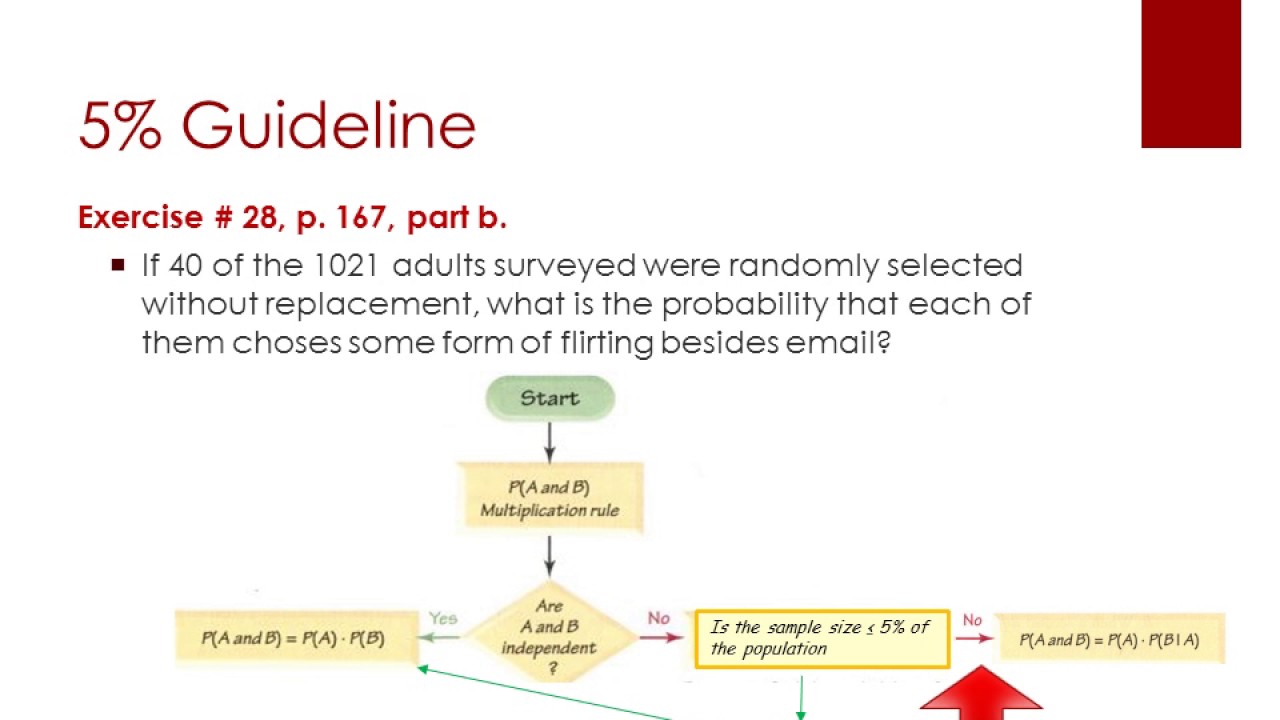
What is the 5 percent rule for probability
When sampling without replacement, the events can be treated as if they were independent if the sample size is no more than 5% of the population size. That is, 0.05 . (This is the 5% Guideline.)
What is the rule of five in sampling
The rule of five is a rule of thumb in statistics that estimates the median of a population by choosing a random sample of five from that population. It states that there is a 93.75% chance that the median value of a population is between the smallest and largest values in any random sample of five.
What is the 5 percent rule in AP stats
The traditional cutoff for a small p-value is 0.05, which means that there is only a 5% chance of obtaining the observed results, or something more extreme, if the null hypothesis is true. If the p-value is below this threshold, it is considered statistically significant and you can reject the null hypothesis.
What is the rule of statistics
What Is an Empirical Rule in Statistics The empirical rule, also known as the three-sigma rule or the 68-95-99.7 rule, is a statistical rule that states that almost all observed data for a normal distribution will fall within three standard deviations (denoted by σ) of the mean or average (denoted by µ).
What does a 5% chance mean
With a 5% probability of your desired outcome (“success") per attempt, assuming each attempt is independent, then there is a 95% chance of another outcome (“failure") per attempt. In all series of attempts, 95% of first attempts will fail, and 95% of that 95% of scenarios will fail the second attempt , and so on.
What is the 10% rule in probability
10 Percent Rule: The 10 percent rule is used to approximate the independence of trials where sampling is taken without replacement. If the sample size is less than 10% of the population size, then the trials can be treated as if they are independent, even if they are not.
Is 5% a good sample size
The value we are willing to accept as error in the estimate obtained by the study. The smaller the sample error, the larger the sample size and the greater the precision. In health studies, values between two and five percentage points are usually recommended.
What is the 10% rule in sampling
10 Percent Rule: The 10 percent rule is used to approximate the independence of trials where sampling is taken without replacement. If the sample size is less than 10% of the population size, then the trials can be treated as if they are independent, even if they are not.
Why is 5% used in statistics
In practical terms a 5% level of significance (i.e. p<0.05) means that there is a 1 in 20 chance that the result of the study is not true; or that if you conducted the trial 20 times, you could expect that there would be only 1 trial which showed a p value on a different side of 0.05.
How hard is it to get a 5 on AP Statistics
Getting a 5 takes careful content knowledge, targeted practice and dedicated studying. Only around 14% earn the top score for the AP® Statistics exam. To get a 5, start studying ASAP® and focus on applying concepts to specific situations.
What are the 5 elements of statistics
The five words population, sample, parameter, statistic (singular), and variable form the basic vocabulary of statistics.
What is the percentage of 3 standard deviations
99.7%
The Empirical Rule states that 99.7% of data observed following a normal distribution lies within 3 standard deviations of the mean. Under this rule, 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation, 95% percent within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three standard deviations from the mean.
How likely is a 10% chance
A probability of 0.1 means there is a 1 in 10 chance of an event happening, or a 10% chance that an event will happen.
What is 10% chance in odds
To convert from a probability to odds, divide the probability by one minus that probability. So if the probability is 10% or 0.10 , then the odds are 0.1/0.9 or '1 to 9' or 0.111. To convert from odds to a probability, divide the odds by one plus the odds.
What is 10% rule examples
For example, a plant will use 90% of the energy it gets from the sun for its own growth and reproduction. When it is eaten by a consumer, only 10% of its energy will go to the animal that eats it. That consumer will use 90% of that energy and only 10% will go on to the animal that eats it.
What is the probability rule 4
Probability Rule Four (The Addition Rule for Disjoint Events): If A and B are disjoint events, then P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B).
Is 4% a good sample size
A good maximum sample size is usually around 10% of the population, as long as this does not exceed 1000. For example, in a population of 5000, 10% would be 500. In a population of 200,000, 10% would be 20,000. This exceeds 1000, so in this case the maximum would be 1000.
What sample size is needed for a 95 confidence interval
To be 95% confident that the true value of the estimate will be within 5 percentage points of 0.5, (that is, between the values of 0.45 and 0.55), the required sample size is 385.
What is the sampling 30% rule
A sample size of 30 often increases the confidence interval of your population data set enough to warrant assertions against your findings.4 The higher your sample size, the more likely the sample will be representative of your population set.
Is 10% sample size good
For populations under 1,000, a minimum ratio of 30 percent (300 individuals) is advisable to ensure representativeness of the sample. For larger populations, such as a population of 10,000, a comparatively small minimum ratio of 10 percent (1,000) of individuals is required to ensure representativeness of the sample.
What is 5% level of significance
Solution: Here the level of significance(α) is 5% or 0.05 which means that any p-values less than the α will conclude to reject the null hypothesis. As we have p-value 3% which is less than 5%, so we reject the null hypothesis.
Is more than 5% statistically significant
A statistically significant test result (P ≤ 0.05) means that the test hypothesis is false or should be rejected. A P value greater than 0.05 means that no effect was observed.
Is statistics harder than calculus
At an advanced level, statistics is considered harder than calculus, but beginner-level statistics is much easier than beginner calculus.
Is AP stat or Calc harder
No, AP Statistics is not harder than calculus. Students who take both will typically say statistics is easier to understand and requires less study time overall. While not considered the toughest of all AP courses, calculus is the hardest math subject.
What are the 5 key principles of statistical analysis
The five basic methods are mean, standard deviation, regression, hypothesis testing, and sample size determination.