Is RAID 6 any good
Thanks to its double parity storage structure, RAID 6 is ideal for any service or application that contains sensitive information and/or requires high availability. RAID 6 is also an ideal choice for applications with high read performance and low write requests.
Is RAID 6 slow
RAID 6 arrays are even slower because they store a greater volume of parity data than RAID 5 arrays do. Organizations must consider how they will implement the RAID 5 or RAID 6 array.
What is better RAID 5 or 6
RAID5 allows for a single drive to fail without any data loss. RAID6 allows for two drive failures without any data loss. RAID5 rebuild times tend to be quite a bit faster, ranging from 50% to 200% faster, depending on capacity, RAID controller and the amount of data you have.
Which is better RAID 6 or RAID 10
RAID 6 stores double parity bits that are striped across a minimum of five drives. Compared to RAID 10, storing a byte with RAID 6 on a 10-drive array requires only 10 bits of space, resulting in greater capacity and higher performance. In addition, any two drives in a RAID 6 volume can fail without losing data.
What raid level is safest
RAID 10 is the safest of all choices, it is fast and safe. The obvious downsides are that RAID 10 has less storage capacity from the same disks and is more costly on the basis of capacity. It must be mentioned that RAID 10 can only utilize an even number of disks as disks are added in pairs.
What are the disadvantages of RAID 6
What are the disadvantages of RAID 6 Each set of parities must be calculated separately using RAID 6. This slows write performance. RAID 6 is also more expensive because of the two extra disks required for parity.
Is RAID 6 fast
RAID 5 and RAID 6 both offer fast reads because of striping. Data is read from multiple disks in parallel, which speeds up reads. Write performance is slow, however, due to the overhead of calculating parity information. RAID 6 is a little slower than RAID 5 for write performance.
Is RAID 6 safer than RAID 10
Because RAID 6 uses a double parity scheme, it can protect against the simultaneous failure of two disks. RAID 10 may or may not be able to protect against two disk failures depending on where they occur. If both failed disks are in the same mirror, then the other mirror can take over.
Is RAID 1 better than RAID 6
RAID 1 of a pair of drives is easy to do, but only 50% usable space. RAID 6 of a handful of drives will survive 2 failures, very slightly slower due to parity calculations. RAID 10 is striped RAID 1, can survive at least 1 failure, and is quite fast, but 50% usable capacity may be too expensive compared to RAID 6.
Is there a RAID 7
RAID 7 has integrated cache and a purpose-built processor for managing the array that helps in achieving faster data read/write operations.
Which RAID is safest
RAID 10 is ideal for situations where performance and safety are the priorities. RAID 10 has much faster write performance and is safe regardless of disk type used (low cost consumer disks can still be extremely safe, even in large arrays.)
What is RAID 6 limitations
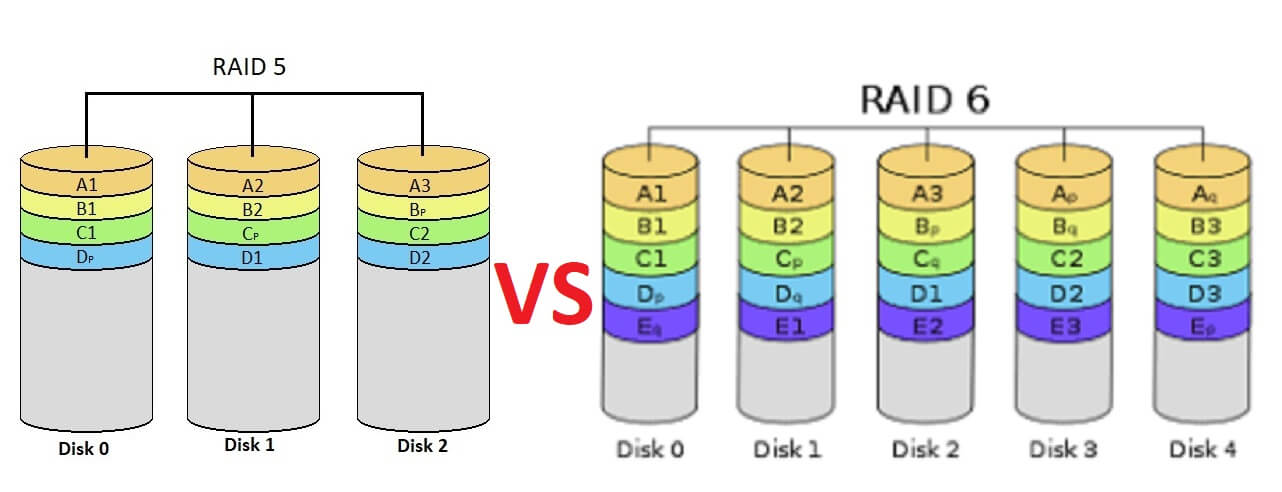
RAID 6 (Striping with Dual Parity)
RAID 6 requires a minimum of 4 drives and a maximum of 32 drives to be implemented. Usable capacity is always two less than the number of available drives in the RAID set. Usage: Similar to RAID 5, including file servers, general storage servers, backup servers, etc.
Is there a RAID 10
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a RAID configuration that combines disk mirroring and disk striping to protect data. It requires a minimum of four disks and stripes data across mirrored pairs. As long as one disk in each mirrored pair is functional, data can be retrieved.
Is there a RAID 50
RAID 50, also known as RAID 5+0, combines distributed parity (RAID 5) with striping (RAID 0). It requires a minimum of six drives. This RAID level offers better write performance, increased data protection and faster rebuilds than RAID 5.
How many drives can fail in RAID 6
two disk failures
RAID 6 uses two parity stripes, the practice of dividing data across the set of hard disks or SSDs, on each disk. It allows for two disk failures within the RAID set before any data is lost.
Is there a RAID 60
RAID 60 (also known as RAID 6+0) is a nested or “hybrid” RAID configuration that provides the distributed double parity of RAID 6 with the straight block-level striping of RAID 0. As a RAID 0 array striped across RAID 6 elements, minimal RAID 60 configuration requires eight drives.
Is RAID 10 faster than no RAID
RAID 10 Performance
Because RAID 10 is a RAID 0 stripe of mirror sets, we have no overhead to worry about from the stripe, but each mirror has to write the same data twice to create the mirroring. This cuts our write performance in half compared to a RAID 0 array of the same number of drives.
Is RAID 6 faster than single drive
RAID5/RAID6 arrays also generally manage to outperform a single disk when doing 1MiB asynchronous writes, but not by much—and the effect doesn't scale up with the number of disks.
How many disks RAID 6 can lose without losing data
two disk failures
RAID 6 uses two parity stripes, the practice of dividing data across the set of hard disks or SSDs, on each disk. It allows for two disk failures within the RAID set before any data is lost.
Is RAID 50 the best
RAID 50 is best used for applications that need high reliability and that need to handle high request rates and high data transfer with lower cost of disks than a RAID 10 (1+0, mirrored and striped) array.
Is RAID 5 still good
RAID 5 is ideal for application and file servers with a limited number of drives. Considered a good all-around RAID system, RAID 5 combines the better elements of efficiency and performance among the different RAID configurations. Fast, reliable read speed is a major benefit.
What happens if a drive fails in RAID 6
If a third disk in a RAID 6 disk array fails, the array is marked as Failed and its data is not accessible. If a third disk in a RAID 6 disk array fails, you must replace the failed disks, then delete and recreate the disk array.
Is RAID 10 faster than 5
RAID 10 offers fantastic performance for random reads and writes because all operations occur in parallel on separate physical drives. RAID 5 also offers great read performance because of striping. However, writes are slower because of the overhead of calculating parity.
Is RAID 5 slower than RAID 6
RAID 5 and RAID 6 both offer fast reads because of striping. Data is read from multiple disks in parallel, which speeds up reads. Write performance is slow, however, due to the overhead of calculating parity information. RAID 6 is a little slower than RAID 5 for write performance.
Why is RAID 10 better
RAID 10 provides data redundancy and improves performance. It is the a good option for I/O-intensive applications — including email, web servers, databases and operations that require high disk performance. It's also good for organizations that require little to no downtime.