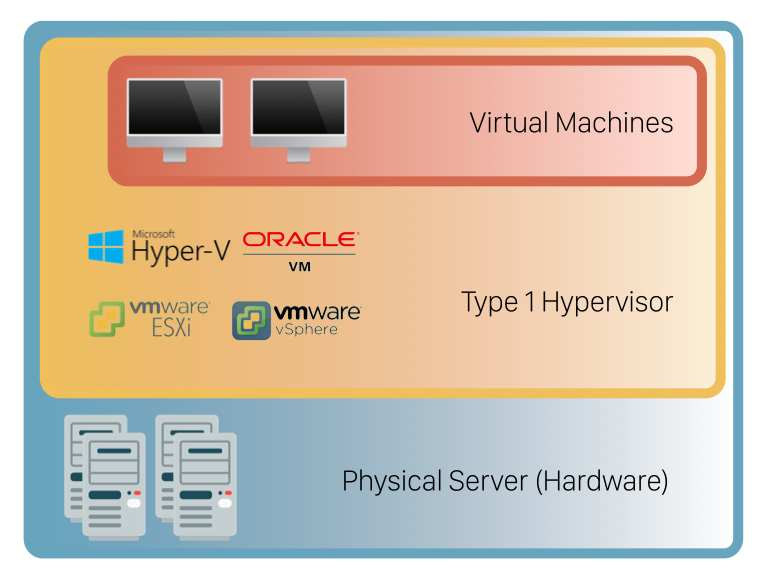
Is Hyper-V Level 1 or 2
Hyper-V is a Type 1 hypervisor which is installed on bare-metal servers, or on the Windows 10 operating system, but then boots up before the operating system does and runs it as a guest OS. In both cases, Hyper-V interacts directly with the CPU, without going through the host operating system.
Is Hyper-V a Type 1
Hyper-V features a Type 1 hypervisor-based architecture. The hypervisor virtualizes processors and memory. It provides mechanisms for the virtualization stack in the root partition to manage child partitions, virtual machines (VMs) and expose services such as I/O (input/output) devices to the VMs.
What is Hyper-V Type 1 and Type 2
Type 1 runs directly on the hardware with Virtual Machine resources provided. Type 2 runs on the host OS to provide virtualization management and other services.
Is Hyper-V outdated
The good news is that Hyper-V Server 2019 is going to continue to be supported until its extended support lifecycle runs out in 2029. This means that many organizations will have plenty of time to migrate to an alternative.
Is Xen a Type 1 or 2
Xen (pronounced /ˈzɛn/) is a free and open-source type-1 hypervisor, providing services that allow multiple computer operating systems to execute on the same computer hardware concurrently.
Why is Hyper-V so fast
This design means that Hyper-V has less overhead for maintaining and managing devices and services that are not dependent on the hypervisor. This makes Hyper-V fast and scalable, as it directly accesses the hardware and does not need to load drivers and services during initialization.
What is Type 1 virtual machine
A Type 1 hypervisor runs directly on the underlying computer's physical hardware, interacting directly with its CPU, memory, and physical storage. For this reason, Type 1 hypervisors are also referred to as bare-metal hypervisors. A Type 1 hypervisor takes the place of the host operating system.
What is a Type 2 VM
A Type 2 hypervisor, also called a hosted hypervisor, is a virtual machine (VM) manager that is installed as a software application on an existing operating system (OS).
Why is Hyper-V laggy
Common Hyper-V Issues
Processor (e.g. overloading logical or virtual processors, CPU lags) Memory (e.g. memory overcommitment, running out of RAM, failure to start VMs) Network (e.g. network-bound hosts and VMs, imbalance of networking resources)
Is KVM a Type 1 hypervisor
How does KVM work KVM converts Linux into a type-1 (bare-metal) hypervisor.
Is Citrix a Type 1 hypervisor
Examples of type 1 hypervisors are VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Citrix XenServer.
Is Hyper-V better than VMware
Hyper-V also has some advantages over VMware in terms of integration with other Windows features, such as networking, security, and management. Hyper-V also has streamlined connection bridging, allowing your VMs to communicate with other devices on your network. Hyper-V isn't available on Windows Home editions.
Is VMware a Type 1
VMware offers Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors. Type 1 hypervisors include: ESXi hypervisor. VMware ESXi (Elastic Sky X Integrated) is a Type 1 (or bare-metal) hypervisor targeting server virtualization in the data center.
Is VirtualBox Type 1
VirtualBox is a Type 2 hypervisor. Unlike Hyper-V, which takes control of the BIOS or UEFI automatically when the computer starts, users can start or stop VirtualBox manually on demand.
Is Microsoft killing Hyper-V
While Microsoft has discontinued the Hyper-V Free SKU, they are still allowing you to purchase Windows Server 2022 and install the Hyper-V role to get the features you're used to.
Is Hyper-V bad for gaming
From what I've seen, enabling Hyper-V in the OS means your Windows install is actually running virtualized on Hyper-V itself even if you don't have any VMs. Because of this, Hyper-V reserves part of the GPU for virtualization even if it's not used and this reduces your gaming performance.
Is KVM a Type 1 or Type 2
KVM converts Linux into a type-1 (bare-metal) hypervisor. All hypervisors need some operating system-level components—such as a memory manager, process scheduler, input/output (I/O) stack, device drivers, security manager, a network stack, and more—to run VMs.
Is KVM better than Hyper-V
If a highly flexible solution is needed, KVM is a great choice. In contrast, if a reliable and robust solution tailored to a Windows-based environment is necessary, Hyper-V is the way to go. In either case, both solutions offer a great variety of features and are suitable for various IT environments.
Is VMware hypervisor 1 or 2
type 2 hypervisor
A type 2 hypervisor is better for individual users who want to run multiple operating systems on a personal computer. VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox are examples of a type 2 hypervisor.
Why is Hyper-V so good
Hyper-V creates a cost-effective, stable, and productive server virtualization environment by running multiple operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, and more, in parallel on one machine or server.
Does Hyper-V make VM faster
Install Hyper-V on Windows Server Core
As a result, fewer hardware resources are consumed and the entire system has fewer vulnerabilities. Those saved resources can now be used for provisioning VMs running in the system, which can significantly improve VM performance in a Hyper-V environment.
Is VMware a Type 1 or 2
Some popular Type 2 hypervisors used today include VirtualBox, VMware Workstation, and VMware Fusion.
Is VirtualBox Type 1 or Type 2
They support guest VMs by coordinating calls for the CPU, memory, and storage resources through the underlying physical host's OS. VirtualBox is a Type 2 hypervisor. Unlike Hyper-V, which takes control of the BIOS or UEFI automatically when the computer starts, users can start or stop VirtualBox manually on demand.
Is Xen Type 1 or Type 2
Xen (pronounced /ˈzɛn/) is a free and open-source type-1 hypervisor, providing services that allow multiple computer operating systems to execute on the same computer hardware concurrently.
Is KVM Type 1 or Type 2
KVM converts Linux into a type-1 (bare-metal) hypervisor. All hypervisors need some operating system-level components—such as a memory manager, process scheduler, input/output (I/O) stack, device drivers, security manager, a network stack, and more—to run VMs.


