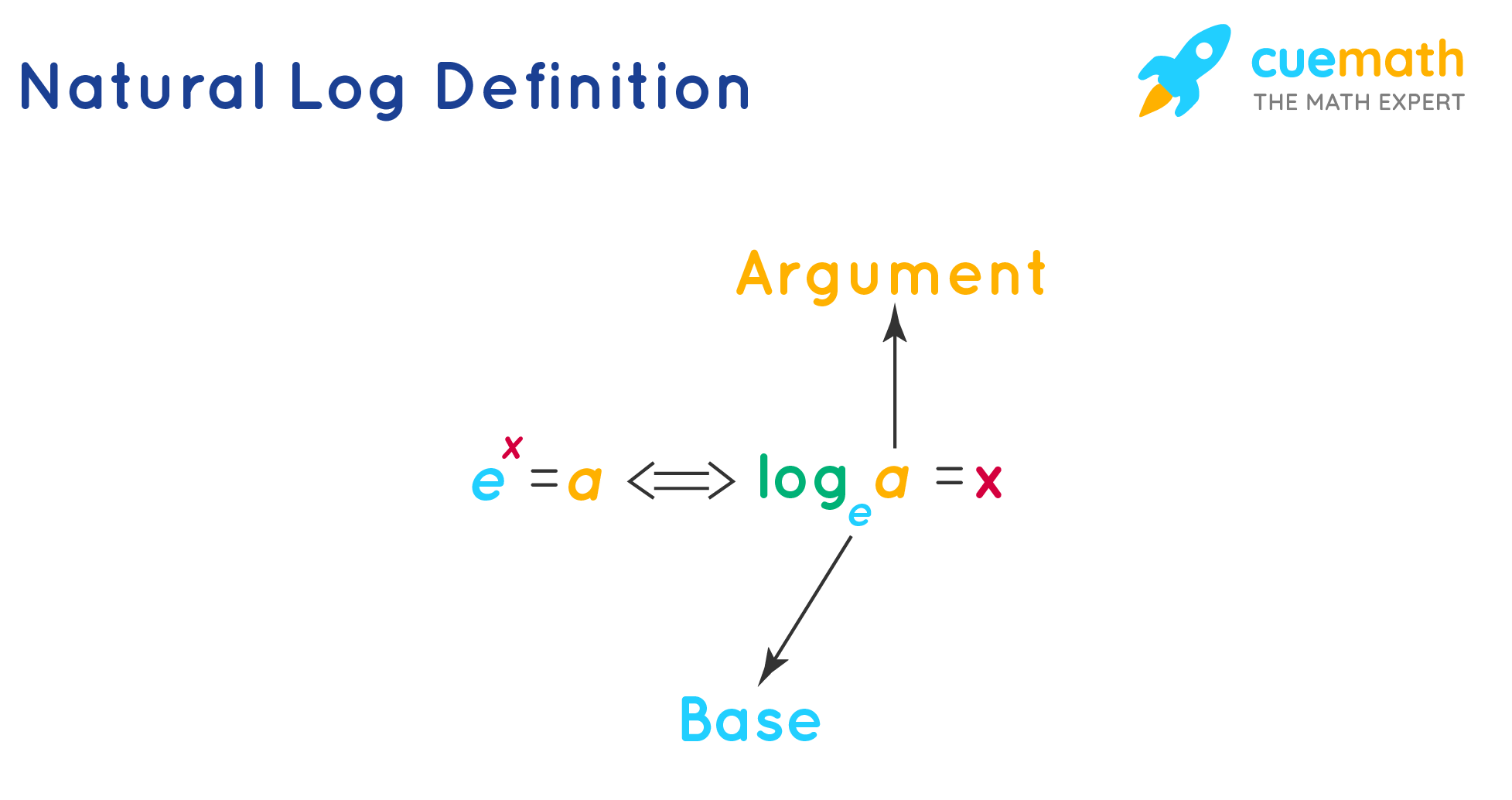
What is the value of the natural log E
equal to 1
Since the natural log function to the base e (loge e) is equal to 1, The derivative of log e is equal to zero, because the derivative of any constant value is equal to zero.
What is the base of LN10
LN10 is a constant. The value of the natural logarithm of 10 is approximately 2.302585092994046. This constant is equivalent to Math. log(10) .
Does natural log e equal 1
ln(e) = ln(e) is the number we should raise e to get e. So the natural logarithm of e is equal to one.
Is log e equivalent to ln
For example, log of base 2 is represented as log2 and log of base e, i.e. loge = ln (natural log). A natural logarithm can be referred to as the power to which the base 'e' that has to be raised to obtain a number called its log number.
Is log10 equal to ln10
The difference between log and ln is that log is defined for base 10 and ln is denoted for base e. For example, log of base 2 is represented as log2 and log of base e, i.e. loge = ln (natural log).
What is log with base e
A logarithm with base e, loge (x), is called a natural logarithm, and it is denoted as ln(x). That is, ln(x) = loge (x). Therefore, a logarithm with base e is written as ln(x), and it represents the number we need to raise e to, to get x.
Does the natural log of 1 equal 0
To what power should. I raise e. To get e to the zero. Well that power obviously is zero Ln 1 is equal to log base e of e to the zero. Which is zero in conclusion Ln 1 is equal to zero.
How do you convert log e to ln
Seven except log base E. We write Ln. So we would just say Ln x equals seven let's try one the other direction so we have Ln 9 equals y well Ln nine is the log base e of nine.
Is ln 10 equal to log e
The difference between log and ln is that log is defined for base 10 and ln is denoted for base e. For example, log of base 2 is represented as log2 and log of base e, i.e. loge = ln (natural log).
Is Log10 the same as e
The log of 10 is equal to 1. The natural log (ln) of e is also 1, but the log of e is equal to some value, x, such that 10^x =e. For e the solution is 0.43429.
Is log base e equal to ln
For example, log of base 2 is represented as log2 and log of base e, i.e. loge = ln (natural log). A natural logarithm can be referred to as the power to which the base 'e' that has to be raised to obtain a number called its log number.
Are ln and e the same
The natural log, or ln, is the inverse of e.
The letter 'e' represents a mathematical constant also known as the natural exponent. Like π, e is a mathematical constant and has a set value.
What is the relationship between E and ln
The natural log, or ln, is the inverse of e.
Like π, e is a mathematical constant and has a set value. The value of e is equal to approximately 2.71828.
How does ln 1 equal 0
Second ln of 1 is ln of 1 to 0th power and 0 can come in front so 0 times ln of 1. And therefore. It's here third ln of 1 is ln of e to the 0th power because anything to the 0th.
Is Lnx the same as log e
Definition of ln
It is also called the logarithm of the base e. Here, the constant e denotes a number that is a transcendental number and an irrational which is approximately equal to the value 2.71828182845. The natural logarithm (ln) can be represented as ln x or loge x.
Does log e equal 1
The logarithmic value of any number is equal to one when the base is equal to the number whose log is to be determined. Example: Log e base e is equal to 1, whereas log 10 base e is not equal to one. Common logarithm of one is equal to zero.
Why is log base e called ln
It's called the Natural Logarithm because so many processes in nature can be described mathematically using it.
What is natural base e
What is the natural base e The natural base e is an irrational number, meaning the decimal places are infinite and do not show a pattern. The first digits of e are: 2.718281828459… . The number e is is used in exponential and logarithm functions as a base.
How is ln the inverse of e
The exponential function, exp : R → (0,∞), is the inverse of the natural logarithm, that is, exp(x) = y ⇔ x = ln(y). Remark: Since ln(1) = 0, then exp(0) = 1. Since ln(e) = 1, then exp(1) = e.
How do you get rid of ln with e
So we're going to get rid of e by applying ln to both sides. So ln e 2x equals ln 5. Lne cancels so that's two x equals ln five and then divide both sides by two.
Does ln cancel out with e
e and ln cancel each other out leaving us with a quadratic equation. x = 0 is impossible as there is no way of writing 0 as a power. Write the left side as one logarithm.
Is natural log of 1 always 0
log 1 = 0 means that the logarithm of 1 is always zero, no matter what the base of the logarithm is. This is because any number raised to 0 equals 1. Therefore, ln 1 = 0 also.
How do you simplify ln 1 e
The parentheses. So here in this problem. Instead of x it's just 1 over x. So this is just equal to 1 over x. Basically the natural log and the e you can think of them as canceling.
What is Lnx in terms of e
ln(x) = loge(x) = y. The e constant or Euler's number is: e ≈ 2.71828183.
Is the natural log of e 1
The natural logarithm of e itself, ln e, is 1, because e1 = e, while the natural logarithm of 1 is 0, since e0 = 1.