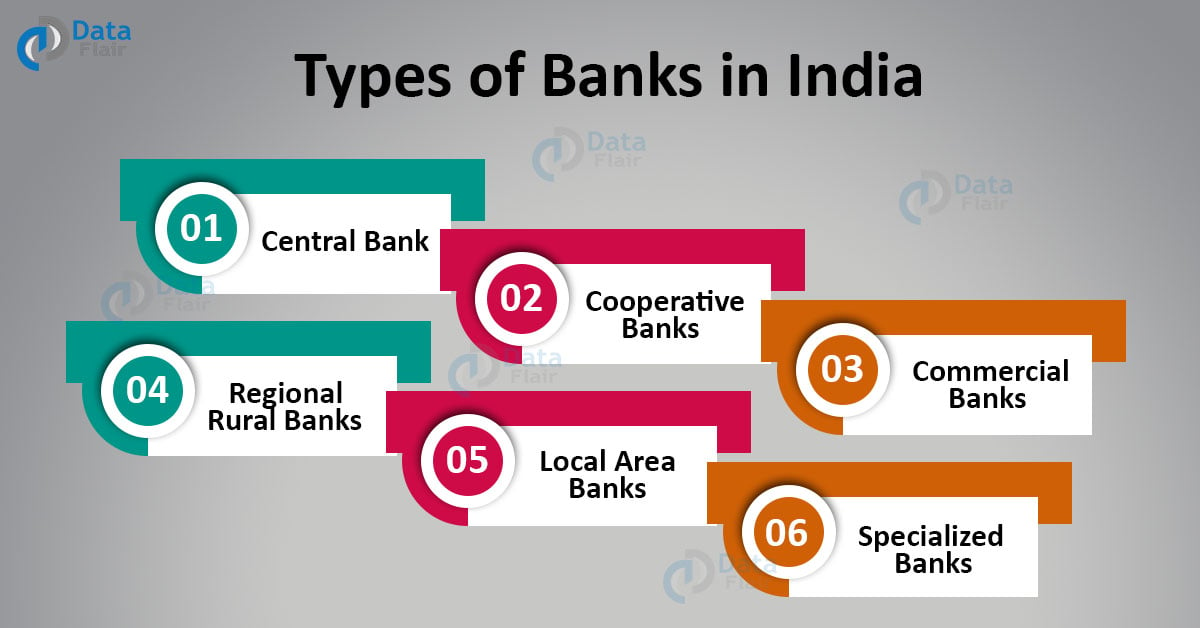
What are the classification of banks in India
Bank Classification in India
| 1. Central Bank | |
|---|---|
| 2. Commercial Banks | a) Private Sector Banks b) Public Sector Banks c) Regional Rural Banks d) Foreign Banks |
| 3. Co-operative Banks | a) State Co-operative Banks b) Urban Co-operative Banks |
| 4. Payments Banks | |
| 5. Scheduled Banks |
What are the different types of banks
Daily Current AffairsCentral Bank.Cooperative Banks.Commercial Banks.Regional Rural Banks (RRB)Local Area Banks (LAB)Specialized Banks.Small Finance Banks.Payments Banks.
How many banks are in India
Apart from this, the bank bank in India also provide various kinds of banking services such as loan facilities, fixed deposit schemes, debit & credit card facilities, etc. Currently, there are a total of 34 nationalized banks in India of which 12 are Indian government banks and the rest 22 are private sector banks.
What are the three types of banks
Banks, Thrifts, and Credit Unions – What's the Difference There are three major types of depository institutions in the United States. They are commercial banks, thrifts (which include savings and loan associations and savings banks) and credit unions.
What is Category 1 bank in India
What is an AD Category-1 Bank The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) gives an AD Category-1 Bank permission to deal in foreign exchange transactions. AD stands for Authorised Dealer, and Category-1 is the highest authorised dealer category in India's foreign exchange transactions.
How many types of private banks are there in India
21 private sector banks
At present, there are 21 private sector banks in India. In India, there are two categories of commercial banks: scheduled commercial banks and non-scheduled commercial banks.
What are the 4 types of banks
The 4 different types of banks are Central Bank, Commercial Bank, Cooperative Banks, Regional Rural Banks.
What is the most common type of bank
The most common financial institution the public uses is commercial banks. It is because commercial banks offer lower service fees that enable clients to keep their accounts open without worrying about them being closed. Their services are not limited as they offer plenty of products to their clients.
What are the 14 major Indian banks
The 14 private banks which were nationalized in 1969 are Allahabad Bank, UCO Bank, Canara Bank, United Bank of India, Central Bank of India, Syndicate Bank, Indian Overseas Bank, Bank of Baroda, Punjab National Bank, Dena Bank, Bank of India, Bank of Maharashtra, Indian Bank, and Union Bank.
What are the 12 Indian banks
The 12 public sector banks are – State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank, Bank of Baroda, Bank of India, Central Bank of India, Canara Bank, Union Bank of India, Indian Overseas Bank, Punjab and Sind Bank, Indian Bank, UCO Bank, and Bank of Maharashtra.
What is a Category 4 bank
(1) A banking organization with average total consolidated assets of $100 billion or more is a Category IV banking organization if the banking organization: (i) Is not a Category II banking organization; and. (ii) Is not a Category III banking organization.
What is Tier 1 bank vs Tier 2
Tier 1 and tier 2 capital are two types of assets held by banks. Tier 1 capital is a bank's core capital, which it uses to function on a daily basis. Tier 2 capital is a bank's supplementary capital, which is held in reserve. Banks must hold certain percentages of different types of capital on hand.
What are the 14 private banks in India
List of Private Indian BanksAxis Bank. Mumbai, Maharashtra. 1993.Bandhan Bank. Kolkata, West Bengal. 2015.CSB Bank. Thrissur, Kerala. 1920.City Union Bank. Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu. 1904.DCB Bank. Mumbai, Maharashtra. 1930.Dhanlaxmi Bank. Thrissur, Kerala. 1927.Federal Bank. Aluva, Kerala. 1931.HDFC Bank. Mumbai, Maharashtra. 1994.
What are the four private bank in India
List of Top 10 Best Private Banks in India 2023
| Bank Name | Total Branches | Total ATMs |
|---|---|---|
| HDFC Bank | 6,342 | 18,130 |
| ICICI Bank | 5,275 | 15,589 |
| Axis Bank | 4,758 | 10,990 |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank | 1,600 | 2,519 |
What are the 4 types of banks in India
Classification of Banks in IndiaCommercial Banks.Small Finance Banks.Payments Banks.Co-operative Banks.
Which banking is popular in India
Summary: 10 Best Banks in India 2023
| Company | Industry | Market Cap (Rs. Cr.) |
|---|---|---|
| State Bank of India (SBI) | Banking | 505,579 |
| HDFC Bank | Banking | 884,252 |
| ICICI Bank | Banking | 648,053 |
| Punjab National Bank (PNB) | Banking | 55,495 |
What are the 20 bank in India
Top 20 Best Banks in India 2023Bank of India. Bank of India (BOI) is a leading public sector bank in India, with a history that spans over a century.HDFC Bank.ICICI Bank.Punjab National Bank.Bank of Baroda.Canara Bank.Union Bank of India.Axis Bank.
What are the 15 banks name in India
These are YES Bank, Tamilnad Mercantile Bank, South Indian Bank, RBL Bank, Nainital Bank, IDBI Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, Karur Vysya Bank, Karnataka Bank, Jammu & Kashmir Bank, IDFC FIRST Bank, IndusInd Bank, ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, Federal Bank, Dhanlaxmi Bank, DCB Bank, City Union Bank, CSB Bank, Bandhan Bank, and …
Who are Category 1 banks
3 Category I would include JPMorgan Chase & Co., Bank of America Corporation, Citigroup, Inc., Wells Fargo & Company, The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc., Morgan Stanley, The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation, and State Street Corporation.
What is D1 D2 D3 d4 in banking
(D1 = doubtful up to 1 year, D2= doubtful 1 to 3 years, and D3= doubtful more than 3 years). For commercial banks 100 percent of the extent to which the advance is not covered by the realisable value of the security to which the bank has a valid recourse and the realisable value is estimated on a realistic basis.
What is Tier 1 Tier 2 and Tier 3 in banking
Tier 1 and tier 2 capital are two types of assets held by banks. Tier 1 capital is a bank's core capital, which it uses to function on a daily basis. Tier 2 capital is a bank's supplementary capital, which is held in reserve. Banks must hold certain percentages of different types of capital on hand.
What are Tier 3 banks
Key Takeaways. Tier 3 capital was unsecured debt banks held to support market risk in their trading activities. Unsecured, subordinated debt made up tier 3 capital and was of lower quality than tier 1 and tier 2 capital.
Why 14 banks nationalised in India
In 1969, 14 banks were nationalized by the Government of India to utilize their resources in the development of the country. These banks constituted more than Rs 50 crore, which was intended to be used to meet the development needs of the economy for agriculture, exports, small-scale industries, etc.
Who is the No 1 bank in India
State Bank of India (SBI)
Top 10 Banks in India 2022 vs 2023
| Rank | Bank Name | Net Profit 2023 (Rs. Cr.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | State Bank of India (SBI) | 56,558 |
| 2 | HDFC Bank | 46,149 |
| 3 | ICICI Bank | 34,463 |
| 4 | Punjab National Bank (PNB) | 3,069 |
What is the difference between public and private banks in India
Public sector banks are those in which the union or state government owns more than 50% of the stock. Private sector banks are those in which private firms or individuals own the majority of the stock. Acts of parliament are used to establish public sector banks.


