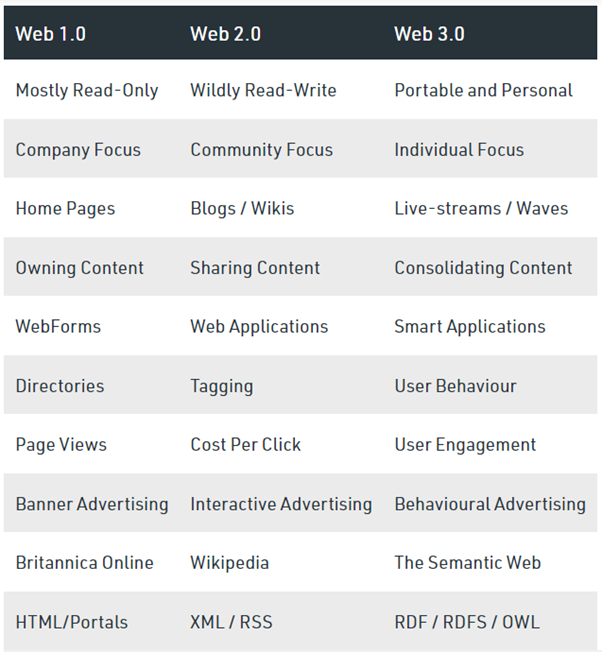
How does Web 1.0 Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 different from each other
Web 1.0 is the "read-only Web," Web 2.0 is the "participative social Web," and Web 3.0 is the "read, write, execute Web." This Web interaction and utilization stage moves users away from centralized platforms like Facebook, Google, or Twitter and towards decentralized, nearly anonymous platforms.
What is the difference between Web 1.0 Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 PDF
The first stage, web 1.0, was about connecting information and getting on the net. Web 2.0 is about connecting people putting the "I" in user interface, and the "we" into a web of social participation. The next stage, web 3.0, is starting now.
What is Web 3.0 and its examples
Web 3.0, or Web3, is a set of values and technical applications that define a new era of the World Wide Web. Prime Web 3.0 examples include ubiquity, decentralization, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and connectivity.
What is Web 1.0 and its examples
Web 1.0 sites are static.
They contain information that might be useful, but there's no reason for a visitor to return to the site later. An example might be a personal webpage that gives information about the site's owner, but never changes.
What is the difference between the internet and the web
The Internet is a global network of networks while the Web, also referred to formally as World Wide Web (www) is a collection of information that is accessed via the Internet. Another way to look at this difference is; the Internet is infrastructure while the Web is served on top of that infrastructure.
What is the difference between Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 quizlet
Web 1.0 is static and read only, it has little interaction between the user and the website. Web 2.0 supports participation by users and the general public as they can interact with the website and book classes.
How are Web 1.0 2.0 3.0 and 4.0 different
Web 1.0 as a web of cognition, web 2.0 as a web of communication, web 3.0 as a web of co-operation and web 4.0 as a web of integration are introduced such as four generation of the web since the advent of the web.
What is Web 3.0 in your own words
Web 3.0, sometimes known as Web 3, is the concept of the next generation of the web, in which most users will be connected via a decentralized network and have access to their own data. This article taught us about the technologies that are anticipated to advance and change in the upcoming years.
What is the difference between Web2 and Web3
Web2 is often limited by factors such as cost, location and technical expertise. Web3 technologies, such as peer-to-peer networks and blockchain-based systems, have the potential to help bridge these gaps by making it possible for individuals and communities to share resources and access regardless of economic status.
What is Web 2.0 and its examples
Examples of Web 2.0 features include social networking sites or social media sites (e.g., Facebook), blogs, wikis, folksonomies ("tagging" keywords on websites and links), video sharing sites (e.g., YouTube), image sharing sites (e.g., Flickr), hosted services, Web applications ("apps"), collaborative consumption …
What is Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 examples
Web 1.0 contains pages and lists, similar to a book for its reader, with the information presented in a linear format, whereas Web 2.0 has non-linear information. Web 1.0 sites include Slashdot and Craigslist, while Web 2.0 sites include Twitter and Facebook.
What are three differences between the internet and the World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a collection of information accessible through the Internet. The Internet is a worldwide network of interconnected computer networks that connect devices using the TCP/IP protocol. The World Wide Web refers to HTML-formatted online material that may be accessed using the HTTP protocol.
What is the difference between the internet and the World Wide Web essay
In simple terms, the World Wide Web is just one common area for information exchange, facilitated by global computer networks — or the Internet. You connect to this Internet to access the Web, but the Internet is just the connection between countless, separate servers, computers, and devices.
When was Web 1.0 created
1989
Web 1.0 was first implementation of the web and it lasted from 1989 to 2005. It was define as web of information connections. According to the innovator of World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee considers the Web as “read-only” Web [1].
What generation of WWW is being described by web of People Connections
Web 1.0 as a web of information connections, Web 2.0 as a web of people connections, Web 3.0 as a web of knowledge connections and web 4.0 as a web of intelligence connections are described as four generations of the web in the paper.
What are three differences between the Internet and the World Wide Web
The internet is primarily hardware-based. In comparison to the Internet, WWW is more software-oriented. The Internet utilizes the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). The World Wide Web utilizes the Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
What is the difference between the Internet and the Web
The Internet is a global network of networks while the Web, also referred to formally as World Wide Web (www) is a collection of information that is accessed via the Internet.
What is Web 2.0 and 3.0 also describe Web 3.0 with its features
Web 2.0 is all about reading, writing, creating, and interacting with the end user. It was famously called the participative social web. Web 3.0 is the third generation of the World Wide Web, and is a vision of a decentralized web which is currently a work in progress. It is all about reading, writing, and owning.
What is Web 3.0 and its benefits
One of the most significant benefits of Web 3.0 is the transformation towards being able to access the data from anywhere and is mainly driven by the heavy usage of Smartphone and Cloud applications. The vision is to ensure the user can have access to information as much as possible from anywhere in the world.
What is the difference between Web1 Web2 and Web3
You primarily interact with the chain of information via digital wallet transactions. Just like Web2 evolved from Web1 where it added a social dimension to information sharing, Web3 is the next evolution of Web2 where information is exchanged in full transparency with no central governance.
What is the difference between Web 1.0 2.0 and 3.0 Brainly
Web 1.0 was all about reading, and getting information. Web 2.0 was all about reading, writing, and creating. So, users joined social platforms, and these platforms got big because of this created content. Web 3.0 is all about reading, writing and owning.
What is Web 2.0 and examples
Examples of Web 2.0 features include social networking sites or social media sites (e.g., Facebook), blogs, wikis, folksonomies ("tagging" keywords on websites and links), video sharing sites (e.g., YouTube), image sharing sites (e.g., Flickr), hosted services, Web applications ("apps"), collaborative consumption …
What is the basic difference between World Wide Web and website
A combination of related web pages is called a website. A web browser and HTTP protocol help to access webpages or websites in World Wide Web. HTTP protocol is a set of rules for transferring files such as text, images, audio, video and other multimedia files on WWW.
What is the main difference between the web and the internet
The Internet is a global network of networks while the Web, also referred to formally as World Wide Web (www) is a collection of information that is accessed via the Internet. Another way to look at this difference is; the Internet is infrastructure while the Web is served on top of that infrastructure.
What is an example of the difference between the internet and World Wide Web
In simple terms, the World Wide Web is just one common area for information exchange, facilitated by global computer networks — or the Internet. You connect to this Internet to access the Web, but the Internet is just the connection between countless, separate servers, computers, and devices.