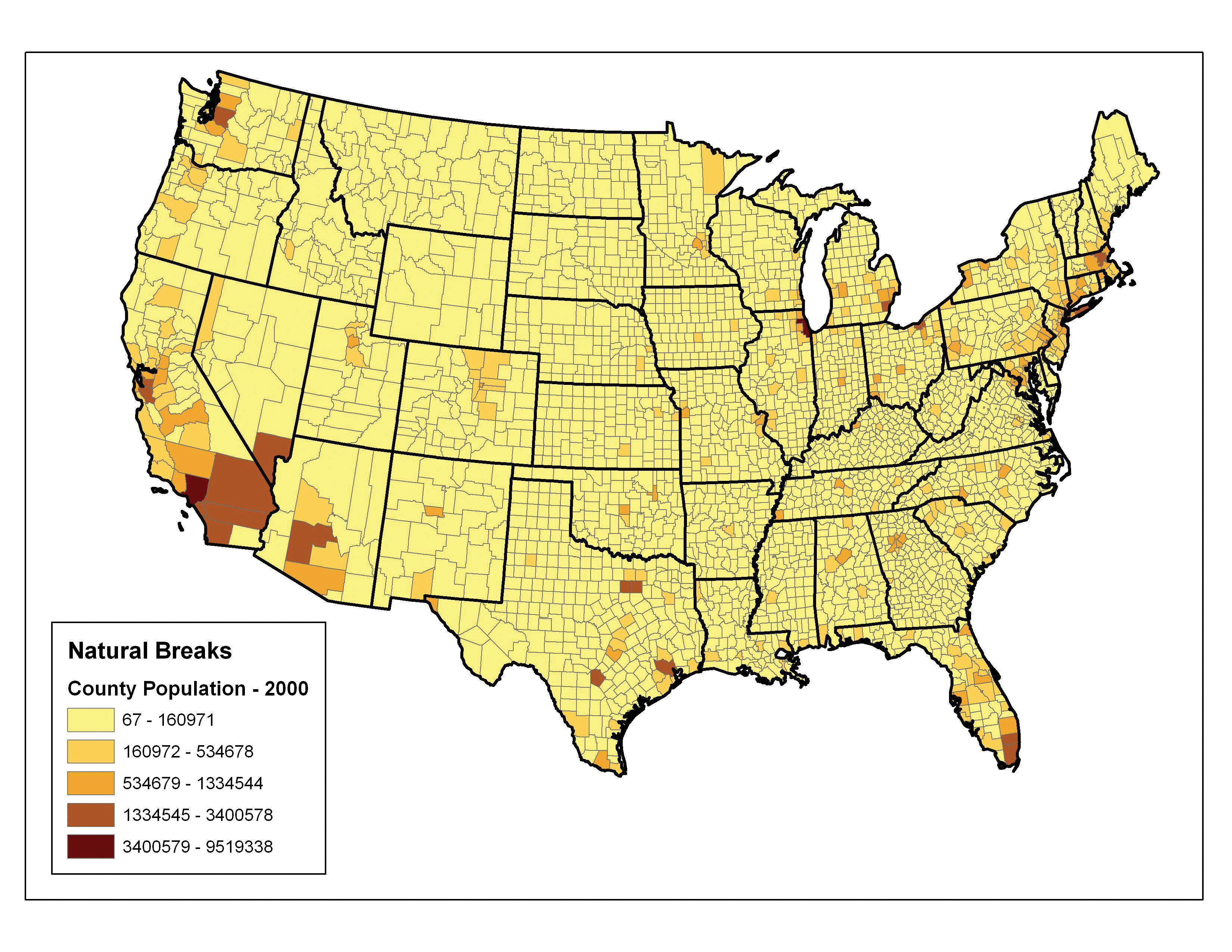
What is a classified map
Maps may be classified according to scale, content, or derivation. The latter refers to whether a map represents an original survey or has been derived from other maps or source data.
What is classification of geographic data
When data are classified with reference to geographical locations such as countries, states, cities, districts, etc., it is known as geographical classification. It is also known as 'spatial classification'. A classification where data are grouped according to time is known as a chronological classification.
What are the classification of GIS applications
Within the spatial referenced data group, the GIS data can be further classified into two different types: vector and raster. Most GIS software applications mainly focus on the usage and manipulation of vector geodatabases with added components to work with raster-based geodatabases.
What is the standard deviation in cartography
Standard deviation is a statistical technique type of map based on how much the data differs from the mean. You measure the mean and standard deviation for your data. Then, each standard deviation becomes a class in your choropleth maps.
What is classification in map generalization
Classification is a second part of cartographic generalization. It involves reducing data to a form that can be easily represented on a map. An example of this type of generalization would be to arrange data on poverty into five classes of counties with each group having a mutually exclusive value range.
What is the difference between a map and a scale
Generally, scale is a form of size. Map or cartographic scale is the ratio of a distance on Earth compared to the same distance on a map.
What are the 4 types of data classification
Data types with similar levels of risk sensitivity are grouped together into data classifications. Four data classifications are used by the university: Controlled Unclassified Information, Restricted, Controlled and Public.
What are the 3 main types of data classification
Data classification generally includes three categories: Confidential, Internal, and Public data. Limiting your policy to a few simple types will make it easier to classify all of the information your organization holds so you can focus resources on protecting your most critical information.
What are the four types of GIS data
The three types of GIS Data are -spatial, –attribute, & —metadataPoint Data — layers containing by points (or “events”) described by x,y (lat,long; easting, northing)Line/Polyline Data — layers that are described by x,y points (nodes, events) and lines (arcs) between points (line segments and polylines)
What is standard deviation on MAP test
An SD is simply a measure of dispersion of scores around the mean value; the smaller the SD, the more compact the scores are around the mean.
What does a standard deviation of 1.15 mean
The Standard Deviation of 1.15 shows that the individual responses, on average*, were a little over 1 point away from the mean. Respondent: Rating "A" Rating "B"
What is map classification in remote sensing
Image classification refers to the task of assigning classes—defined in a land cover and land use classification system, known as the schema—to all the pixels in a remotely sensed image. The output raster from image classification can be used to create thematic maps.
What is an example of map generalization
As an example a 6 m width road represented by a line of 0.6 mm on a map is enlarged 10 times at 1:100,000 and 100 times at 1:1,000,000! Of course, when the scale decreases it is physically not possible to enlarge and displace all objects: many objects are removed, some are aggregated, and they are all simplified.
What is the difference between map scale and scale of analysis
As example, the 1:400.000 map scale means that 1 centimetre represents 4 kilometres on the ground. The scale of analysis is the scale used to analyse the event. It is defined by the type of analysis and the image resolution reflecting the user's need as expressed in the Service Request Form (SRF).
What is the relationship between map and scale
All maps will have an indicator of the scale of the map. The purpose of a scale is to show the relationship of the map distance to the ground distance. In other words, how much does a distance measured on the map represent in the real world Scales are a ratio of the map units to the real world units.
What are the 5 classification of data
Data Classification Levels
Data Classification in Government organizations commonly includes five levels: Top Secret, Secret, Confidential, Sensitive, and Unclassified. These can be adopted by commercial organizations, but, most often, we find four levels, Restricted, Confidential, Internal, Public.
What are 3 main types of data classifications
Data classification generally includes three categories: Confidential, Internal, and Public data. Limiting your policy to a few simple types will make it easier to classify all of the information your organization holds so you can focus resources on protecting your most critical information.
What are the 4 data classification levels
Data classification with GDPR uses the four data classification levels: public data, internal data, confidential data, and restricted data.
What are the 5 data classification categories
The following are five common categories used for data classification:Public data.Private data.Internal data.Confidential data.Restricted data.
What are the 3 types of image data in GIS
Types of GIS Imagery
Hyperspectral, multispectral and panchromatic are general terms that describe imagery types. Hyperspectral imagery is imagery that is used for classifying different land types on the Earth (Dempsey, 2011).
What are three types of GIS data
The three types of GIS Data are -spatial, –attribute, & —metadataPoint Data — layers containing by points (or “events”) described by x,y (lat,long; easting, northing)Line/Polyline Data — layers that are described by x,y points (nodes, events) and lines (arcs) between points (line segments and polylines)
What is acceptable standard deviation SD
Statisticians have determined that values no greater than plus or minus 2 SD represent measurements that are are closer to the true value than those that fall in the area greater than ± 2SD. Thus, most QC programs require that corrective action be initiated for data points routinely outside of the ±2SD range.
How much standard deviation is acceptable
The empirical rule, or the 68-95-99.7 rule, tells you where most of the values lie in a normal distribution: Around 68% of values are within 1 standard deviation of the mean. Around 95% of values are within 2 standard deviations of the mean. Around 99.7% of values are within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
Is 1.2 A High standard deviation
In simple terms, the CV is the ratio between the standard deviation and the mean. The higher the CV, the higher the standard deviation relative to the mean. In general, a CV value greater than 1 is often considered high.
What does a standard deviation of 1.8 mean
Standard Deviation, where N is sample size and. The value of 1.8 tells us that our values have a spread of approximately 1.8 from the center, which makes sense given the set of numbers we started with.