What is Tier 1 and Tier 2 and Tier 3 capital
Tier 1 capital is intended to measure a bank's financial health; a bank uses tier 1 capital to absorb losses without ceasing business operations. Tier 2 capital is supplementary capital, i.e., less reliable than tier 1 capital. A bank's total capital is calculated as a sum of its tier 1 and tier 2 capital.
What is Tier 1 risk ratio
The Tier 1 capital ratio compares a bank's equity capital with its total risk-weighted assets (RWAs). These are a compilation of assets the bank holds that are weighted by credit risk. Under the Basel III accord, the value of a bank's Tier 1 capital must be greater than 6% of its risk-weighted assets.
What is the difference between Tier 1 and Tier 2 banks
Tier 1 and tier 2 capital are two types of assets held by banks. Tier 1 capital is a bank's core capital, which it uses to function on a daily basis. Tier 2 capital is a bank's supplementary capital, which is held in reserve. Banks must hold certain percentages of different types of capital on hand.
Why is capital classified as Tier 1 and Tier 2
First, it defined what banks could hold as capital, as well as designating capital as Tier 1 or Tier 2 according to its loss-absorbing or creditor- protecting characteristics. The second key concept introduced in Basel I was that capital should be held by banks in relation to the risks that they face.
What is tier 1 vs tier 2 vs Tier 3 vs Tier 4
As a general rule, the difference between data center tiers is that tier 1 offers no redundancy of any critical system, tier 2 has partial redundancy in their electrical & HVAC systems, tier 3 contains dual redundancy for power & cooling equipment, and tier 4 possesses fully redundant infrastructure.
What is the difference between it tier 2 and Tier 3
Tier 2 staff have the knowledge base and skills to handle more complex customer issues and will often use remote control tools. Tier 3: Tier 3 is usually the highest level of technical skill in the organization, and often includes the product engineers or developers.
What is Tier 1 and Tier 2 in risk
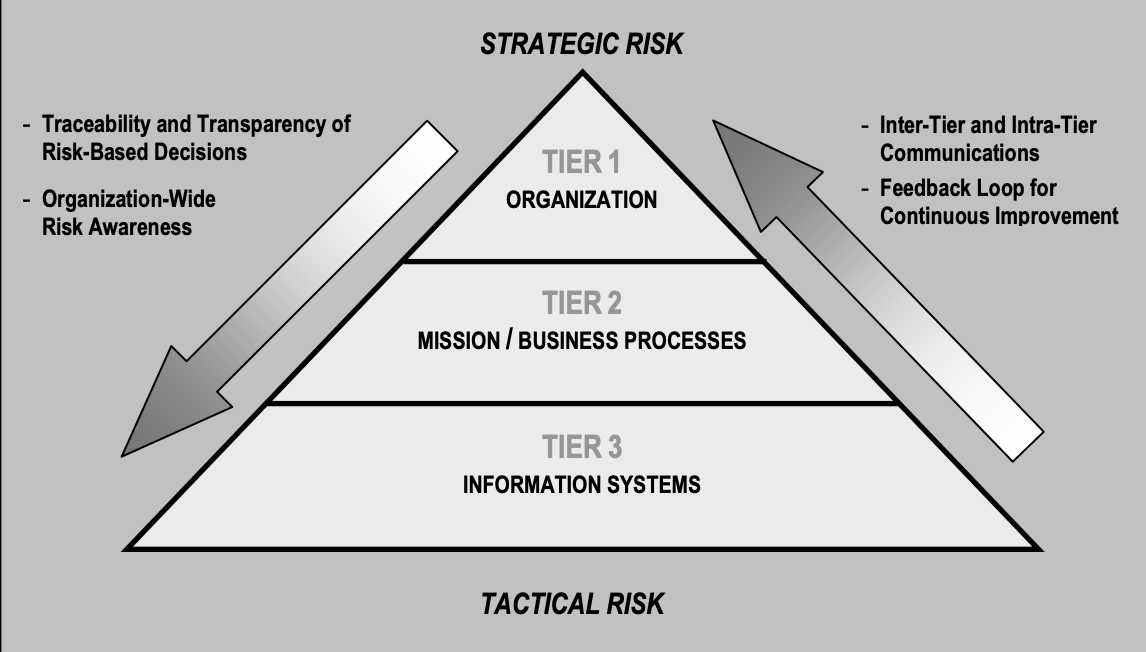
Broadly, the degree of detail and quality of the data at each level can be described as: Tier 1: Qualitative (Introductory Risk Assessment) Tier 2: Semi-quantitative (Advanced Risk Assessment) Tier 3: Quantitative (Advanced Risk Assessment)
What is Tier 3 risk
A risk assessments on tier 3 is a risk assessment partially focussed on a singular for a set of information systems. These assessments is the bottom tier of the tier defined by NIST and provide risk specifically to these information systems.
What is a Tier 1 2 and 3 account
Tier one account is the least of savings account types in Nigeria. Tier two account is at mid-range of savings account type in Nigeria. Tier 3 account is the highest class of savings account in Nigeria. May require just a passport photograph as opening document.
What is tier 3
Tier 3 systems are meant to provide individualized and intensive interventions and supports to students to ensure positive behavioral outcomes. Schools are shifting their focus from compliance with regulations to achieving positive student outcomes.
What is difference between Tier 1 and 2
Tier 1 and Tier 2 NPS accounts are two different categories. As opposed to Tier 1, which serves as the principal NPS account for building a retirement fund, Tier 2 is similar to a voluntary savings account and provides greater flexibility for deposits and withdrawals.
What is Tier 1 and tier 2 companies
Tier 1 Suppliers: These are direct suppliers of the final product. Tier 2 suppliers: These are suppliers or subcontractors for your tier 1 suppliers. Tier 3 suppliers: These are suppliers or subcontractors for your tier 2 suppliers. These tiers can extend longer than three.
What is Tier 2 vs Tier 3 vs Tier 4
As a general rule, the difference between data center tiers is that tier 1 offers no redundancy of any critical system, tier 2 has partial redundancy in their electrical & HVAC systems, tier 3 contains dual redundancy for power & cooling equipment, and tier 4 possesses fully redundant infrastructure.
What are Tier 1 Tier 2 and Tier 3 interventions
For this reason, school-specific terms for these levels of support were developed: Tier 1 = Universal or core instruction. Tier 2 = Targeted or strategic instruction/intervention. Tier 3 = Intensive instruction/intervention.
What is different Tier 1 and Tier 3
Tier 1 Suppliers: These are direct suppliers of the final product. Tier 2 suppliers: These are suppliers or subcontractors for your tier 1 suppliers. Tier 3 suppliers: These are suppliers or subcontractors for your tier 2 suppliers. These tiers can extend longer than three.
What are Level 1 Level 2 and Level 3 risks
For that reason, it is important for public managers to be aware of three levels of risk and how to manage them. Level 1, the lowest category, encompasses routine operational and compliance risks. Level 2, the middle category, represents strategy risks. Level 3 represents unknown, unknown risks.
What are Tier 2 and 3 risks
Broadly, the degree of detail and quality of the data at each level can be described as:Tier 1: Qualitative (Introductory Risk Assessment)Tier 2: Semi-quantitative (Advanced Risk Assessment)Tier 3: Quantitative (Advanced Risk Assessment)
What is level 1 level 2 level 3 risk
For that reason, it is important for public managers to be aware of three levels of risk and how to manage them. Level 1, the lowest category, encompasses routine operational and compliance risks. Level 2, the middle category, represents strategy risks. Level 3 represents unknown, unknown risks.
What is a Tier 2 risk
Broadly, the degree of detail and quality of the data at each level can be described as: Tier 1: Qualitative (Introductory Risk Assessment) Tier 2: Semi-quantitative (Advanced Risk Assessment) Tier 3: Quantitative (Advanced Risk Assessment)
What is tier 2 vs Tier 3 vs Tier 4
As a general rule, the difference between data center tiers is that tier 1 offers no redundancy of any critical system, tier 2 has partial redundancy in their electrical & HVAC systems, tier 3 contains dual redundancy for power & cooling equipment, and tier 4 possesses fully redundant infrastructure.
What is Tier 1 and tier 2 account
Tier 1 and Tier 2 NPS accounts are two different categories. As opposed to Tier 1, which serves as the principal NPS account for building a retirement fund, Tier 2 is similar to a voluntary savings account and provides greater flexibility for deposits and withdrawals.
What is Tier 2 vs Tier 3 it
Tier 2 staff have the knowledge base and skills to handle more complex customer issues and will often use remote control tools. Tier 3: Tier 3 is usually the highest level of technical skill in the organization, and often includes the product engineers or developers.
What is the meaning of 2 tier and 3 tier
The two-tier DB architecture is a client-server architecture. The three-tier DB architecture is a type of web-based application. Number of Layers. It contains mainly two layers- the Data Tier (Database Tier), and the Client Tier. It mainly contains three layers- the Data Layer, the Business Layer, and the Client Layer.
What is the difference between Tier 2 and Tier 3
Compared to Tier 2, Tier 3 is more explicit, focuses on remediation of skills, is provided for a longer duration of time (both in overall length of intervention and regularly scheduled minutes of instructional time), and occurs in smaller groups (i.e., groups of 1–3 students; Haager et al., 2007; Harn, Kame'enui, & …
What does Tier 3 company mean
In layman's terms, tier 1 companies are the big guns, and the tier 3 ones are the more modest firms. Over time, companies can move up the tiers if they fit the criteria.