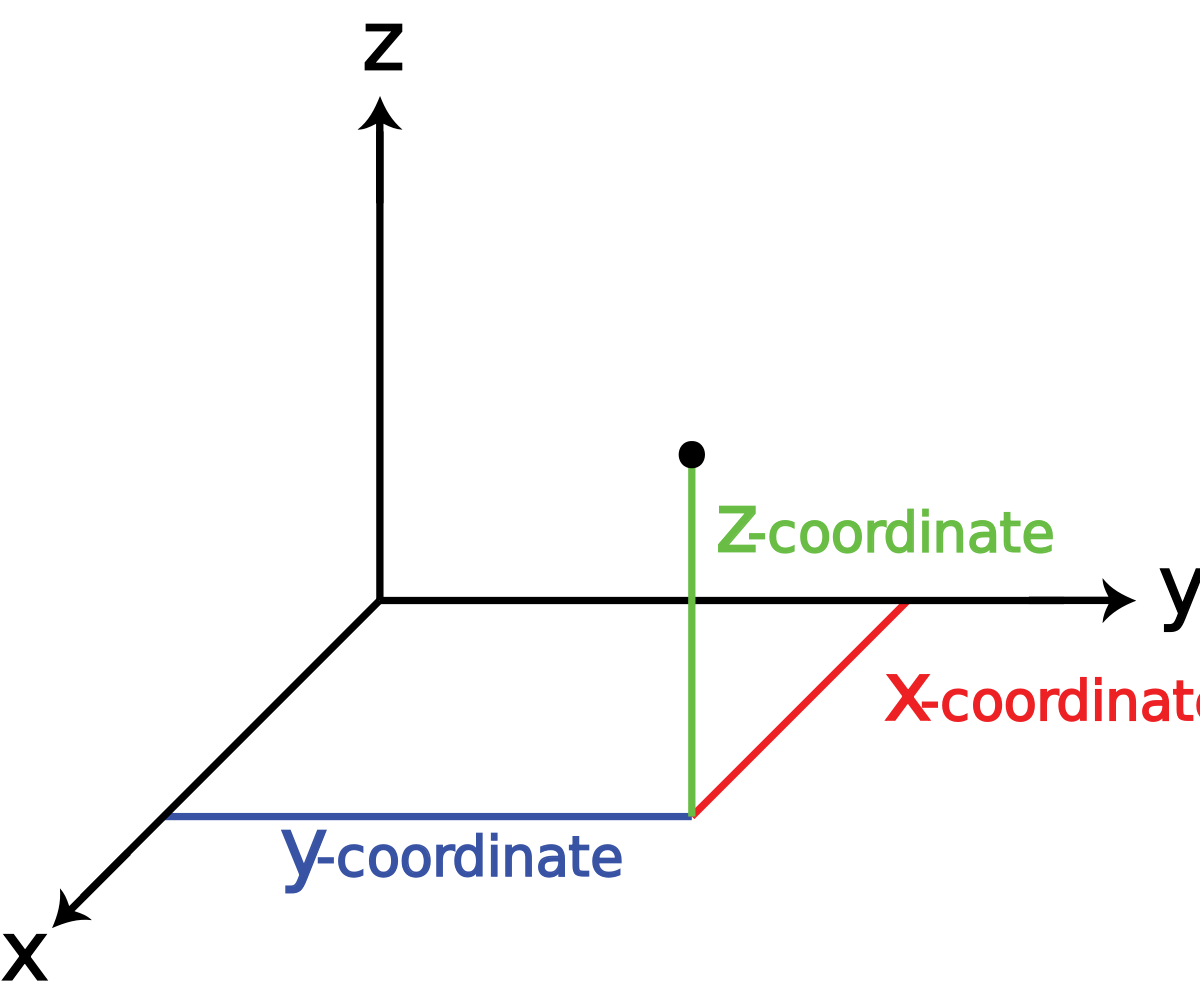
What is Z on coordinates
Usually, the x-coordinate is measured along the eastwest axis, the y-coordinate is measured along the northsouth axis, and the z-coordinate measures height or elevation.
What is the Z axis
z-axis (plural z-axes) (algebraic geometry) The axis on a graph of at least three dimensions that is usually drawn vertically and usually shows the range of values of a variable dependent on two other variables or the third independent variable.
What is Z coordinate vector
Vectors in Three Dimensions
To specify the location of a point in space, we need three coordinates (x, y, z), where coordinates x and y specify locations in a plane, and coordinate z gives a vertical position above or below the plane.
What is xy and z coordinate plane
The coordinate planes are: the xy-plane, the set of all points whose z-coordinate is zero; the yz-plane, the set of all points whose x-coordinate is zero; and the xz-plane, the set of all points whose y-coordinate is zero. The projection of a point P = (x, y, z) onto the xy-plane is the point (x, y,0).
What is the Z direction called
As shocking asw it may sound, it is usually called "the z – axis" … sometimes it is also called "the vertical axis", but this depends on the point of view.
What does Z mean in surveying
As far as surveyors in USA and Canada are concerned: X increases from south to north, and is called "northing" Y increases from west to east, and is called "easting" Z increases from down to up, and is called "elevation"
What does Z do in a graph
The Z axis allows you to add information from an additional variable to the graph, either: Adding color (either shading by a numerical value in Z, or coloring by a category of Z) Grouping the samples according to a category of Z.
Why is Z the vertical axis
This convention developed in the 1960s (or earlier) from the way that images were originally stored in display buffers. For three-dimensional systems, a convention is to portray the xy-plane horizontally, with the z-axis added to represent height (positive up).
What is Z in XYZ graph
The x-axis and y-axis represent the first two dimensions; the z-axis, the third dimension. In a graphic image, the x and y denote width and height; the z denotes depth.
What is Z coordinate in 3D
The third coordinate is often called z. The z-axis is perpendicular to both the x-axis and the y-axis. This demo illustrates a 3D coordinate system. The positive directions of the x, y, and z axes are shown as big arrows. The x-axis is green, the y-axis is blue, and the z-axis is red.
Is the Z-axis a plane
When referring to a three-dimensional plane, a z-axis refers to the depth of a three-dimensional object. In the illustration, the z-axis plane goes front to back, and intersects with the y-axis and x-axis at the origin.
Is Z 0 the XY plane
The xy-plane contains the x- and y-axes and its equation is z = 0, the xz-plane contains the x- and z-axes and its equation is y = 0, The yz-plane contains the y- and z-axes and its equation is x = 0. These three coordinate planes divide space into eight parts called octants.
Is Z up or down
The Z axis is perpendicular to the ground plane; think of it as a line drawn between the device and the center of the Earth. The value of the Z coordinate is positive upward (away from the center of the Earth) and negative downward (toward the center of the Earth).
What is the origin of an XYZ coordinate system
Definitions of origin and coordinate system
What is an origin The origin is the location at which x, y and z are all zero ({0,0,0}).
What is the Z axis value
The Z axis is perpendicular to the ground plane; think of it as a line drawn between the device and the center of the Earth. The value of the Z coordinate is positive upward (away from the center of the Earth) and negative downward (toward the center of the Earth).
How do you find Z on a graph
To find the z-score, subtract the mean from the quantity in question, and then divide by the standard deviation of the whole set. Remember that negative z-scores are on the left of the curve, while positive z-scores are on the right.
Is Y or Z vertical
These axes are normally taken so that X axis is the longitudinal axis pointing ahead, Z axis is the vertical axis pointing downwards, and the Y axis is the lateral one, pointing in such a way that the frame is right-handed.
Why is the Z axis important
So Z-axis capability is always going to be very important because it extends location accuracy to the person and not just the vehicle.” Location-based services, including the Z-axis or vertical location, have many potential benefits for law enforcement: Officer safety.
What does Z mean in 3D printing
vertical movement
The 3D positioning system is therefore composed of 3 axes. The x and y axes correspond to the 3D printer's lateral movement, and the z-axis corresponds to vertical movement.
Is Z the vertical axis
[coordinate systems] In a spherical coordinate system, the vertical line that runs parallel to the earth's rotation, passing through 90 degrees north latitude, and perpendicular to the equatorial plane, where it crosses the x- and y-axes at the origin (0,0,0).
What does Z 0 plane mean
Answer: In a z-coordinate of any point on the x-y plane is always 0. Therefore, the equation z = 0 can denote every point that has its z-coordinate equal to 0. Hence the equation z = 0 represents the entire x-y plane.
Is the Z axis a plane
When referring to a three-dimensional plane, a z-axis refers to the depth of a three-dimensional object. In the illustration, the z-axis plane goes front to back, and intersects with the y-axis and x-axis at the origin.
Is Z or Y vertical
The x-axis is the horizontal line along which the wall to your left and the floor intersect. The y-axis is the horizontal line along which the wall to your right and the floor intersect. The z-axis is the vertical line along which the walls intersect.
What does Z mean in XYZ
The x-axis and y-axis represent the first two dimensions; the z-axis, the third dimension. In a graphic image, the x and y denote width and height; the z denotes depth.
Where is the Z axis
The Y axis follows along the ground plane, and is positive toward true north (that is, the North Pole, not magnetic north) and negative toward true south. The Z axis is perpendicular to the ground plane; think of it as a line drawn between the device and the center of the Earth.