What is full backup backup
A full backup is a complete copy of a business or organization's data assets in their entirety. This process requires all files to be backed up into a single version. It is the best data protection option in terms of speed of recovery and simplicity because it creates a complete copy of the source data set.
What is an example of a full data backup
Example of a full backup
For example, the admin might determine that a specific hard disk needs to execute a full backup twice a week, on Tuesdays and Fridays. On Tuesday, the entire directory of folders and files on that drive will be copied.
What is full backup and partial backup
Types of Backups
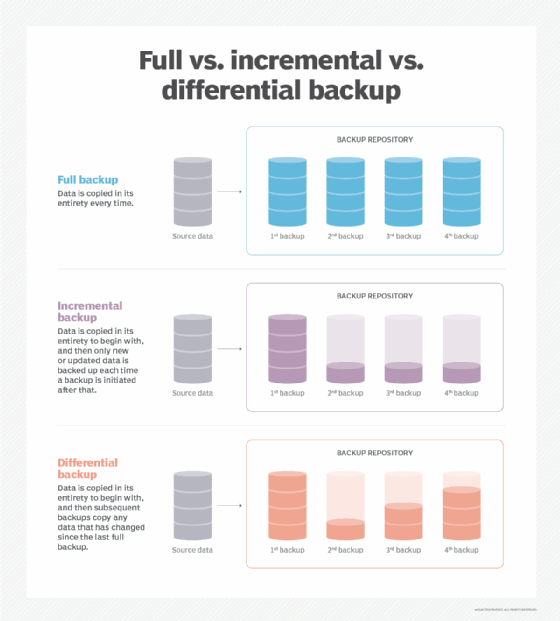
Full backup: The most basic and comprehensive backup method, where all data is sent to another location. Incremental backup: Backs up all files that have changed since the last backup occurred. Differential backup: Backs up only copies of all files that have changed since the last full backup.
What happens during a full backup
Full backups
As the name implies, this type of backup makes a copy of all data to a storage device, such as a disk or tape. The primary advantage to performing a full backup during every operation is that a complete copy of all data is available with a single set of media.
What is the difference between full backup and whole backup
A whole database backup includes all data files and at least one control file. (Remember that all control files within a database are identical.). Full backups make a copy of each data block that contains data and which is within the files being backed up.
What is the difference between full backup and copy backup
The difference between copy-only and a full backup is that a copy-only backup doesn't become a base for the next differential backup.
What is full backup and what are its advantages and disadvantages
The full backup type copies all selected files and folders. Full backup is time consuming (when compared to incremental and differential backup types), but it allows the fastest and easiest restore. It is the starting point of all other backup types.
What are the three 3 types of backup
There are 3 main types of backup: Full, differential and incremental.
What is full backup advantages and disadvantages
A full backup ensures that you have a complete and consistent copy of your data, which can be easily restored in case of a failure. However, a full backup also has some disadvantages. It requires a lot of storage space, bandwidth, and time to perform.
What are the three types of backup
There are 3 main types of backup: Full, differential and incremental.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a full backup
A full backup ensures that you have a complete and consistent copy of your data, which can be easily restored in case of a failure. However, a full backup also has some disadvantages. It requires a lot of storage space, bandwidth, and time to perform.
What are full backup methods
A full backup is the most complete type of backup where you clone all the selected data. This includes files, folders, SaaS applications, hard drives and more.
How many types of data backup are there
There are mainly three types of backups: Full backup, differential backup, and incremental backup. Let's take a look at each type of backup, their impact on data security, and their respective pros and cons.
What are the four types of backup
Each backup program has its own approach in executing the backup, but there are four common types of backup implemented and generally used in most of these programs: full backup, differential backup, incremental backup and mirror backup.
What is the difference between full backup and differential backup
Full backups comprise entire data backup sets, regardless of already existing backups or data change circumstances. Differential backups comprise data files that have changed since the most recently completed full backup.
How often should you run a full backup
Important data should be backed up at least once a week, but preferably once every twenty-four hours. These backups can be performed manually or automatically. A lot of automatic software options are available that you can set to make a backup of your data at a set time of the day or week.
What is difference between full backup and differential backup
Full backups comprise entire data backup sets, regardless of already existing backups or data change circumstances. Differential backups comprise data files that have changed since the most recently completed full backup.
What are the three types of data backup
There are 3 main types of backup: Full, differential and incremental.
How long should a 500 GB backup take
A 500 GB backup may take a few hours (maybe up to 10, give or take). If it's a USB connected drive, it may take longer.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of full backup
A full backup ensures that you have a complete and consistent copy of your data, which can be easily restored in case of a failure. However, a full backup also has some disadvantages. It requires a lot of storage space, bandwidth, and time to perform.
How long does a 100 GB backup take
Speeds are slower than download speeds, a quick calculation will probably show that your backup would still complete in a reasonable amount of time if size and speed were the only impacting factors. At 5Mbps, for example, 100GB should take about 48 hours to backup. A terabyte backup would take less than three weeks.
Is 250 GB enough storage
250GB: operating system or entertainment and backups
A 250GB internal SSD is only enough if you just install the operating system on it or use it for entertainment and backups only. In this case, you choose speed over a large storage capacity.
What are the characteristics of a full backup
A full backup is the most complete type of backup where you clone all the selected data. This includes files, folders, SaaS applications, hard drives and more. The highlight of a full backup is the minimal time it requires to restore data.
How do I backup 1TB of data
Google Drive is a very popular cloud storage platform offering free cloud storage 1TB and more space. It lets you share files, manage different file versions, and restore files easily. However, it is not a zero-knowledge cloud storage provider.
How many GB is 1 TB
1,000 gigabytes
1 terabyte (TB) equals 1,000 gigabytes (GB) or 1,000,000 megabytes (MB).