What are the differences between hot warm and cold backup sites
As the name suggests, a warm site is in between a hot site and a cold site. A hot site is fully functional and allows immediate recovery from a disaster while a cold site only includes infrastructure but no technology until a disaster hits.
What is the difference between hot and warm backup
Warm sites are "ready to go" in one sense, but they still need to have data transported for use in recovery should a disaster occur. Hot Computing Sites – a fully functional backup site that already has important data mirrored to it. This is the ideal disaster recovery site, but it can be challenging to attain.
What is a cold backup
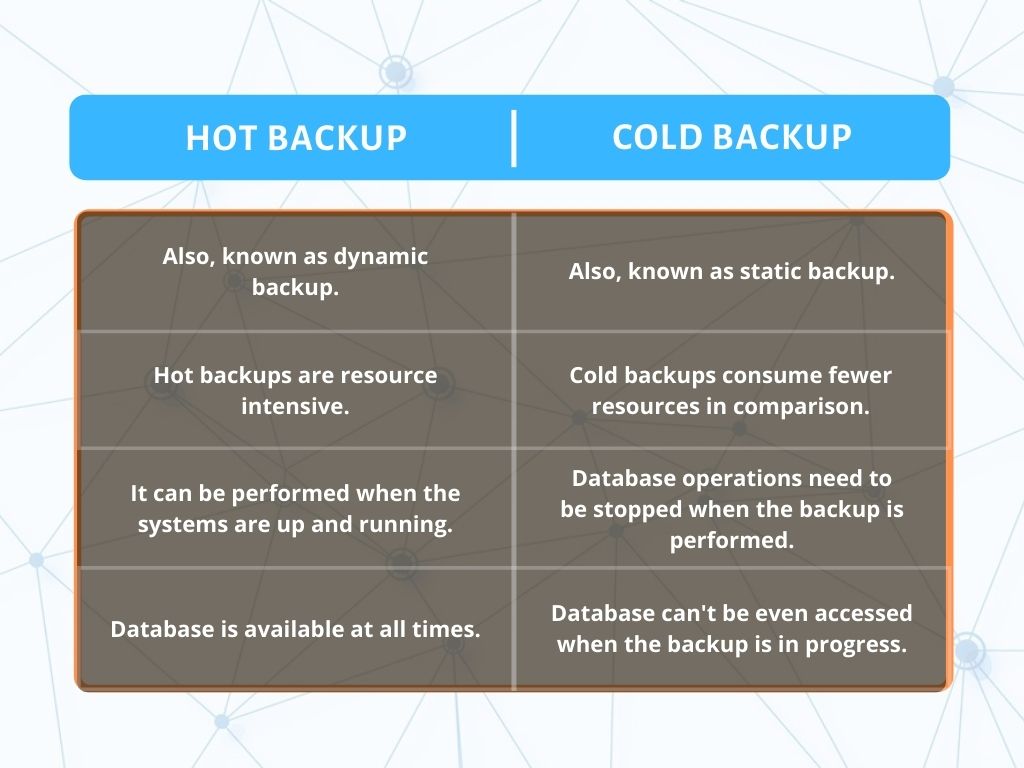
A cold backup, also called an offline backup, is a database backup during which the database is offline and not accessible to update. This is the safest way to back up because it avoids the risk of copying data that may be in the process of being updated.
What is a hot backup
Hot backup, also known as dynamic or online backup, is a backup performed on data while the database is actively online and accessible to users. A hot backup is the standard way of doing most database backups.
What is the difference between the 3 types of backup
Types of Backups
Full backup: The most basic and comprehensive backup method, where all data is sent to another location. Incremental backup: Backs up all files that have changed since the last backup occurred. Differential backup: Backs up only copies of all files that have changed since the last full backup.
What is cold and hot backup
Availability: A cold backup requires the system or application to be shut down during the backup process, which means it is not available for use during that time. In contrast, a hot backup can be taken while the system or application is still running, so it remains available to users.
What are the 3 types of backups
Types of BackupsFull backup: The most basic and comprehensive backup method, where all data is sent to another location.Incremental backup: Backs up all files that have changed since the last backup occurred.Differential backup: Backs up only copies of all files that have changed since the last full backup.
What are the three 3 types of backup
There are mainly three types of backup: full, differential, and incremental. Let's dive in to know more about the types of backup, the difference between them and which one would be the best fit for your business.
What are the four 4 types of backup systems
The most common backup types are a full backup, incremental backup and differential backup. Other backup types include synthetic full backups and mirroring. In the debate over cloud vs. local backup, there are some types of backup that are better in certain locations.
What is warm backup
Warm backups are backups that are usually used for mirroring or replication – in a warm backup scenario the server is powered on, but it's not performing any work. The server might also be turned on only from time to time to get updates from the server being backed up.
What are the four types of computer backups
Each backup program has its own approach in executing the backup, but there are four common types of backup implemented and generally used in most of these programs: full backup, differential backup, incremental backup and mirror backup.
What are the main 3 types of backups in SQL
Microsoft SQL Server allows three basic types of SQL Server backup:Full backup.Differential backup.Transaction log backup.
What are the 3 backups
The 3-2-1 backup rule has been the most effective approach in data protection for decades. By keeping three different copies of your data, stored on two storage media with one kept offsite, you significantly reduce the chances of losing all of your data.
What is the 3-2-1 1 0 backup strategy
The modern 3-2-1-1-0 rule stipulates that backup admins need at least three copies of data in addition to the original data. The 2 in the 3-2-1-1-0 rule directs organizations to back up data on two different types of media.
What is 4-3-2 backup rule
Another relatively new option is 4-3-2. In this case, four copies of the data are stored in three locations, but two of these must be off-site. The 4-3-2 strategy means that backups are duplicated and geographically distant from one another to protect against natural disasters.
What is 3-2-1 backup rule examples
A 3-2-1 backup strategy reduces the impact of a single point of failure, such as a disk drive error or stolen device. For example, you may keep a backup on an external hard drive, a USB drive and cloud storage. If a disaster wipes out your on-site backups, your off-site cloud-based backup can save the day.
What is 3-2-1 1 backup strategy
You may have heard of the 3-2-1 backup strategy. It means having at least three copies of your data, two local (on-site) but on different media (read: devices), and at least one copy off-site. We'll use “socialsecurity.
What is the 3-2-1 0 backup rule
You should have at least 3 copies of your data, including the production copy. At least 2 different storage media should be used; for instance, a tape and a cloud storage. At least 1 of the copies should be kept off-site, in case your machines are physically damaged.
What is 4 3 2 backup rule
Another relatively new option is 4-3-2. In this case, four copies of the data are stored in three locations, but two of these must be off-site. The 4-3-2 strategy means that backups are duplicated and geographically distant from one another to protect against natural disasters.
What is the 3 3 2 backup rule
It breaks down like this: keep at least 3 copies of your data, store 2 copies on different storage media, and make sure 1 of them is stored offsite. With today's greater risks the 3-2-1 rule has evolved into the 3-2-2 rule. (It really could be called the 3-2-1+1 rule, but we're keeping things simple).
What are the 3 ways to backup
6 Effective Strategies to Safely Back Up Your DataUse an External Hard Drive. There are two types of external drives you can buy: HDDs (hard disk drives) or SSDs (solid-state drives).Use a USB Flash Drive.Use Optical Media.Use Cloud Storage.Use an Online Backup Service.Invest in a Network Attached Storage (NAS) Device.
What is the 5 4 3-2-1 backup rule
We decided to supercharge our backup strategy by making it a 5-4-3-2-1. We have 5 copies of our data, on 4 different types of storage, 3 being off-site, with at least 2 off-site locations that are physically distanced, and 1 being offline.
What is the 3 2 2 1 0 backup rule
You should have at least 3 copies of your data, including the production copy. At least 2 different storage media should be used; for instance, a tape and a cloud storage. At least 1 of the copies should be kept off-site, in case your machines are physically damaged.
What is 3-2-1 1 0 backup rule
You should have at least 3 copies of your data, including the production copy. At least 2 different storage media should be used; for instance, a tape and a cloud storage. At least 1 of the copies should be kept off-site, in case your machines are physically damaged.
What is the 4-3-2 1 rule
One simple rule of thumb I tend to adopt is going by the 4-3-2-1 ratios to budgeting. This ratio allocates 40% of your income towards expenses, 30% towards housing, 20% towards savings and investments and 10% towards insurance.