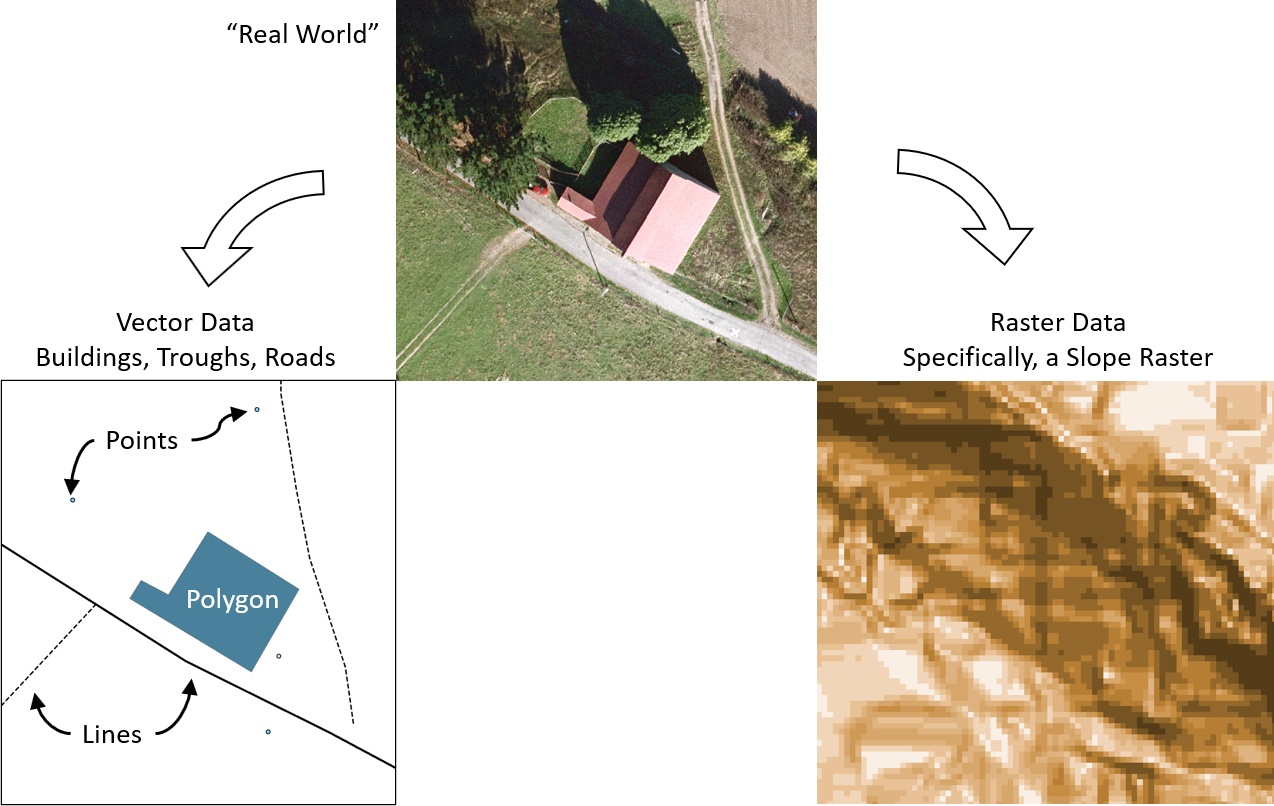
What is two 2 types of GIS data
The two major types of GIS file formats are raster and vector. Raster formats are grids of cells or pixels. Raster formats are useful for storing GIS data that vary, such as elevation or satellite imagery. Vector formats are polygons that use points (called nodes) and lines.
What are the types of data type in GIS
The three types of GIS Data are -spatial, –attribute, & —metadataPoint Data — layers containing by points (or “events”) described by x,y (lat,long; easting, northing)Line/Polyline Data — layers that are described by x,y points (nodes, events) and lines (arcs) between points (line segments and polylines)
What are the two basic types of data layer used in a GIS
A data layer provides access to geographic data that is displayed in a map or scene. Each layer references a file or service data source . The data source contains either as vector data (points, lines, polygons and attributes) or raster data (images).
What are the two main types of dataset in geography
Vector and raster are common data formats used to store geospatial data. Vectors are graphical representations of the real world. There are three main types of vector data: points, lines and polygons. The points help create lines, and the connecting lines form enclosed areas or polygons.
What are 2 functions of GIS
Functions of GIS include: data entry, data display, data management, information retrieval and analysis. A more comprehensive and easy way to define GIS is the one that looks at the disposition, in layers (Figure 1), of its data sets.
What is GIS primary and secondary data
– Primary data sources : those collected in digital format specifically for use in a GIS project. –Secondary data sources: digital and analog datasets that were originally captured for another purpose and need to be converted into a suitable digital format for use in a GIS project.
What are the different types of data
4 Types of Data: Nominal, Ordinal, Discrete, Continuous.
What is spatial and non spatial data in GIS
Spatial data provides the location information of the features whereas non-spatial data describes characteristics of the features. Non-spatial data is also known as attribute data. A combination of both data is known as geospatial data.
What are 2 types of data
There are two general types of data – quantitative and qualitative and both are equally important. You use both types to demonstrate effectiveness, importance or value.
What are the 2 types of data and how are they different
There are two main data types: numerical and categorical. Numerical data is quantitative and can be represented by numbers. Categorical data is qualitative and can be represented by labels or names.
What are two characteristics of GIS data
Characteristics of data in geographical information system (GIS)Location –Temporality –Complex spatial –Thematic Values – The different properties and qualities of an object may be represented as attributes.Fuzzy objects –Entity versus field based data –Generalization –Roles –
What is spatial data in GIS
Spatial data can be referred to as geographic data or geospatial data. Spatial data provides the information that identifies the location of features and boundaries on Earth. Spatial data can be processed and analysed using Geographical Information Systems (GIS) or Image Processing packages.
What are the two types of data primary and secondary
Primary data refers to the first hand data gathered by the researcher himself. Secondary data means data collected by someone else earlier. Surveys, observations, experiments, questionnaire, personal interview, etc.
What is secondary data in GIS
Secondary GIS data sources are digital and analog datasets that were originally captured in another format (such as papers or films). We will need to convert (by scanning or digitizing) the original format of data into digital GIS data formats.
What are the 2 types of data in
Types of DataQualitative Data: They represent some characteristics or attributes. They depict descriptions that may be observed but cannot be computed or calculated.Quantitative Data: These can be measured and not simply observed. They can be numerically represented and calculations can be performed on them.
What are the two types of data
There are two general types of data – quantitative and qualitative and both are equally important. You use both types to demonstrate effectiveness, importance or value.
What is spatial data and temporal data in GIS
Spatial Data Mining needs space information within the data. For example, any data with location coordinates can be treated as a Spatial Data set. Temporal Data Mining needs time information. For example, any data set containing the events over time can be treated as temporal data.
What is spatial vs attribute data GIS
Spatial data represents various aspects of geography as layers on a map. Attribute data stores information about those layers as rows and columns in a table. Layers can be queried, symbolized, and analyzed by their attributes to uncover geographic patterns and relationships.
What are the two 2 sources of data
Data can be gathered from two places: internal and external sources. The information collected from internal sources is called “primary data,” while the information gathered from outside references is called “secondary data.” For data analysis, it all must be collected through primary or secondary research.
What are types of data
The data is classified into majorly four categories:Nominal data.Ordinal data.Discrete data.Continuous data.
What are the 2 methods of data
The data gathered by primary data collection methods are specific to the research's motive and highly accurate. Primary data collection methods can be divided into two categories: quantitative methods and qualitative methods.
What are the two class data types
Data types are divided into two groups:Primitive data types – includes byte , short , int , long , float , double , boolean and char.Non-primitive data types – such as String , Arrays and Classes (you will learn more about these in a later chapter)
What are the types of spatial data
Spatial data are of two types according to the storing technique, namely, raster data and vector data. Raster data are composed of grid cells identified by row and column. The whole geographic area is divided into groups of individual cells, which represent an image.
What is spatial and non spatial data types in GIS
Spatial data provides the location information of the features whereas non-spatial data describes characteristics of the features. Non-spatial data is also known as attribute data. A combination of both data is known as geospatial data.
What is spatial vs non spatial data in GIS
Generally speaking, Spatial data represents the location, size and shape of an object on earth surface such as mountain, plain, township, people etc. it also provides all the attributes of an entity that is being represented. Non Spatial data cannot be related to a location on the earth surface.