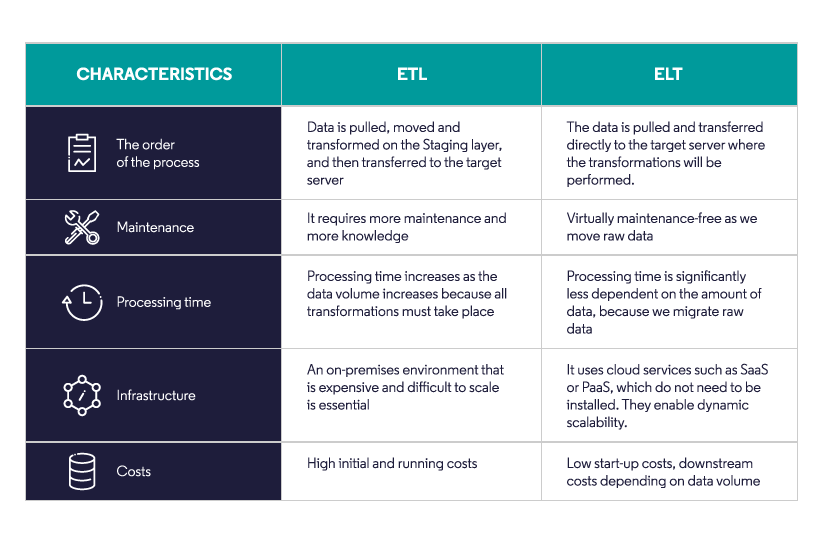
What is the difference between ELT and ETL
ETL, which stands for Extract, Transform, and Load, involves transforming data on a separate processing server before transferring it to the data warehouse. On the other hand, ELT, or Extract, Load, and Transform, performs data transformations directly within the data warehouse itself.
What is the difference between ELT and ETL Azure
Extract, load, and transform (ELT) differs from ETL solely in where the transformation takes place. In the ELT pipeline, the transformation occurs in the target data store. Instead of using a separate transformation engine, the processing capabilities of the target data store are used to transform data.
What is the difference between ETL and ELT explain the technology that can be used to load your data in its native format provided by Azure cloud with its main features
ELT is a variation of the Extract, Transform, Load (ETL), a data integration process in which transformation takes place on an intermediate server before it is loaded into the target. In contrast, ELT allows raw data to be loaded directly into the target and transformed there.
What is the difference between ETL and ELT components in Talend
Both ETL and ELT processes involve staging areas. In ETL, these staging areas are found within the ETL tool. In ELT, by contrast, the staging area is within the data warehouse and the database engine performs the transformations. It is within these staging areas where the data quality tools must also go to work.
What is the difference between ETL and data engineer
ETL developers are a part of the data engineering team. They are mainly responsible for performing the ETL process, i.e., extract, transform, and load functions while data moves from source to target location. Data engineers are responsible for designing and maintaining data pipelines and infrastructures.
What is the difference between ETL and ETL pipeline
An ETL pipeline is a set of processes to extract data from one system, transform it, and load it into a target repository. ETL is an acronym for “Extract, Transform, and Load” and describes the three stages of the process.
What is the difference between ETL and ELT in Azure data Factory
ETL is a time-consuming method as it first loads the data into staging, then into the target system. Lastly, it waits for data transformation to occur, so the waiting time increases as data size grows. The ELT method is faster since the data loading into the target system happens only once.
What is ETL and ELT data pipelines
ETL and ELT are data integration pipelines that transfer data from multiple sources to a single centralized source and perform some transformation and processing steps to it. The difference between these two is ETL transforms the data before loading, and ELT transforms the data after loading.
What are the main differences between ETL and ELT and what are the advantages and disadvantages of each
ETL is most appropriate for processing smaller, relational data sets which require complex transformations and have been predetermined as being relevant to the analysis goals. ELT can handle any size or type of data and is well suited for processing both structured and unstructured big data.
What is the difference between ETL and ELT in Snaplogic
An ELT pipeline is like ETL, but the data is loaded into a data store before the transformation process. ELT pipelines are used to handle large volumes of unstructured data for machine learning use cases.
What is the difference between ETL and ELT in data warehousing
The ETL process transforms data on a secondary processing server. In contrast, the ELT process loads raw data directly into the target data warehouse. Once there, you can transform the data whenever you need it.
What is the difference between ELT and ETL spark
ETL: The raw data is stored in some file storage (s3, local, etc), transformed with a python/spark/scala or other non-sql languages, and loaded into the tables to be used by the end-user. ELT: The raw data is loaded into the data warehouse and transformed using SQL into the final table to be used by the end-user.
What is the difference between ETL engineer and ETL developer
ETL developers are a part of the data engineering team. They are mainly responsible for performing the ETL process, i.e., extract, transform, and load functions while data moves from source to target location. Data engineers are responsible for designing and maintaining data pipelines and infrastructures.
What is the difference between ETL and database
Both ETL testing and database testing involve data validation, but they are not the same. ETL testing is normally performed on data in a data warehouse system, whereas database testing is commonly performed on transactional systems where the data comes from different applications into the transactional database.
What is the difference between ETL and data warehouse
While the data warehouse is the storage place for all your data, and BI tools serve as the mechanism that consumes the data to give you insights, ETL is the intermediary that pushes all the data from your tech stack and customer tools into the data warehouse for analysis.
What is the difference between ETL process and ETL pipeline
ETL refers to a set of processes extracting data from one system, transforming it, and loading it into a target system. A data pipeline is a more generic term; it refers to any set of processing that moves data from one system to another and may or may not transform it.
What is the difference between ETL and EDA
ETL is focused on moving and transforming data, while EDA is focused on understanding and analyzing data. While ETL is a necessary step for making data usable for analysis, EDA is where the real insights are gained and where the value of the data is realized.
What is ELT vs ETL spark
ETL: The raw data is stored in some file storage (s3, local, etc), transformed with a python/spark/scala or other non-sql languages, and loaded into the tables to be used by the end-user. ELT: The raw data is loaded into the data warehouse and transformed using SQL into the final table to be used by the end-user.
What is the difference between ETL and ELT in Javatpoint
ETL stands for Extract Transform and Load while ELT stands for Extract Load and Transform. In ETL data flows from the source to the staging and then to the target. In ELT target system do the transformation. The staging system is not involved in ELT.
What is the difference between ETL and ELT in Snowflake
Faster load times, as ETL typically takes longer as it uses a staging area and system. With ELT, there is only one load to the destination system. Faster transformation times, as ETL is typically slower and dependent on the size of the data set(s). ELT transformation is not dependent on data size.
What is the difference between ETL engineer and data engineer
ETL developers are a part of the data engineering team. They are mainly responsible for performing the ETL process, i.e., extract, transform, and load functions while data moves from source to target location. Data engineers are responsible for designing and maintaining data pipelines and infrastructures.
What is the difference between ETL and data quality
The purpose of the ETL process is to load the warehouse with integrated and cleansed data. Data quality focuses on the contents of the individual records to ensure the data loaded into the target destination is accurate, reliable and consistent.
What is the difference between ELT and data pipeline
How ETL and Data Pipelines Relate. ETL refers to a set of processes extracting data from one system, transforming it, and loading it into a target system. A data pipeline is a more generic term; it refers to any set of processing that moves data from one system to another and may or may not transform it.
Is ELT replacing ETL
Whether ELT replaces ETL depends on the use case. While ELT is adopted by businesses that work with big data, ETL is still the method of choice for businesses that process data from on-premises to the cloud. It is obvious that data is expanding and pervasive.
When to choose ETL vs ELT
ETL is most appropriate for processing smaller, relational data sets which require complex transformations and have been predetermined as being relevant to the analysis goals. ELT can handle any size or type of data and is well suited for processing both structured and unstructured big data.