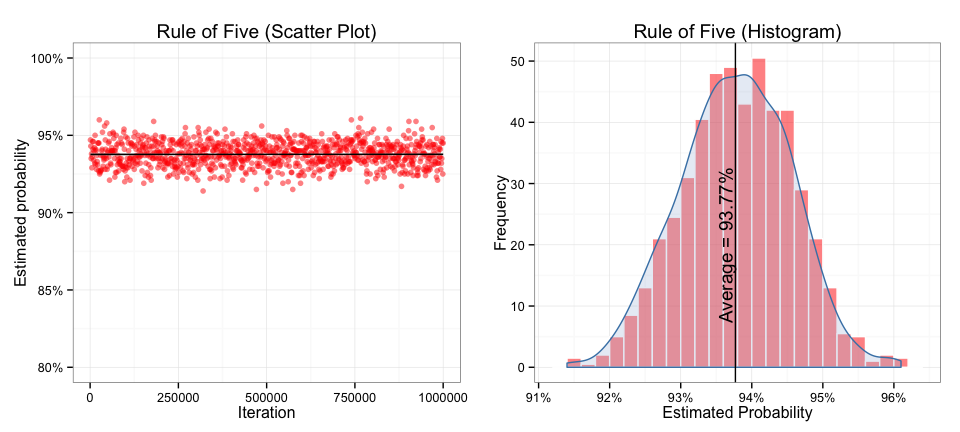
What is the 5 rule in statistics
The rule of five is a rule of thumb in statistics that estimates the median of a population by choosing a random sample of five from that population. It states that there is a 93.75% chance that the median value of a population is between the smallest and largest values in any random sample of five.
What is the rule of statistics
What Is an Empirical Rule in Statistics The empirical rule, also known as the three-sigma rule or the 68-95-99.7 rule, is a statistical rule that states that almost all observed data for a normal distribution will fall within three standard deviations (denoted by σ) of the mean or average (denoted by µ).
What is the 5 percent rule in AP stats
The traditional cutoff for a small p-value is 0.05, which means that there is only a 5% chance of obtaining the observed results, or something more extreme, if the null hypothesis is true. If the p-value is below this threshold, it is considered statistically significant and you can reject the null hypothesis.
What is Rule 5 of probability
Rule 5: If two events A and B are independent, then the probability of both events is the product of the probabilities for each event: P(A and B) = P(A)P(B). The chance of all of two or more events occurring is called the intersection of events.
Why is 5 statistically significant
Role in statistical hypothesis testing
is set to 5%, the conditional probability of a type I error, given that the null hypothesis is true, is 5%, and a statistically significant result is one where the observed p-value is less than (or equal to) 5%.
What is rule 2 in statistics
Rule 2: For S the sample space of all possibilities, P(S) = 1. That is the sum of all the probabilities for all possible events is equal to one.
What is the 5 percent rule for probability
When sampling without replacement, the events can be treated as if they were independent if the sample size is no more than 5% of the population size. That is, 0.05 . (This is the 5% Guideline.)
What is the 5 percent rule in probability
When sampling without replacement, the events can be treated as if they were independent if the sample size is no more than 5% of the population size. That is, 0.05 . (This is the 5% Guideline.)
What is the probability at most a total of 5
A fair die is numbered from 1 to 6 with probability of coming of each number being 1/6. Calculation: Getting a total of at most 5 means getting a total of 5 or total equal to less than 5. ∴ Probability of getting a total of at most 5 is 5/18.
What is the probability of 5 or 6
The formula to calculate the probability of an event is as follows. Given, a six-sided die is rolled once. We have to find the probability of rolling either a 5 or a 6. Therefore, the probability of rolling either a 5 or a 6 is 1/3.
Is less than 5 statistically significant
A statistically significant test result (P ≤ 0.05) means that the test hypothesis is false or should be rejected. A P value greater than 0.05 means that no effect was observed.
Why the researcher decided to use the 5% level of significance rather than the 1% level in this study
Psychologists use the significance level of 0.05 in research as it best balances the risk of making type 1 and type 2 errors. *This would need to be a clear statement in the exam in order to get the mark.
What is rule 1 in statistics
Rule 1: The probability of an impossible event is zero; the probability of a certain event is one. Therefore, for any event A, the range of possible probabilities is: 0 ≤ P(A) ≤ 1.
What is the rule of 10 sample size
The 10% rule states that trials can be viewed as independent as long as the sample size does not exceed 10% of the population size.
How do you use the 5% rule
Re: 5% rule
So you find your x value through the approximation method then divide by your initial amount of weak acid or base and multiply by 100. If the number calculated is greater than 5 then the quadratic formula should be used to solve for x. (x/[HA]) x 100 = some percent.
What is the 5% rule physics
The 5% error rule = the absolute value of the y intercept / highest y value *100. If above 5% you keep the y intercept. If below 5 % you can cancel the y intercept.
What is the probability of a 5
Probability of rolling a certain number or less with one die
| Roll a…or less | Probability |
|---|---|
| 3 | 3/6 (50.000%) |
| 4 | 4/6 (66.667%) |
| 5 | 5/6 (83.333%) |
| 6 | 6/6 (100%) |
How do you find the probability of 5
Expert-Verified Answer
The correct answer is probability of getting five in throwing a dice is 1/6.
What is the possibility of 5
If a die is rolled there are 6 possible outcomes—1,2,3,4,5,6. So the probability of getting a 5 is 1/6.
What does 5 statistical significance mean
The significance level is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. For example, a significance level of 0.05 indicates a 5% risk of concluding that a difference exists when there is no actual difference.
Why do we use 5% significance level
The researcher determines the significance level before conducting the experiment. The significance level is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. For example, a significance level of 0.05 indicates a 5% risk of concluding that a difference exists when there is no actual difference.
Which is better 1 or 5 level of significance
Traditionally, researchers have used either the 0.05 level (5% level) or the 0.01 level (1% level), although the choice is largely subjective. The lower the significance level, the more conservative the statistical analysis and the more the data must diverge from the null hypothesis to be significant.
What is the rule of 2 in statistics
An empirical rule stating that, for many reasonably symmetric unimodal distributions, approximately 95% of the population lies within two standard deviations of the mean. See also three-sigma rule.
What is the probability rule 4
Probability Rule Four (The Addition Rule for Disjoint Events): If A and B are disjoint events, then P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B).
What is rule of 10 in analysis
The rule states that one predictive variable can be studied for every ten events. For logistic regression the number of events is given by the size of the smallest of the outcome categories, and for survival analysis it is given by the number of uncensored events.