What causes exchange rates to change
Inflation and interest rates are closely related, and both affect exchange rates. Some inflation – rising prices of goods and services – is healthy for an economy, as it shows increasing demand versus supply.
What shifts foreign exchange rates
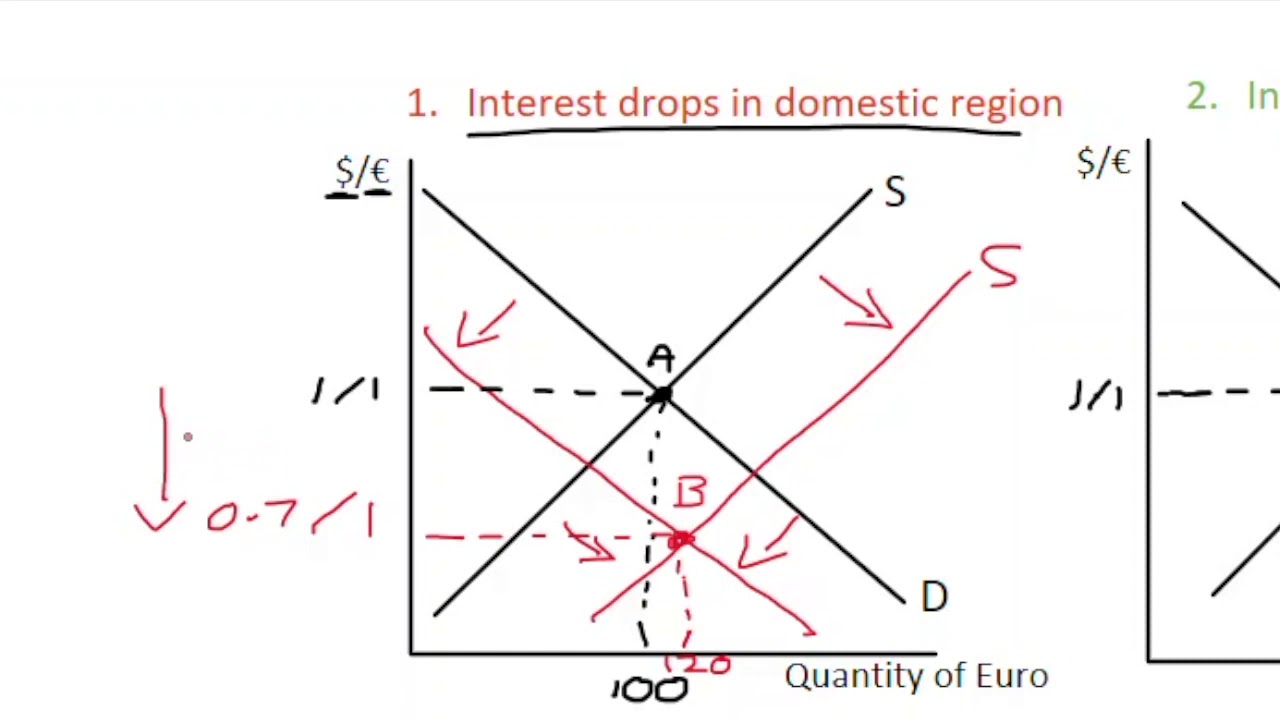
The shifts in demand and supply curves both cause the exchange rate to shift in the same direction; in this example, they both make the peso exchange rate stronger. However, the shifts in demand and supply work in opposing directions on the quantity traded.
What controls the exchange rate
The monetary authority
The monetary authority manages its exchange rate by intervening (buying and selling currency) in the foreign exchange market to minimise fluctuations and keep the currency close to its target (or within its target band).
What changes real exchange rate
Real Exchange Rate – Key takeaways
There are three main determinants of the real interest rate: nominal interest rate, foreign prices, and domestic price level. Factors that influence the real exchange rate are: Terms of trade, Monetary policy, Capital inflows, Trade restrictions.
Does inflation affect exchange rate
In general, when inflation is high, it makes a currency weaker, suppressing investment, and thus negatively impacting the exchange rate. When inflation is low, a currency is stronger, improving its exchange rate.
How do interest rates affect exchange rates
Generally, higher interest rates increase the value of a country's currency. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, increasing the demand for and value of the home country's currency.
How does exchange rate go down
If a country has a balance of trade deficit, then imports will exceed exports. As this happens, demand for foreign exchange will exceed supply and in turn, the local currency will depreciate in value. Likewise, a positive balance of trade will cause the local currency to increase in value.
What are the seven factors that influence the exchange rate
7 factors affecting exchange ratesInterest and inflation rates. Inflation is the rate at which the cost of goods and services rises over time.Current account deficits.Government debt.Terms of trade.Economic performance.Recession.Speculation.
How does inflation affect exchange rate
In general, inflation tends to devalue a currency since inflation can be equated with a decrease in a currency's buying power. As a result, countries experiencing high inflation tend to also see their currencies weaken relative to other currencies.
What makes a currency strong or weak
A currency's strength is determined by the interaction of a variety of local and international factors such as the demand and supply in the foreign exchange markets; the interest rates of the central bank; the inflation and growth in the domestic economy; and the country's balance of trade.
Do interest rates affect exchange rates
A country's currency will rise in value when interest rates are high because higher rates will attract more foreign capital. This will lead to an increase in exchange rates and a strong currency. As a general rule, the higher the interest rates, the more foreign investment a country is likely to attract.
What causes exchange rate volatility
In particular, exchange rate volatility is a risk associated with uncertainty in the exchange rate in international trade and is often driven by macroeconomic factors including the interest rate, the balance of payments, and inflation.
What affects exchange rates economics
Numerous factors influence exchange rates, including a country's economic performance, the outlook for inflation, interest rate differentials, capital flows and so on. A currency's exchange rate is typically determined by the strength or weakness of the underlying economy.
How do inflation rates affect exchange rates
In general, inflation tends to devalue a currency since inflation can be equated with a decrease in a currency's buying power. As a result, countries experiencing high inflation tend to also see their currencies weaken relative to other currencies.
What are the six 6 causes of exchange rate fluctuation
7 Main Causes of Fluctuations in Exchange Rates | InternationalTrade Movements:Capital Movements:Stock Exchange Operations:Speculative Transactions:Banking Operations:Monetary Policy:Political Conditions:
What are the 8 factors that affect foreign exchange rate
10 Factors that influence currency exchange rates:Inflation >Interest rates >Government Debt/Public >Political Stability >Economic Recession >Terms of Trade >Current account deficit >Confidence and speculation >
What happens when exchange rate rises
In the goods market, a positive shock to the exchange rate of the domestic currency (an unexpected appreciation) will make exports more expensive and imports less expensive. As a result, the competition from foreign markets will decrease the demand for domestic products, decreasing domestic output and price.
What causes currency to strengthen
Typically, if a country has relatively strong economic growth and low debt, its currency will be sought after in global markets which will cause its price to rise.
Why is the U.S. dollar so strong
What makes the US dollar so strong Most countries worldwide rely on the US dollar to support their economy. Today, the US dollar (USD) is the most prominent currency in the world. This is tied to the fact that the US has the largest economy in the world, along with the dollar's use globally.
Does currency rise when interest rates rise
The answer is yes. Interest rates and currency are very much related. High and low exchange rates effect the value of the currency. If you're looking for your currency's value to skyrocket, keep an eye on interest rates – the higher they rise, the higher your money's worth!
What affects exchange rate risk
It is caused by the effect of unexpected currency fluctuations on a company's future cash flows and market value and is long-term in nature. The impact can be substantial, as unanticipated exchange rate changes can greatly affect a company's competitive position, even if it does not operate or sell overseas.
What affects the foreign exchange market
Macroeconomic statistics, such as inflation, have the greatest impact on forex markets. Stock, bond, commodity, and other capital markets also have a strong influence on exchange rates. International trade numbers, such as trade deficits and surpluses, play a vital role in forex markets.
Does inflation affect the real exchange rate
When inflation is higher, this tends to have a depressing affect on the value of a country's currency. This is because increased inflation reduces the currency's buying power, which weakens it against other currencies. The impact of increasing inflation on currency conversion rates is usually downwards.
What are the 5 conditions of exchange
There must be at least two parties, each party has something that might be of value to the other party, each party is capable of communication and delivery, each party is free to accept or reject the exchange offer, each party believes it is appropriate or desirable to deal with the other party.
What are the 3 factors affecting the demand for foreign currency
The demand for foreign-currency denominated assets is in turn affected by the expected returns on those assets, the risks of those assets as well as the liquidity of those assets, all relative to domestic assets.