What is the 3-2-1 rule for backup and disaster recovery
The 3-2-1 backup strategy simply states that you should have 3 copies of your data (your production data and 2 backup copies) on two different media (disk and tape) with one copy off-site for disaster recovery.
What is the 321 backup strategy
You may have heard of the 3-2-1 backup strategy. It means having at least three copies of your data, two local (on-site) but on different media (read: devices), and at least one copy off-site. We'll use “socialsecurity.
What’s the 321 rule
Here's what the 3-2-1 backup rule involves: 3: Create one primary backup and two copies of your data. 2: Save your backups to two different types of media. 1: Keep at least one backup file offsite.
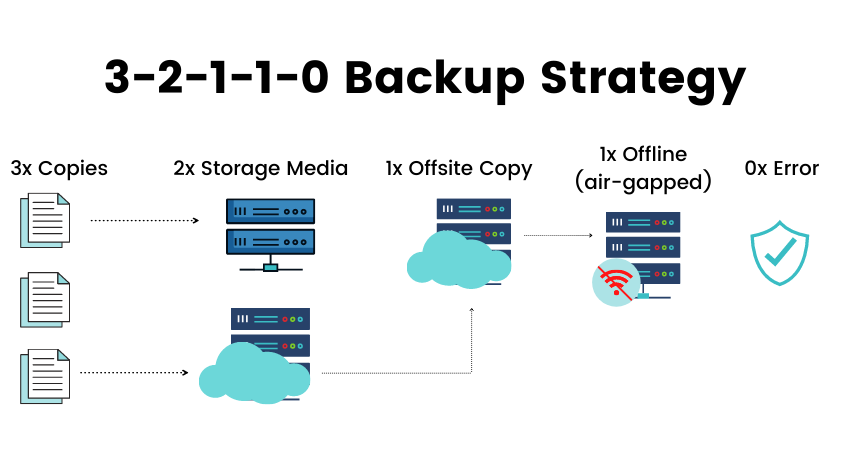
What is 3-2-1 1 0 backup rule
You should have at least 3 copies of your data, including the production copy. At least 2 different storage media should be used; for instance, a tape and a cloud storage. At least 1 of the copies should be kept off-site, in case your machines are physically damaged.
What is the 3-2-1 rule and its importance in formulating a successful backup strategy
The 3-2-1 rule, attributed to photographer Peter Krogh, follows these requirements: 3 Copies of Data – Maintain three copies of data—the original, and at least two copies. 2 Different Media – Use two different media types for storage.
Why is backup and disaster recovery important
The purpose of the backup is to create a copy of data that can be recovered in the event of a primary data failure. Primary data failures can be the result of hardware or software failure, data corruption, or a human-caused event, such as a malicious attack (virus or malware), or accidental deletion of data.
What are the best backup strategies
Continue to follow the 3-2-1 backup rule
The 3-2-1 rule of backup states that organizations should keep three complete copies of their data, two of which are local but on different types of media, with at least one copy stored off site.
What is the best backup rule
According to the 3-2-1 backup rule, you should keep at least two backup copies to protect your data against natural disasters, accidental deletions, hardware failure and cyberattacks.
What is the golden rule of backup
Follow the 3-2-1 Rule
This rule suggests that your business should do the following: Store a minimum of three copies of your data. Two of these backups should remain on separate storage media. One backup stays stored offsite, such as in the cloud.
What is the most secure backup strategy
The 3-2-1 rule of backup states that organizations should keep three complete copies of their data, two of which are local but on different types of media, with at least one copy stored off site.
Why is backup strategy important
The purpose of the backup is to create a copy of data that can be recovered in the event of a primary data failure. Primary data failures can be the result of hardware or software failure, data corruption, or a human-caused event, such as a malicious attack (virus or malware), or accidental deletion of data.
What is the 3 1 1 backup rule
Complete Ransomware Protection Starts With 3-2-1-1
It says to keep three copies of your data—one primary and two backups—with two copies stored locally on two formats (network-attached storage, tape, or local drive) and one copy stored offsite in the cloud or secure storage.
Why is backup system important
The Importance of Backups
Making backups of collected data is critically important in data management. Backups protect against human errors, hardware failure, virus attacks, power failure, and natural disasters. Backups can help save time and money if these failures occur.
Why is data recovery so important
Data recovery is an aspect of backup and recovery and an integral component of your overall disaster recovery plan (DRP). Companies rely on data to inform business decisions and to support day-to-day operations. As such, any data loss can seriously impact continuity, which is why data recovery is so critical.
Which backup is most efficient
Incremental backups take the least space and time to perform than differential and full backups, but it's the most time-consuming out of all of the methods to restore a full system.
What are the golden rules of backup
Follow the 3-2-1 Rule
This rule suggests that your business should do the following: Store a minimum of three copies of your data. Two of these backups should remain on separate storage media. One backup stays stored offsite, such as in the cloud.
Who invented the 3 2 1 backup rule
photographer Peter Krogh’s
(3-2-1 Backup Strategy Guide)
The rule was first coined in photographer Peter Krogh's 2005 book on digital asset management. Over time, people have adapted it to suit a changing business and technical landscape, but the core concepts remain the same.
Who invented the 3-2-1 backup rule
photographer Peter Krogh’s
(3-2-1 Backup Strategy Guide)
The rule was first coined in photographer Peter Krogh's 2005 book on digital asset management. Over time, people have adapted it to suit a changing business and technical landscape, but the core concepts remain the same.
What is the best type of backup
Full backups
The primary advantage to performing a full backup during every operation is that a complete copy of all data is available with a single set of media. This results in a minimal time to restore data, a metric known as a recovery time objective.
What is the benefit of a backup plan
One is the psychological comfort it brings: People think, “I'm going to be OK even if I fail, because I can then do X or Y.” It reduces the perceived uncertainty of the situation. Another benefit is that if you fail, you don't have to dwell on it; you can quickly implement your backup plan.
Why is the 3-1-1 rule important
The 3-1-1 Rule refers to three core components that govern how many liquids you can bring in your carry-on bags: Each liquid must be in a 3.4-ounce or less container ("3"), all containers must be placed inside one clear quart-sized plastic bag ("1"), and each passenger is only allowed one plastic bag ("1").
Why does the 3-1-1 rule exist
That rule was imposed after terrorists in Britain tried to sneak liquid explosives in planes in August 2006.
How many backups should you make
According to the 3-2-1 backup rule, you should keep at least two backup copies to protect your data against natural disasters, accidental deletions, hardware failure and cyberattacks.
Why is backup and replication important
Backup remains the go-to solution for many industries that must keep long-term records for compliance purposes. Data replication, on the other hand, focuses on business continuity—delivering uninterrupted operation of mission-critical and customer-facing applications after a disaster.
What is the main importance of backup and recovery
The purpose of the backup is to create a copy of data that can be recovered in the event of a primary data failure. Primary data failures can be the result of hardware or software failure, data corruption, or a human-caused event, such as a malicious attack (virus or malware), or accidental deletion of data.