What is cold and hot backup
Availability: A cold backup requires the system or application to be shut down during the backup process, which means it is not available for use during that time. In contrast, a hot backup can be taken while the system or application is still running, so it remains available to users.
What explains hot backup
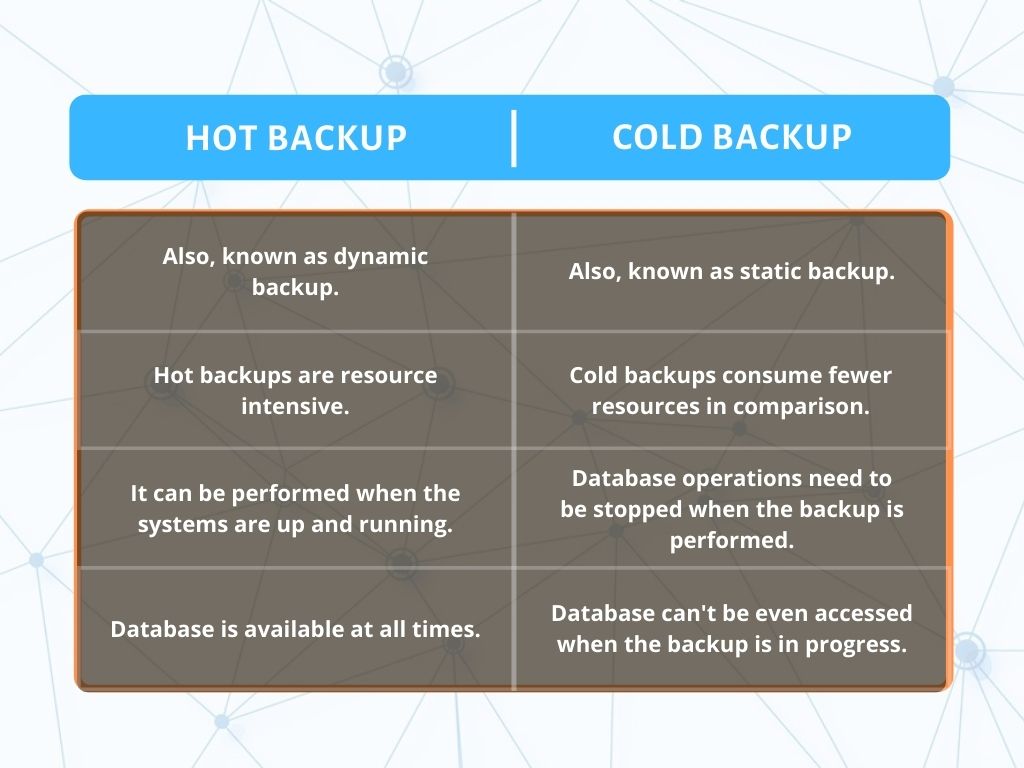
Hot backup, also known as dynamic or online backup, is a backup performed on data while the database is actively online and accessible to users. A hot backup is the standard way of doing most database backups.
What is cold backup
A cold backup, also called an offline backup, is a database backup during which the database is offline and not accessible to update. This is the safest way to back up because it avoids the risk of copying data that may be in the process of being updated.
What is hot backup and cold backup in SQL Server
A hot backup is performed whilst users are still logged into a system, whereas a cold backup is done with all users offline. The reason for performing hot backups is that it minimises downtime on a day-to-day basis, which is especially useful for systems that require 24/7 operation.
What are the 3 types of backups
Types of BackupsFull backup: The most basic and comprehensive backup method, where all data is sent to another location.Incremental backup: Backs up all files that have changed since the last backup occurred.Differential backup: Backs up only copies of all files that have changed since the last full backup.
What is the difference between hot and warm backup
Warm sites are "ready to go" in one sense, but they still need to have data transported for use in recovery should a disaster occur. Hot Computing Sites – a fully functional backup site that already has important data mirrored to it. This is the ideal disaster recovery site, but it can be challenging to attain.
What are the three 3 types of backup
There are mainly three types of backup: full, differential, and incremental. Let's dive in to know more about the types of backup, the difference between them and which one would be the best fit for your business.
How to do hot backup
How to take a Hot backup of Oracle database put the db in archive log mode. set the db_sid to correct one. login to sqlplus. verify the name of the db that you are connected to. check if the db is in archive log made. find where on disk oracle writes archive log when it is in archive log mode.
What is hot backup in SQL
Hot Backup in SQL Server
Hot backup is done when the database is online. The process is simple. To do a hot backup, simply right-click the database and select Tasks > Back Up. Then, select a path and configure the backup according to your needs.
What are the four 4 types of backup systems
The most common backup types are a full backup, incremental backup and differential backup. Other backup types include synthetic full backups and mirroring. In the debate over cloud vs. local backup, there are some types of backup that are better in certain locations.
Which type of backup is fastest
Incremental backups are completed quickly and require fewer resources. Disadvantage: While incremental backups have the fastest backup time, they also boast the slowest data recovery time.
Is hot or cold standby better
If you think of latency as the speed at which data is shipped back and forth to be backed up, a cold standby would see this data backed up significantly less than that of a warm or hot standby for example. This means that when there is a sudden interruption, the system takes a very long time to get back up again.
How do I take a hot backup
How to take a Hot backup of Oracle database put the db in archive log mode. set the db_sid to correct one. login to sqlplus. verify the name of the db that you are connected to. check if the db is in archive log made. find where on disk oracle writes archive log when it is in archive log mode.
What is the difference between hot back up site and cold backup site
A hot site is fully functional and allows immediate recovery from a disaster while a cold site only includes infrastructure but no technology until a disaster hits.
What is hot or online backup
An online or hot backup is a backup performed while the database is online and available for read/write operations. Except for Oracle exports, you can only perform online backups when running in ARCHIVELOG mode. An offline or cold backup is a backup performed while the database is offline and unavailable to its users.
Is hot backup done in offline mode
An online or hot backup is a backup performed while the database is online and available for read/write operations. Except for Oracle exports, you can only perform online backups when running in ARCHIVELOG mode. An offline or cold backup is a backup performed while the database is offline and unavailable to its users.
What happens during hot backup in Oracle
* During the hot backups the entire block containing a changed record, not just the changed record, is written to the archive log, requiring more archive space for this period. The hot backup consists of three processes: The tablespace data files are backed up. The archived redo logs are backed up.
Why does hot backup generate lots of redo
Normally only the changed bytes (a redo vector) is written. In hot backup mode, the entire block is logged the FIRST TIME. This is because you can get into a situation where the process copying the datafile and DBWR are working on the same block simultaneously.
What are the two types of backup
The most common backup types are a full backup, incremental backup and differential backup. Other backup types include synthetic full backups and mirroring. In the debate over cloud vs. local backup, there are some types of backup that are better in certain locations.
What is hot vs cold failover
There are 2 primary types of failover, hot and cold. A hot failover immediately detects a failure and switches over to a secondary running system. There's usually no interruption visible to the operator. A cold failover is a manual, and therefore, delayed switch-over to a secondary system.
What is the difference between hot backup and online backup
Online backup can also be known as “remote backup” or “offsite backup”. You may also see this process referred to as “hot backup”, which means the backup happens while the data is still accessible to users.
Which backup is more efficient
Incremental Backup
Only the recent changes (increments) are backed up, consuming less storage space and resulting in a speedy backup. However, the recovery time is longer since more backup files will need to be accessed.
What is hot vs cold memory
What Is Hot Storage and Cold Storage Hot storage refers to fast, easy-to-access data storage like your local hard drive or a quick-access cloud storage provider like Google Drive. In contrast, cold storage is for archival data that is rarely accessed and usually stored off site.
What is hot memory
Hot memory refers to memories created as a result of an emotionally charged situation; one example of such an emotional memory which is created and maintained by the hot memory system would be an association between a song and a person.
What is cold data vs hot data
In computer storage, cold data refers to data that is rarely accessed, therefore considered "cold". Cold data is the opposite of hot data, which is data that is frequently accessed. To optimize storage costs, cold data can be stored on lower performing and less expensive storage media.