What are any 3 concepts of economics
The three basic concepts are supply & demand, scarcity, and opportunity cost.
What are the 3 basic problems of economics
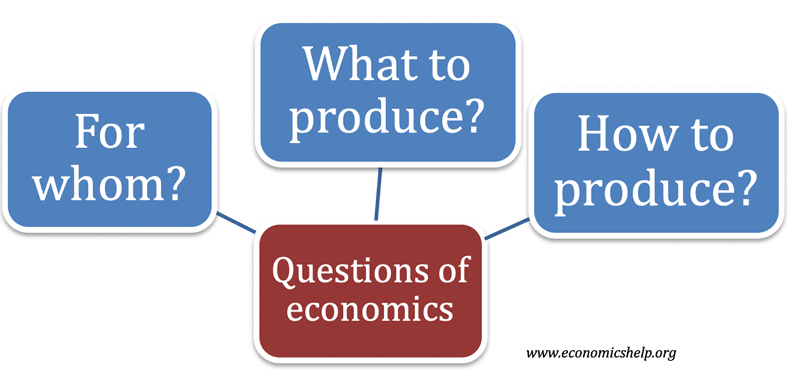
The three basic problem of economics are:What to produce.How to produce.For whom to produce.
What are the 4 key economic issues
Answer: The four basic problems of an economy, which arise from the central problem of scarcity of resources are:What to produceHow to produceFor whom to produceWhat provisions (if any) are to be made for economic growth
What are the 5 basic economic problems
The 5 basic problems of an economy are as follows:What to produce and what quantity to produceHow to produceFor whom to produce the goodsHow efficient are the resources being utilisedIs the economy growing
What are the 4 economic systems
Each economy functions based on a unique set of conditions and assumptions. Economic systems can be categorized into four main types: traditional economies, command economies, mixed economies, and market economies.
What are the 4 main economic issues
1.1 Basic Problems of an Economy – #1 – What to Produce 1.3 Basic Problems of an Economy – #2 – How to Produce 1.4 Basic Problems of an Economy – #3 – For whom to Produce 1.5 Basic Problems of an Economy – #4 – What provision should be made for economic growth
What are the 4 basic economic questions
The Four Basic Economic QuestionsAssignment.Question 4: How much to produceQuestion 1: What to produceQuestion 2: For whom to produceThe Four Basic Economic Questions.Question 3: How to produce it
What are types of economics
The two branches of economics are microeconomics and macroeconomics. Economics focuses on efficiency in production and exchange.
What are 5 examples of economic systems
The different kinds of economic systems are Market Economy, Planned Economy, Centrally Planned Economy, Socialist, and Communist Economies. All these are characterized by the ownership of the economics resources and the allocation of the same.
What are the five 5 economic problems
The 5 basic problems of an economy are as follows:What to produce and what quantity to produceHow to produceFor whom to produce the goodsHow efficient are the resources being utilisedIs the economy growing
What are the top 3 economic questions
In order to meet the needs of its people, every society must answer three basic economic questions:What should we produceHow should we produce itFor whom should we produce it
What are the 4 types of economic systems
Economic systems are classified into four types:command economic system.market economic system.mixed economic system.traditional economic system.
What are the 4 main types of economics
The four main types of economic systems are a pure market economy, a pure command economy, a mixed economy, and a traditional economy.
What are the 4 basic economics
At the most basic level, economics attempts to explain how and why we make the purchasing choices we do. Four key economic concepts—scarcity, supply and demand, costs and benefits, and incentives—can help explain many decisions that humans make.
What are the 4 types of economy
Each economy functions based on a unique set of conditions and assumptions. Economic systems can be categorized into four main types: traditional economies, command economies, mixed economies, and market economies.
What are the 7 economic systems
The different kinds of economic systems are Market Economy, Planned Economy, Centrally Planned Economy, Socialist, and Communist Economies. All these are characterized by the ownership of the economics resources and the allocation of the same.
What are the big five economics
Traditionally the top five journals in economics are: the American Economic Review, Econometrica, the Quarterly Journal of Economics, the Journal of Political Economy, and the Review of Economic Studies.
Why are the 3 economic questions important
The three basic economic questions are what to produce, how to produce it, and for whom to produce it. All three are to answer how we allocate resources to meet our needs and wants. But, then, the way we answer them also depends on the economic system we adopt. The basic problem in economics is scarcity.
What are the 4 types of economies
Each has its own distinguishing characteristics, although they all share some basic features. Each economy functions based on a unique set of conditions and assumptions. Economic systems can be categorized into four main types: traditional economies, command economies, mixed economies, and market economies.
What are 2 branches of economics
There are two main branches of economics, microeconomics, and macroeconomics. Microeconomics deals with the behavior of individual households and firms and how that behavior is influenced by government. Macroeconomics is concerned with economy-wide factors such as inflation, unemployment, and overall economic growth.
What are the 4 steps of an economic system
What Are the Stages of an Economic Cycle An economic cycle, or business cycle, has four stages: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough.
What are the 5 parts of economics
Here are five key concepts that form the basis of all economics.Scarcity. Look around and you will realise that there is a gap between the resources available and the wants that need to be satisfied.Competition. Scarcity leads to competition.Demand & supply.Inflation.Trade deficit.
What are 3 of the four basic economic questions
Economists address these three questions: (1) What goods and services should be produced to meet consumer needs (2) How should they be produced, and who should produce them (3) Who should receive goods and services
What are the 5 elements of economics
Here are five key concepts that form the basis of all economics.Scarcity. Look around and you will realise that there is a gap between the resources available and the wants that need to be satisfied.Competition. Scarcity leads to competition.Demand & supply.Inflation.Trade deficit.
What are the 4 steps of economy
There are four stages in the economic cycle: expansion (real GDP is increasing), peak (real GDP stops increasing and begins decreasing), contraction or recession (real GDP is decreasing), and trough (real GDP stops decreasing and starts increasing).