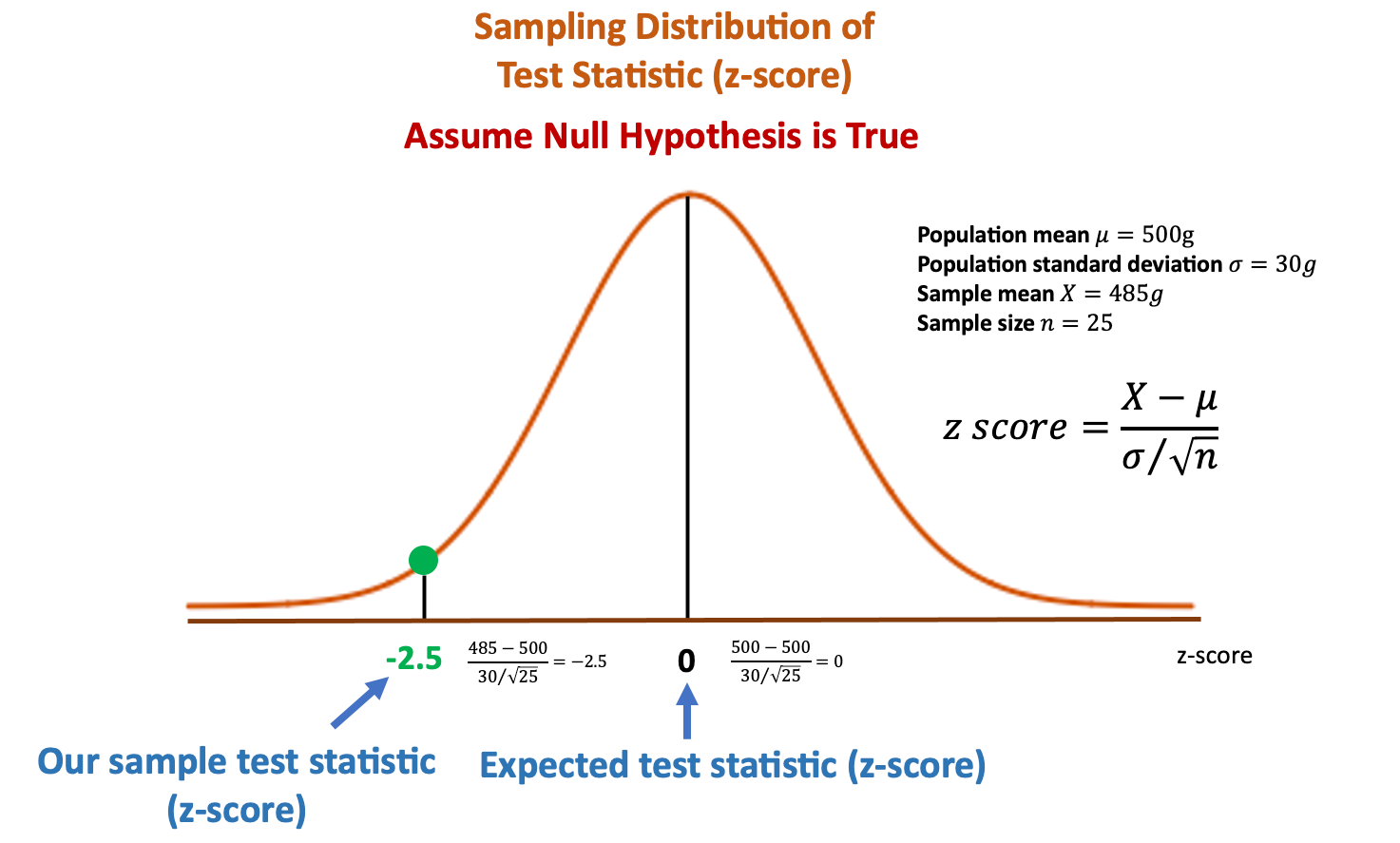
What is z in p-value
For each test, the z-value is a way to quantify the difference between the population means and the p-value is the probability of obtaining a z-value with an absolute value at least as large as the one we actually observed in the sample data if the null hypothesis is actually true.
Bản lưu
What is the z-score for 0.05 significance level
-1.645
a z-score less than or equal to the critical value of -1.645. Thus, it is significant at the 0.05 level. z = -3.25 falls in the Rejection Region. A sample mean with a z-score greater than or equal to the critical value of 1.645 is significant at the 0.05 level.
What does Z mean in statistics probability
A z-score, or z-statistic, is a number representing how many standard deviations above or below the mean population the score derived from a z-test is. Essentially, it is a numerical measurement that describes a value's relationship to the mean of a group of values.
Bản lưu
What is Z at 5% level of significance
A sample mean with a z-score less than or equal to the critical value of -1.645 is significant at the 0.05 level. There is 0.05 to the left of the critical value. Any z-score to the left of -1.645 will be rejected.
What is the Z value for 5% level of significance
For example, the critical values for a 5 % significance test are: For a one-tailed test, the critical value is 1.645 . So the critical region is Z<−1.645 for a left-tailed test and Z>1.645 for a right-tailed test. For a two-tailed test, the critical value is 1.96 .
How do you interpret Z
A positive z-score says the data point is above average. A negative z-score says the data point is below average. A z-score close to 0 says the data point is close to average. A data point can be considered unusual if its z-score is above 3 or below −3 .
What do z-scores tell you
Z-score indicates how much a given value differs from the standard deviation. The Z-score, or standard score, is the number of standard deviations a given data point lies above or below mean. Standard deviation is essentially a reflection of the amount of variability within a given data set.
What is the Z value at 95% level of significance
The critical z-score values when using a 95 percent confidence level are -1.96 and +1.96 standard deviations.
What is the Z value for 2.5 significance level
For α = . 05, this means 2.5% of the area is in each tail, which, based on the z-table, corresponds to critical values of z∗ = ±1.96. This is shown in Figure 7.5. 2.
Can Z value be greater than 5
You can certainly get a z-score to exceed 5 in absolute size, or indeed any other finite value.
Why is Z 1.96 at 95 confidence
The value of 1.96 is based on the fact that 95% of the area of a normal distribution is within 1.96 standard deviations of the mean; 12 is the standard error of the mean. Figure 1. The sampling distribution of the mean for N=9. The middle 95% of the distribution is shaded.
What do Z values mean
A z-score describes the position of a raw score in terms of its distance from the mean when measured in standard deviation units. The z-score is positive if the value lies above the mean and negative if it lies below the mean.
What does Z measure in statistics
A z-score is an example of a standardized score. A z-score measures how many standard deviations a data point is from the mean in a distribution.
How do you interpret the Z statistic
Z-scores can be positive or negative. The sign tells you whether the observation is above or below the mean. For example, a z-score of +2 indicates that the data point falls two standard deviations above the mean, while a -2 signifies it is two standard deviations below the mean. A z-score of zero equals the mean.
What is the z-value for 5% level of significance
For example, the critical values for a 5 % significance test are: For a one-tailed test, the critical value is 1.645 . So the critical region is Z<−1.645 for a left-tailed test and Z>1.645 for a right-tailed test. For a two-tailed test, the critical value is 1.96 .
What if the z-score is greater than 2
z-score is a measure of how close the given data point is to the mean of the values given with the standard deviation. If the z-score is less than -2 or greater than 2, then the data is unusual. Therefore, a data value is considered unusual if its z-score is less than minus 2 or greater than 2.
What if z is greater than 3
z-scores greater than +3 or less than -3 are considered outliers. This is because an outlier can be defined as a value that is more than 3 standard deviations above or below the mean. Calculating the z-score is used to compare scores from different sets of data that have different means and standard deviations.
What does the z-score +/- 1.96 indicate
The critical z-score values when using a 95 percent confidence level are -1.96 and +1.96 standard deviations. The uncorrected p-value associated with a 95 percent confidence level is 0.05.
What is Z in 95 confidence interval
The value of z* for a specific confidence level is found using a table in the back of a statistics textbook. The value of z* for a confidence level of 95% is 1.96.
Why is Z-value important
Therefore, Z value explains the resistance of an organism to varying temperatures. These measurements are important in different fields, especially during food canning, manufacturing cosmetics and pharmaceuticals and preparation of animal feeds.
What is a good Z-value in statistics
According to the Percentile to Z-Score Calculator, the z-score that corresponds to the 90th percentile is 1.2816. Thus, any student who receives a z-score greater than or equal to 1.2816 would be considered a “good” z-score.
Why is the z-score significant
The standard score (more commonly referred to as a z-score) is a very useful statistic because it (a) allows us to calculate the probability of a score occurring within our normal distribution and (b) enables us to compare two scores that are from different normal distributions.
How do you interpret Z and T scores
Z score is the standardization from the population raw data or more than 30 sample data to a standard score, while the T score is the standardization from the sample data of less than 30 data to a standard score. Z score ranges from -3 to 3, while the T score ranges from 20 to 80.
Does a z-score of 2.5 mean
Z-scores are measured in standard deviation units.
For example, a Z-score of 1.2 shows that your observed value is 1.2 standard deviations from the mean. A Z-score of 2.5 means your observed value is 2.5 standard deviations from the mean and so on.
Can z-value be greater than 5
You can certainly get a z-score to exceed 5 in absolute size, or indeed any other finite value.