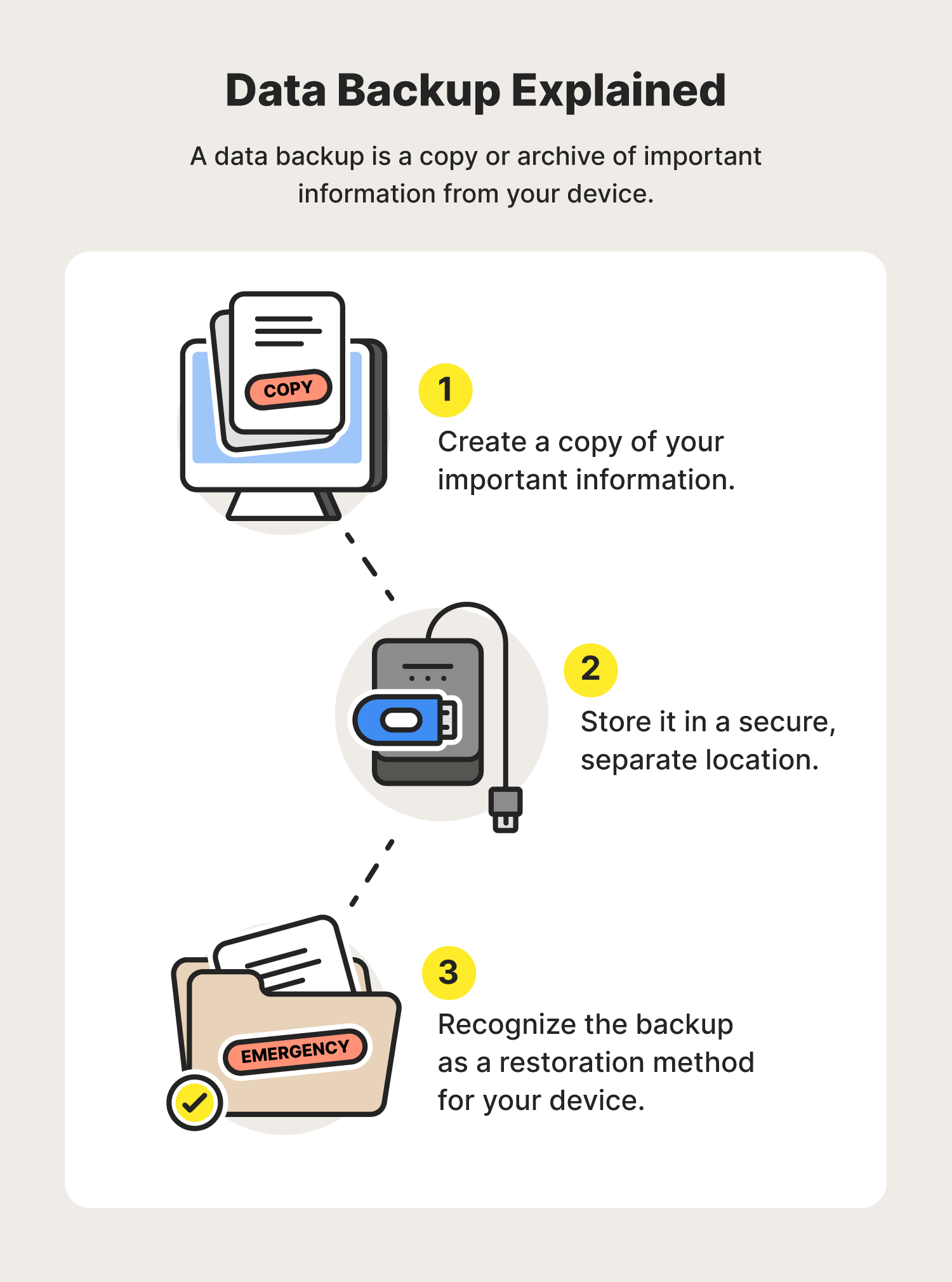
What are the most common backup methods
The most common backup types are a full backup, incremental backup and differential backup. Other backup types include synthetic full backups and mirroring. In the debate over cloud vs. local backup, there are some types of backup that are better in certain locations.
What are backup methods 3-2-1
The basic concept of the 3-2-1 backup strategy is that three copies are made of the data to be protected, the copies are stored on two different types of storage media and one copy of the data is sent off site.
What is the best backup methodology
The 3-2-1 rule of backup states that organizations should keep three complete copies of their data, two of which are local but on different types of media, with at least one copy stored off site.
What are the 3 types of backups
Types of BackupsFull backup: The most basic and comprehensive backup method, where all data is sent to another location.Incremental backup: Backs up all files that have changed since the last backup occurred.Differential backup: Backs up only copies of all files that have changed since the last full backup.
Which backup method is fastest
Incremental backups are completed quickly and require fewer resources. Disadvantage: While incremental backups have the fastest backup time, they also boast the slowest data recovery time.
What is backup method
Backup refers to the copying of physical or virtual files or databases to a secondary location for preservation in case of equipment failure or catastrophe. The process of backing up data is pivotal to a successful disaster recovery plan.
What is 4 3 2 backup strategy
Another relatively new option is 4-3-2. In this case, four copies of the data are stored in three locations, but two of these must be off-site. The 4-3-2 strategy means that backups are duplicated and geographically distant from one another to protect against natural disasters.
Why is 3-2-1 backup important
One additional benefit of using the 3-2-1 rule is the ability to perform certain data analytics functions on the data copies (the data stored in backup or disaster recovery infrastructure) rather than on the original data. Along with its seeming simplicity, another benefit to this rule is its allowance for fine-tuning.
Which backup is faster
Difference Between Full, Differential and Incremental Backups
| Full | Incremental | |
|---|---|---|
| Backup Speed | Slowest | Fastest |
| Restoration Speed | Fastest | Slowest |
| Media Required for Recovery | Most recent backup only | Most recent full backup & all incremental backups since full backup |
| Duplication | Stores a lot of duplicate files | No duplicate files |
Which type of backup is fastest
Incremental backups are completed quickly and require fewer resources. Disadvantage: While incremental backups have the fastest backup time, they also boast the slowest data recovery time.
Which type of database backup is most efficient
A full backup is the most complete type of backup where you clone all the selected data. This includes files, folders, SaaS applications, hard drives and more. The highlight of a full backup is the minimal time it requires to restore data.
Why is incremental backup the fastest
If you do an incremental backup on Tuesday, you only back up the data that changed since the incremental backup on Monday. The result is a much smaller, faster backup. The characteristic of incremental backups is the shorter the time interval between backups, the less data will be backed up.
What is primary backup method
The most widely used approach to building replicated, fault-tolerant services is the primary-backup approach. In this approach, the state of the service is replicated across multiple servers, with one server designated as the primary, and the rest as backups.
What is the 3-2-1 1 0 backup strategy
The modern 3-2-1-1-0 rule stipulates that backup admins need at least three copies of data in addition to the original data. The 2 in the 3-2-1-1-0 rule directs organizations to back up data on two different types of media.
What is the 5 4 3-2-1 backup rule
We decided to supercharge our backup strategy by making it a 5-4-3-2-1. We have 5 copies of our data, on 4 different types of storage, 3 being off-site, with at least 2 off-site locations that are physically distanced, and 1 being offline.
What is the fastest way to backup a drive
But as mentioned above, the quickest way to do so is using a professional backup tool. This is because the manual procedure is time-consuming and laborious. And Windows Easy Transfer is not available on Windows 10 and 11. As for the external hard drive backup software, EaseUS Todo Backup can suit your needs.
Is physical backup faster than logical backup
Physical backup methods are faster than logical because they involve only file copying without conversion. Output is more compact than for logical backup.
What is primary or secondary backup
At their simplest, primary storage is defined as the storage used to host your critical systems and their data, while secondary storage is the storage that hosts all the "other" data that needs to be recovered to make the environment whole after a major outage.
What is the 3-2-1 0 backup rule
You should have at least 3 copies of your data, including the production copy. At least 2 different storage media should be used; for instance, a tape and a cloud storage. At least 1 of the copies should be kept off-site, in case your machines are physically damaged.
What is the 3 1 1 backup rule
Complete Ransomware Protection Starts With 3-2-1-1
It says to keep three copies of your data—one primary and two backups—with two copies stored locally on two formats (network-attached storage, tape, or local drive) and one copy stored offsite in the cloud or secure storage.
Which drive is best for backup
Flash drive (also known as a thumb drive or USB drive/stick) and solid-state drive (SSD) The most effective physical technique to back up your PC is with flash drives and SSDs. Fast backups are made possible by flash drives and solid-state drives' ability to write and scan data.
What is the primary-backup method
The most widely used approach to building replicated, fault-tolerant services is the primary-backup approach. In this approach, the state of the service is replicated across multiple servers, with one server designated as the primary, and the rest as backups.
What is primary and backup
Primary protection (Main protection) is the essential protection provided for protecting an equivalent/machine or a part of the power system. As a precautionary measure, addition protection is generally provided and is called Backup Protection.
What is the 3 3 2 backup rule
It breaks down like this: keep at least 3 copies of your data, store 2 copies on different storage media, and make sure 1 of them is stored offsite. With today's greater risks the 3-2-1 rule has evolved into the 3-2-2 rule. (It really could be called the 3-2-1+1 rule, but we're keeping things simple).
What is the 3 2 2 1 0 backup rule
You should have at least 3 copies of your data, including the production copy. At least 2 different storage media should be used; for instance, a tape and a cloud storage. At least 1 of the copies should be kept off-site, in case your machines are physically damaged.