Is RAID 6 better than 5
RAID 6 can be seen as an extension of RAID 5, and it offers better data security thanks to dual-parity. However, RAID 6 is more costly to implement, and you may want to opt for a RAID 5 configuration if the project you're working on doesn't require additional protections for sensitive data.
What is the difference between RAID 5 and 6
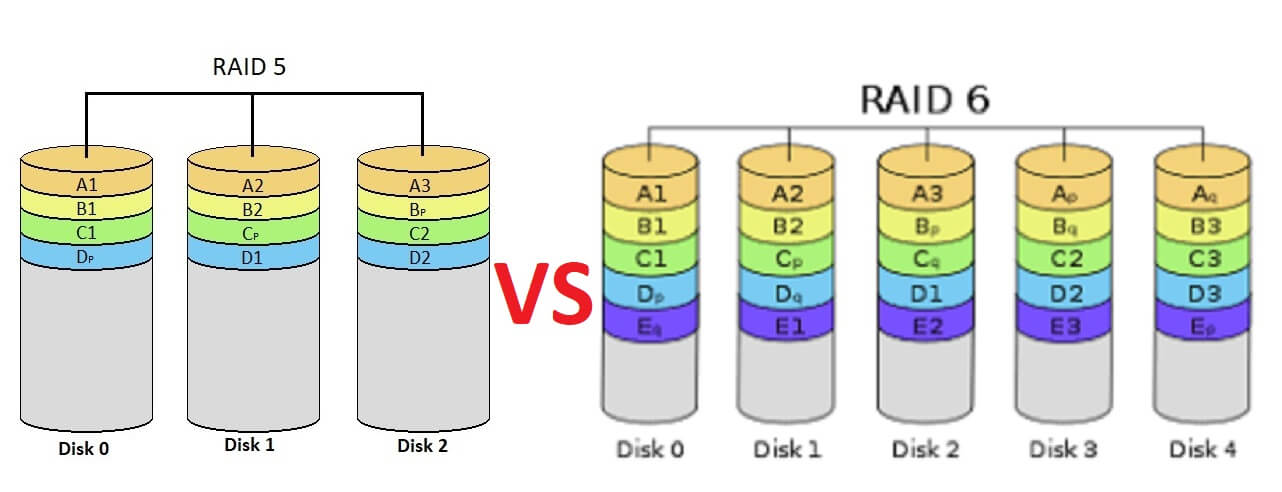
RAID5 allows for a single drive to fail without any data loss. RAID6 allows for two drive failures without any data loss.
Why RAID 6 over RAID 5
The primary difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6 is that a RAID 5 array can continue to function following a single disk failure, but a RAID 6 array can sustain two simultaneous disk failures and still continue to function. RAID 6 arrays are also less prone to errors during the disk rebuilding process.
What is RAID 6 good for
RAID 6 protection protects data from being lost because of a disk unit failure or because of damage to a disk. RAID 6 protection protects up to two disk unit failures.
Why RAID 5 is the best
Advantages of RAID 5
RAID 5 is ideal for application and file servers with a limited number of drives. Considered a good all-around RAID system, RAID 5 combines the better elements of efficiency and performance among the different RAID configurations. Fast, reliable read speed is a major benefit.
Is it safe to use RAID 6
RAID 6 is a fail-safe alternative to the more widely used RAID 5. But redundancy through parity isn't the only option.
Is there a RAID 7
RAID 7 has integrated cache and a purpose-built processor for managing the array that helps in achieving faster data read/write operations.
Why should RAID 5 no longer be used
However, skewing priority towards performance during recover will increase recovery time and increase the likelihood of losing a second drive in the array or encountering a new URE before recovery completes. Losing a second drive in a RAID5 array will result in catastrophic unrecoverable 100% data loss.
What are the disadvantages of RAID 6
RAID 6 – Striping with Double Parity
| Advantages and Disadvantages of RAID 6 | |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Read data transactions are very fast | Due to double parity write data transactions are slow. |
| Data accessibility is high | Rebuilding RAID array takes longer time because of its complex structure. |
Which RAID is safest
RAID 10 is ideal for situations where performance and safety are the priorities. RAID 10 has much faster write performance and is safe regardless of disk type used (low cost consumer disks can still be extremely safe, even in large arrays.)
How many drives do you need for RAID 6
RAID 6 is similar to RAID 5, except it provides another layer of striping and can sustain two drive failure. A minimum of four drives is required.
Is there a RAID 10
RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, is a RAID configuration that combines disk mirroring and disk striping to protect data. It requires a minimum of four disks and stripes data across mirrored pairs. As long as one disk in each mirrored pair is functional, data can be retrieved.
Is there a RAID 50
RAID 50, also known as RAID 5+0, combines distributed parity (RAID 5) with striping (RAID 0). It requires a minimum of six drives. This RAID level offers better write performance, increased data protection and faster rebuilds than RAID 5.
Why is RAID 10 better than 5
RAID 10 offers fantastic performance for random reads and writes because all operations occur in parallel on separate physical drives. RAID 5 also offers great read performance because of striping. However, writes are slower because of the overhead of calculating parity.
Is RAID 5 a bad idea
RAID 5 is ideal for application and file servers with a limited number of drives. Considered a good all-around RAID system, RAID 5 combines the better elements of efficiency and performance among the different RAID configurations. Fast, reliable read speed is a major benefit.
Is RAID 6 safer than RAID 10
Because RAID 6 uses a double parity scheme, it can protect against the simultaneous failure of two disks. RAID 10 may or may not be able to protect against two disk failures depending on where they occur. If both failed disks are in the same mirror, then the other mirror can take over.
Can RAID 5 have 6 drives
The minimum number of disks in a RAID 5 set is three (two for data and one for parity). The maximum number of drives in a RAID 5 set is in theory unlimited, although your storage array is likely to have built-in limits. However, RAID 5 only protects against a single drive failure.
How many disks can you lose in RAID 6
In RAID 6, two disk drives can fail without total data loss occurring. This means better security than RAID 5, but it also means even slower write speeds since one additional checksum must be created.
Is RAID 6 or 10 better
RAID 6 is better than RAID 10 in terms of security because it can withstand up to two concurrent failures, while RAID 10 can only withstand one. Regarding speed, RAID 10 is considered better than RAID 6 because of the data stripping feature, which allows quicker data access than RAID 6.
Is there a RAID 60
RAID 60 (also known as RAID 6+0) is a nested or “hybrid” RAID configuration that provides the distributed double parity of RAID 6 with the straight block-level striping of RAID 0. As a RAID 0 array striped across RAID 6 elements, minimal RAID 60 configuration requires eight drives.
Is RAID 10 the fastest
Performance. RAID 10 offers fantastic performance for random reads and writes because all operations occur in parallel on separate physical drives. RAID 5 also offers great read performance because of striping. However, writes are slower because of the overhead of calculating parity.
Which is better RAID 5 6 or 10
If you have a limited budget and want to get the most out of the disks you have popped into your array, RAID 5 and RAID 6 are ideal. For big data operations such as server farms and data centers however, where budgets will be bigger and performance more important, RAID 10 still offers the most benefits.
How fast is RAID 5 vs 6
RAID 5 and RAID 6 both offer fast reads because of striping. Data is read from multiple disks in parallel, which speeds up reads. Write performance is slow, however, due to the overhead of calculating parity information. RAID 6 is a little slower than RAID 5 for write performance.
Can you convert RAID 5 to RAID 6
Migrating a RAID 5 to RAID 6 has two slow operations – re-striping the data across the disks and calculating the second parity value for the extra parity disk. Wipe/restore will probably take the same amount of time as the resize. It also requires a certain kernel version. Found this out the hard way.
How many disks can RAID 5 lose
RAID 5 can sustain the loss of a single drive. In the event of a drive failure, data from the failed drive is reconstructed from parity striped across the remaining drives. As a result, both read and write performance are severely affected while a RAID 5 array is in a degraded state.