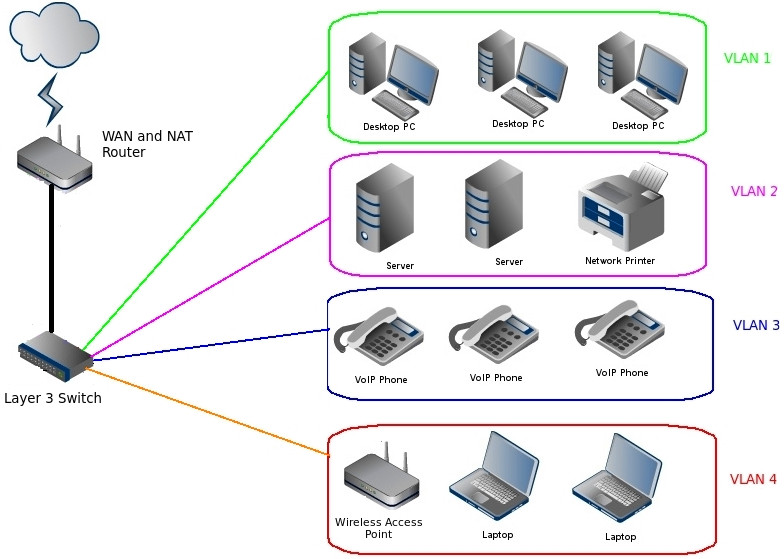
What devices are used in Layer 3
A router is a commonly utilised Layer 3 device. Operating at Layer 3, a router will inspect the IP and IPX addresses of incoming data packets. After determining the packet source, the router will then make routing decisions based on the enclosed destination address and quality of service specifications.
What are Layer 2 and Layer 3 devices
Layer 2 switches offer limited to no routing capabilities within network segments such as VLANs. Layer 3 switches offer routing between different network segments. Limited scalability. Higher scalability enabled by layer 3 switches' cross network segment routing capabilities.
What are Layer 3 devices and give name
Layer 3 Equipment
Routers are the common equipment used at this layer but there are many others. Layer 3 switches are also very common. Those are essentially Layer 2 switches with a router built into the backplane for speed. Firewalls, while able to operate at higher layers, can operate purely at this layer.
What does Layer 3 device mean
A Layer 3 switch is a special network device that has the functionality of a router and a switch combined into one chassis.
Is switch a Layer 3 device
A switch works at Layer 2 of the OSI model — the data-link layer. It is a LAN device that can also be called a multiport bridge. A switch forwards Ethernet frames between Ethernet devices. Switches do not care about IP addresses, nor do they even examine IP addresses as the frames flow through the switch.
Is a firewall a Layer 3 device
A firewall generally works at layer 3 and 4 of the OSI model. Layer 3 is the Network Layer where IP works and Layer 4 is the Transport Layer, where TCP and UDP function. Many firewalls today have advanced up the OSI layers and can even understand Layer 7 – the Application Layer.
What is Layer 3 vs Layer 4 devices
Layer 4 (Transport): This layer coordinates data transfer between system and hosts, including error-checking and data recovery. Layer 3 (Network): This layer determines how data is sent to the receiving device. It's responsible for packet forwarding, routing, and addressing.
What are the Layer 4 devices
Layer 4 of the OSI model, also known as the transport layer, manages network traffic between hosts and end systems to ensure complete data transfers. Transport-layer protocols such as TCP, UDP, DCCP, and SCTP are used to control the volume of data, where it is sent, and at what rate.
What is an example of network layer 3
the Internet Protocol
The most significant protocol at layer 3 (also called the network layer) is the Internet Protocol, or IP. IP is the standard for routing packets across interconnected networks–hence, the name internet. It is an encapsulating protocol similar to the way Ethernet is an encapsulating protocol.
Is router a Layer 3 device only
Basics About Layer 3 Switch and Router
A router is a Layer-3 device that simply does routing only. In the case of a switching router, it is primarily a router that may use switching technology (high-speed ASICs) for speed and performance (as well as also supporting Layer-2 bridging functions).
Is router a Layer 2 or 3
The most common Layer 3 device used in a network is the router. A router is able to look into the Layer 3 portion of traffic passing through it (the source and destination IP addresses) to decide how it should pass that traffic along.
Is VPN a Layer 3
Instead of dedicated connections between networks, VPNs use virtual connections routed (tunneled) through public networks that are typically service provider networks. Layer 3 VPN operates at the Layer 3 level of the OSI model, the Network layer.
Is WIFI a Layer 3
All Wireless LANs operate on the Physical and Data Link layers, layers 1 and 2. All Wi-Fi systems use these layers to format data and control the data to conform with 802.11 standards.
What is an example of layer 4 device
Typical examples of layer 4 are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
What are Layer 7 devices
A Layer 7 switch is a network device that is integrated with routing and switching capabilities. It can pass traffic and make forwarding and routing decisions at Layer 2 speed, but uses information from Layer 7 or application layer.
What is layer 3 vs Layer 4 devices
Layer 4 (Transport): This layer coordinates data transfer between system and hosts, including error-checking and data recovery. Layer 3 (Network): This layer determines how data is sent to the receiving device. It's responsible for packet forwarding, routing, and addressing.
Is a router a Layer 3 device
In the OSI model, we learnt that Switches belong to Layer 2 while Routers belong to Layer 3. Switches are understood to be forward traffic based on MAC address while Routers perform the forwarding based on IP address. ]
Is a firewall a layer 3 device
A firewall generally works at layer 3 and 4 of the OSI model. Layer 3 is the Network Layer where IP works and Layer 4 is the Transport Layer, where TCP and UDP function. Many firewalls today have advanced up the OSI layers and can even understand Layer 7 – the Application Layer.
Is a switch a layer 3 device
A switch works at Layer 2 of the OSI model — the data-link layer. It is a LAN device that can also be called a multiport bridge. A switch forwards Ethernet frames between Ethernet devices. Switches do not care about IP addresses, nor do they even examine IP addresses as the frames flow through the switch.
Is VPN a Layer 3 or 4
As a rule, a traditional VPN sits on Layer 3, the network lay- er, and primarily applies the IPsec standard. With this kind of application, the VPN tunnel is established based on the IP addresses of the client and the server.
Is Ethernet a Layer 3
The Layer 2 protocol you're likely most familiar with is Ethernet. Devices in an Ethernet network are identified by a MAC (media access control) address, which is generally hardcoded to a particular device and doesn't normally change. Layer 3 is the network layer and its protocol is the Internet Protocol or IP.
What is a layer 6 device
Layer 6, or the presentation layer, serves as the data translator between an application or process and the network. This layer is responsible for the formatting and subsequent delivery of data to the application layer either for processing or display.
Why are routers Layer 3 devices
Layer 3, the network layer, is most commonly known as the layer where routing takes place. A router's main job is to get packets from one network to another. Layer 3 protocols and technologies allow for network-to-network communications.
Is Wi-Fi a Layer 3
All Wireless LANs operate on the Physical and Data Link layers, layers 1 and 2. All Wi-Fi systems use these layers to format data and control the data to conform with 802.11 standards.
Is WiFi a layer 3
All Wireless LANs operate on the Physical and Data Link layers, layers 1 and 2. All Wi-Fi systems use these layers to format data and control the data to conform with 802.11 standards.