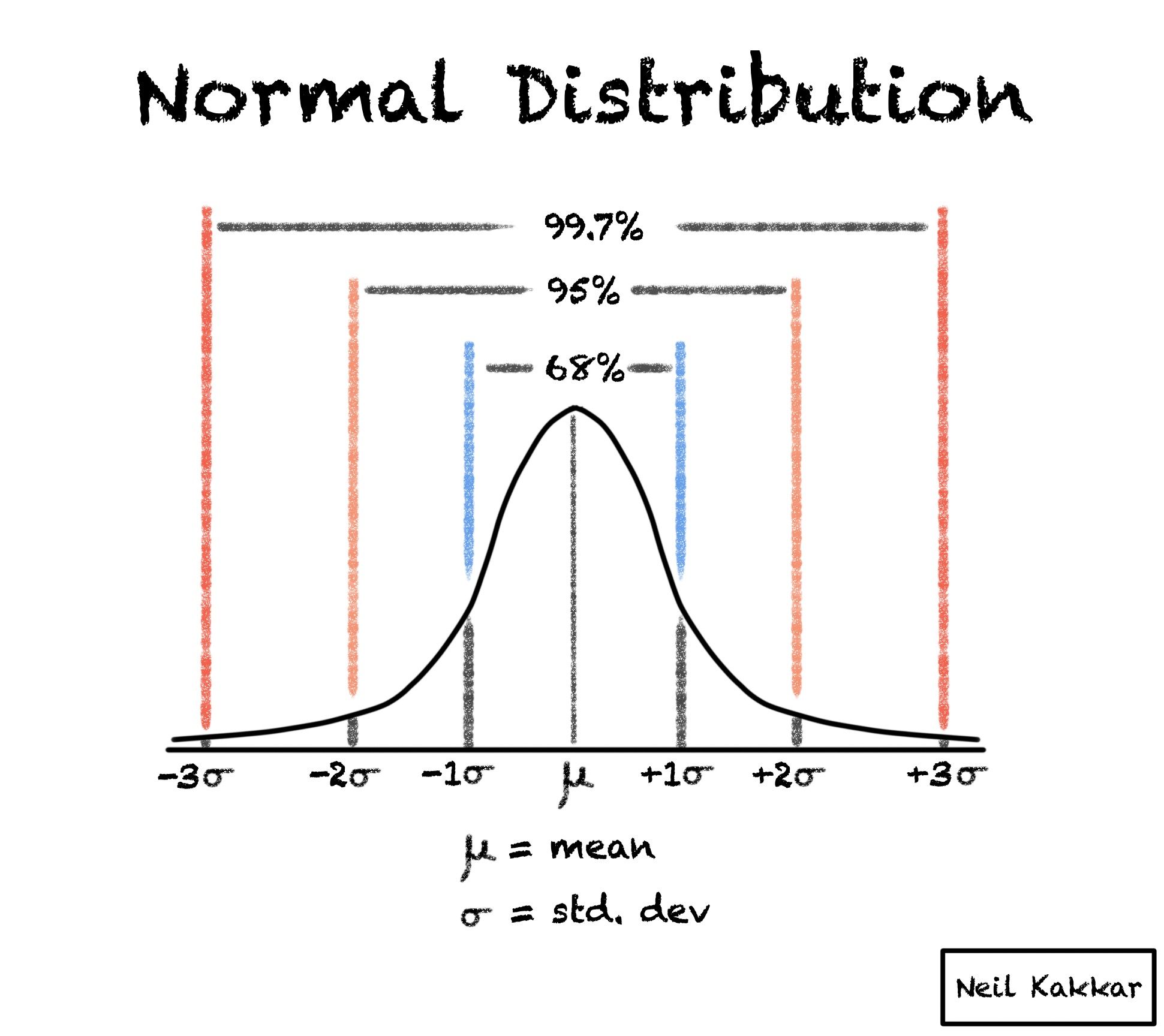
What is the 68 95 99 rule briefly explain
Key Takeaways. The Empirical Rule states that 99.7% of data observed following a normal distribution lies within 3 standard deviations of the mean. Under this rule, 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation, 95% percent within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three standard deviations from the mean.
What is the 68 95 99 rule normal distribution formula
In statistics, the 68–95–99.7 rule, also known as the empirical rule, is a shorthand used to remember the percentage of values that lie within an interval estimate in a normal distribution: 68%, 95%, and 99.7% of the values lie within one, two, and three standard deviations of the mean, respectively.
What is the 68-95-99.7 rule in Excel
68% of information values fall inside one standard deviation of the mean. 95% of information values fall inside two standard deviations of the mean. 99.7% of information values fall inside three standard deviations of the mean.
What is the 68-95-99.7 rule bell curve
Sixty-eight percent of the data is within one standard deviation (σ) of the mean (μ), 95 percent of the data is within two standard deviations (σ) of the mean (μ), and 99.7 percent of the data is within three standard deviations (σ) of the mean (μ).
What is the 68-95-99.7 rule about what of values are within one standard deviation of the mean
Approximately 68%
Empirical Rule or 68-95-99.7% Rule
Approximately 68% of the data fall within one standard deviation of the mean. Approximately 95% of the data fall within two standard deviations of the mean. Approximately 99.7% of the data fall within three standard deviations of the mean.
Who discovered the 68-95-99.7 rule
Abraham de Moivre
The 68–95–99.7 was first discovered and named by Abraham de Moivre in 1733 during his experimentation of flipping 100 fair coins. This term was coined 75 years before the normal distribution model even was introduced.
What is the 68-95-99.7 rule for normal distributions explain how it can be used to answer questions about frequencies of data values in a normal distribution
The empirical rule, or the 68-95-99.7 rule, tells you where most of the values lie in a normal distribution: Around 68% of values are within 1 standard deviation of the mean. Around 95% of values are within 2 standard deviations of the mean. Around 99.7% of values are within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
Do all normal curves satisfy the 68-95-99.7 rule
Remember that the rule applies to all normal distributions.
How do you use the 68 95 and 99.7 rule examples
And half of this is 34%. Giving us our area from zero to one. The next half goes from zero to negative two. But we know that within two standard deviations. From the mean we have an area of 95%.
Does the 68-95-99.7 rule applies only to skewed or almost skewed distributions
No, the rule is specific to normal distributions and need not apply to any non-normal distribution, skewed or otherwise. Consider for example the uniform distribution on [0,1].
What is 1 sigma 2 sigma 3 sigma
One standard deviation, or one sigma, plotted above or below the average value on that normal distribution curve, would define a region that includes 68 percent of all the data points. Two sigmas above or below would include about 95 percent of the data, and three sigmas would include 99.7 percent.
How much is 3 sigma
99.73%
The 3 sigma percentage of accuracy is 99.73% and is used to measure the predictability of outcomes for a desired process.
What is the 68 95 99.7 rule relative frequency
About 68% of values fall within one standard deviation of the mean. About 95% of the values fall within two standard deviations from the mean. Almost all of the values—about 99.7%—fall within three standard deviations from the mean.
What is the 68 95 99.7 rule about what of values are within one standard deviation of the mean
Approximately 68%
Empirical Rule or 68-95-99.7% Rule
Approximately 68% of the data fall within one standard deviation of the mean. Approximately 95% of the data fall within two standard deviations of the mean. Approximately 99.7% of the data fall within three standard deviations of the mean.
How do you tell if data is normally distributed or skewed
In a normal distribution, the mean and the median are the same number while the mean and median in a skewed distribution become different numbers: A left-skewed, negative distribution will have the mean to the left of the median.
What is 3 sigma and 5 sigma
The higher the “-sigma” value, the less likely it is that a signal is just a random fluctuation in the background model. Remember, in simple terms, a “3-sigma” signal has only a 0.3% chance of being a background fluctuation, and a “5-sigma” signal is has just a 0.00006% chance!
How much is 4 sigma
Four Sigma quality – This level of performance yields a defect-free product 99.349% of the time. With four sigma quality 73 applications would need to be corrected every day. Five Sigma quality – Five Sigma performance produces defect-free products and services 99.977% of the time.
What is 3 or 6 sigma
The goal of a three sigma quality program is a deviation from an engineering specification of no more than one-sixth part — 1.66 percent, plus or minus. The goal of a Six Sigma quality program is a deviation of no more than one-twelfth part, or 0.83 percent, plus or minus.
Is 3-sigma better than 6 Sigma
3 sigma percentage is primarily used for manufacturing processes that allow for a 93.73% level of accuracy, and as a potential foundation for further process improvement. 6 sigma percentage is used for business activities that require the higher, 99.9997% positive outcome.
How much skew is acceptable
between -2 and +2
The values for asymmetry and kurtosis between -2 and +2 are considered acceptable in order to prove normal univariate distribution (George & Mallery, 2010). Hair et al. (2010) and Bryne (2010) argued that data is considered to be normal if skewness is between ‐2 to +2 and kurtosis is between ‐7 to +7.
What is a good skewness
As a general rule of thumb: If skewness is less than -1 or greater than 1, the distribution is highly skewed. If skewness is between -1 and -0.5 or between 0.5 and 1, the distribution is moderately skewed. If skewness is between -0.5 and 0.5, the distribution is approximately symmetric.
What is 3-sigma and 6 sigma
The goal of a three sigma quality program is a deviation from an engineering specification of no more than one-sixth part — 1.66 percent, plus or minus. The goal of a Six Sigma quality program is a deviation of no more than one-twelfth part, or 0.83 percent, plus or minus.
What is sigma 5 vs sigma 6
5S focuses on eliminating waste and inefficiencies in the workplace. This methodology can be applied to every department and action that takes place. On the other hand, Six Sigma is a process improvement strategy that eliminates defects by implementing standard processes, identifying problem areas, and more.
How rare is 5 sigma
In most cases, a five-sigma result is considered the gold standard for significance, corresponding to about a one-in-a-million chance that the findings are just a result of random variations; six sigma translates to one chance in a half-billion that the result is a random fluke.
Is there a 5 sigma
A result that has a statistical significance of five sigma means the almost certain likelihood that a bump in the data is caused by a new phenomenon, rather than a statistical fluctuation. Scientists calculate this by measuring the signal against the expected fluctuations in the background noise across the whole range.