What is the 95 rule in statistics
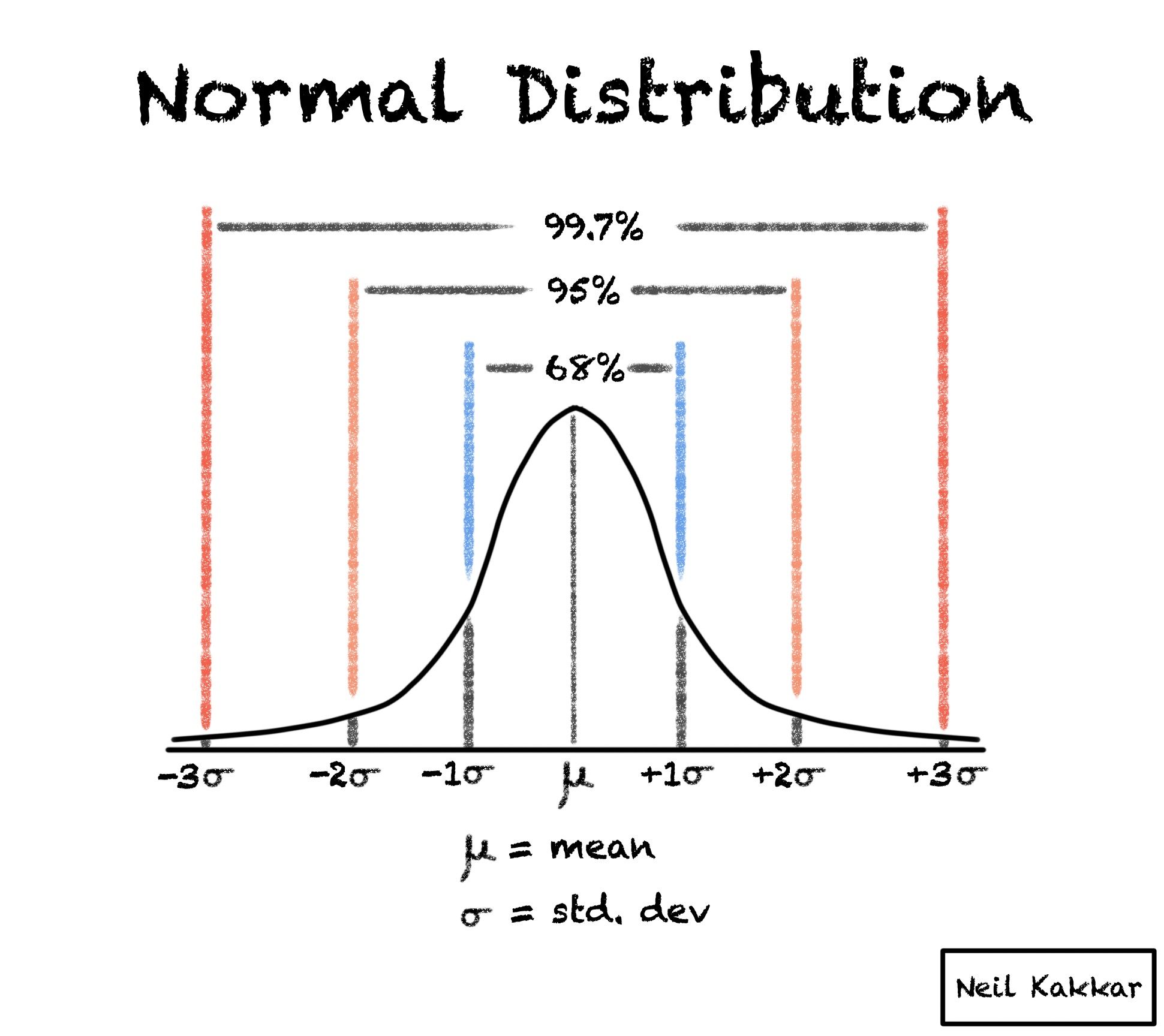
Your textbook uses an abbreviated form of this, known as the 95% Rule, because 95% is the most commonly used interval. The 95% Rule states that approximately 95% of observations fall within two standard deviations of the mean on a normal distribution.
What is the 68% and 95% rule
The empirical rule (also called the "68-95-99.7 rule") is a guideline for how data is distributed in a normal distribution. The rule states that (approximately): – 68% of the data points will fall within one standard deviation of the mean. – 95% of the data points will fall within two standard deviations of the mean.
What is 95 of standard deviation
Since 95% of values fall within two standard deviations of the mean according to the 68-95-99.7 Rule, simply add and subtract two standard deviations from the mean in order to obtain the 95% confidence interval.
What is the middle 95 of a normal distribution
If we wanted to specify the middle 95% of a normal distribution, then the magical number is 1.96: 95% of the probability mass in a normal distribution falls within 1.96 standard deviations on either side of it.
Why do statisticians use 95 confidence
By the book, a 95% confidence interval is a numerical range which upon repeated sampling, will contain the true value 95% of the time. In practice it serves as: A range of plausible values. A measure of precision.
What is 95 confidence level in statistical analysis
A 95% confidence interval is a range of values (upper and lower) that you can be 95% certain contains the true mean of the population.
What is the 68-95-99.7 rule about what of values are within one standard deviation of the mean
Approximately 68%
Empirical Rule or 68-95-99.7% Rule
Approximately 68% of the data fall within one standard deviation of the mean. Approximately 95% of the data fall within two standard deviations of the mean. Approximately 99.7% of the data fall within three standard deviations of the mean.
What is the empirical rule 68-95-99.7 rule to find percentile
Option is is we know that 50% falls by a hundred and eighty. And half of 68 is 34. So we can say that 50. Minus 34 or 16% falls below that so that would be the sixteenth. Percentile.
What is the formula for the 95 confidence interval
The critical value for a 95% confidence interval is 1.96, where (1-0.95)/2 = 0.025. A 95% confidence interval for the unknown mean is ((101.82 – (1.96*0.49)), (101.82 + (1.96*0.49))) = (101.82 – 0.96, 101.82 + 0.96) = (100.86, 102.78).
How many standard deviations do 95% of scores fall within
two standard deviations
Empirical Rule or 68-95-99.7% Rule
Approximately 68% of the data fall within one standard deviation of the mean. Approximately 95% of the data fall within two standard deviations of the mean. Approximately 99.7% of the data fall within three standard deviations of the mean.
What is 95 probability range
between -1.96 and 1.96
For the standard normal distribution, P(-1.96 < Z < 1.96) = 0.95, i.e., there is a 95% probability that a standard normal variable, Z, will fall between -1.96 and 1.96.
What is 95 confidence interval median
The 95% confidence interval for the median will be between the j = 4th and k = 12th observation in the sample dataset. The 4th observation is equal to 13 and the 12th observation is equal to 23: What is this Thus, the 95% confidence interval for the median turns out to be [13, 23].
How do you interpret a 95 confidence interval
A confidence interval indicates where the population parameter is likely to reside. For example, a 95% confidence interval of the mean [9 11] suggests you can be 95% confident that the population mean is between 9 and 11.
Is 95% confidence level significant
In accordance with the conventional acceptance of statistical significance at a P-value of 0.05 or 5%, CI are frequently calculated at a confidence level of 95%. In general, if an observed result is statistically significant at a P-value of 0.05, then the null hypothesis should not fall within the 95% CI.
Is 95% 0.05 confidence level
In accordance with the conventional acceptance of statistical significance at a P-value of 0.05 or 5%, CI are frequently calculated at a confidence level of 95%. In general, if an observed result is statistically significant at a P-value of 0.05, then the null hypothesis should not fall within the 95% CI.
How do you use the 68 95 and 99.7 rule with mean and standard deviation
And half of this is 34%. Giving us our area from zero to one. The next half goes from zero to negative two. But we know that within two standard deviations. From the mean we have an area of 95%.
When can you use the 68 95 and 99.7 rule
The "68–95–99.7 rule" is often used to quickly get a rough probability estimate of something, given its standard deviation, if the population is assumed to be normal. It is also used as a simple test for outliers if the population is assumed normal, and as a normality test if the population is potentially not normal.
How do you find 95% using the empirical rule
To calculate the empirical rule:Determine the mean m and standard deviation s of your data.Add and subtract the standard deviation to/from the mean: [m − s, m + s] is the interval that contains around 68% of data.Multiply the standard deviation by 2 : the interval [m − 2s, m + 2s] contains around 95% of data.
What is 95 confidence interval mean
A 95% confidence interval is a range of values that you can be 95% certain contains the true mean of the population. This is not the same as a range that contains 95% of the values. The graph below emphasizes this distinction.
What is 95 confidence interval simple
For a two-tailed 95% confidence interval, the alpha value is 0.025, and the corresponding critical value is 1.96. This means that to calculate the upper and lower bounds of the confidence interval, we can take the mean ±1.96 standard deviations from the mean.
Does 95 fall within two standard deviations
The empirical rule in statistics, also known as the 68 95 99 rule, states that for normal distributions, 68% of observed data points will lie inside one standard deviation of the mean, 95% will fall within two standard deviations, and 99.7% will occur within three standard deviations.
How many standard deviations is a 95% confidence interval
1.96
For instance, 1.96 (or approximately 2) standard deviations above and 1.96 standard deviations below the mean (±1.96SD mark the points within which 95% of the observations lie.
How many deviations is 95
two standard deviations
Under this rule, 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation, 95% percent within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three standard deviations from the mean.
What is 95 confidence prediction
This means that if you repeat the sampling process many times, 95% of the intervals you get will include the true mean sales. A confidence interval reflects the uncertainty of your estimation, not your prediction. It depends on the sample size, the variability of the data, and the confidence level you choose.
What confidence interval is 90 or 95
The 95% confidence level is often used, though the 99% CI are used occasionally. At 99%, the width of the CI will be larger but it is more likely to contain the true population value, than the narrower 95% CI. Bioequivalence testing makes use of the 90% CI.