 0.15 statistically significant
Most authors refer to statistically significant as P < 0.05 and statistically highly significant as P < 0.001 (less than one in a thousand chance of being wrong).
Is AP value of 0.045 significant
By tradition, alpha is most often set to 0.05. Thus, a p-value of 0.045 might be classified as statistically significant while a p-value of 0.055 might not. However, it is important to keep in mind that the limit 0.05 is not black and white. A finding of p=0.055 or p=0.045 is very similar.
Is 0.52 statistically significant
Below 0.05, significant. Over 0.05, not significant.
Is 0.50 statistically significant
A P-value less than 0.5 is statistically significant, while a value higher than 0.5 indicates the null hypothesis is true; hence it is not statistically significant.
Is p-value of .055 significant
Usually statistical significance in this context is defined as a pre-set P-value <0.05. A p-value of 0.055 is considered not statistically significant.
What happens if the p-value is too small
Ronald Fisher, who introduced the P-value, intended it as an informal way to judge whether evidence was significant in the sense of being worthy of a second look [1]. A very small P-value indicates that the null hypothesis is very incompatible with the data that have been collected.
Do we reject if p-value is less
If your P value is less than the chosen significance level then you reject the null hypothesis i.e. accept that your sample gives reasonable evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.