How does the sun damage DNA
UVA and UVB photons can be directly absorbed not only by DNA, which results in lesions, but also by the chromophores that are present in skin cells. This process leads to the formation of reactive oxygen species, which may indirectly cause DNA damage.
How does melanin protect DNA from UV damage
Instead of becoming very reactive when hit by UV light, melanin releases the extra energy as heat; it reacts less than 1 out of every 1000 times it becomes excited. This allows melanin to protect more sensitive molecules, like DNA, from UV exposure.
What happens when UV light hits a skin cell with less melanin
But melanin can't absorb all the UV rays. And some people don't have much melanin in their skin. A sunburn happens when the amount of UV rays exceeds the protection that the skin's melanin can provide. Sunburn is damage to the skin.
How does UV light damage skin cells
How can UV cause skin cancer Too much UV radiation from the sun or sunbeds can damage the DNA in our skin cells. DNA tells our cells how to function. If enough DNA damage builds up over time, it can cause cells to start growing out of control, which can lead to skin cancer.
Can UV rays cause DNA mutation
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation causes various types of DNA damage, which leads to specific mutations and the emergence of skin cancer in humans, often decades after initial exposure. Different UV wavelengths cause the formation of prominent UV-induced DNA lesions.
Is DNA damage caused by heat
The evidence shows that long exposure and very high temperature can induce an increase in DNA damage through aggregate in natural proteins, ROS generation, cell death, and reproductive damage in hot-humid and hot-dry climate conditions.
How does UV radiation affect DNA replication
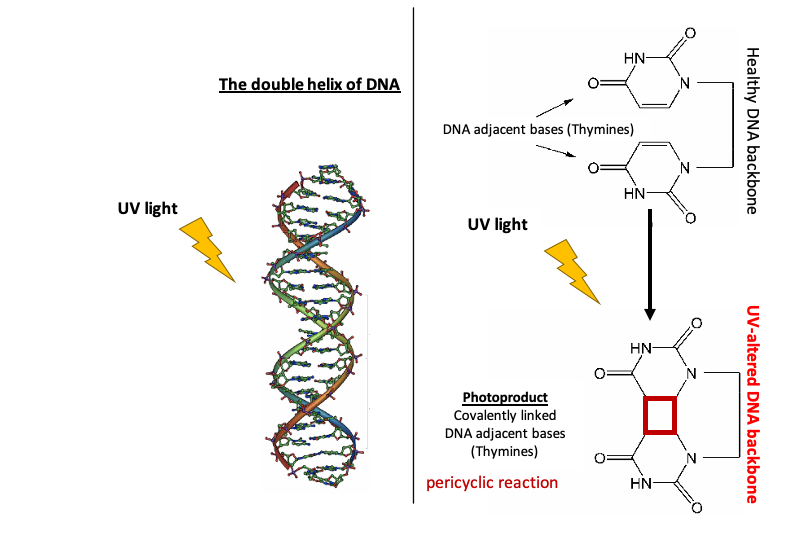
UV radiation causes two classes of DNA lesions: cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs, Figure 1) and 6-4 photoproducts (6-4 PPs, Figure 2). Both of these lesions distort DNA's structure, introducing bends or kinks and thereby impeding transcription and replication.
How does DNA absorb UV light
DNA absorbs UV light due to heterocyclic rings of the nucleotides, its sugar- phosphate backbone does not contribute to this absorption [3]. Factors such as pH and ionic strength can further affect the absorbance spectrum.
Can UV light from sunlight cause damage to DNA in skin cells
Higher-energy UV rays are a form of ionizing radiation. This means they have enough energy to remove an electron from (ionize) an atom or molecule. Ionizing radiation can damage the DNA (genes) in cells, which in turn may lead to cancer.
Why does DNA absorb UV light
DNA absorbs UV light due to heterocyclic rings of the nucleotides, its sugar- phosphate backbone does not contribute to this absorption [3]. Factors such as pH and ionic strength can further affect the absorbance spectrum.
What kind of UV radiation causes direct damage to DNA
DNA is damaged predominantly by longer wavelength radiation—UV-B (280–315 nm) and UV-A (315–400 nm)—while UV-C (<280 nm) is considered less harmful as it is absorbed by oxygen and the ozone layer of the atmosphere.
Does UV radiation cause genetic damage
While UVA and UVB rays differ in how they affect the skin, they both do harm. Unprotected exposure to UVA and UVB damages the DNA in skin cells, producing genetic defects, or mutations, that can lead to skin cancer and premature aging.
What temperature destroys DNA
We found that under dry conditions, DNA degradation begins at 130°C, and continues in a linear manner until complete degradation occurs around 190°C.
What can DNA be damaged by
Endogenous sources of DNA damage include hydrolysis, oxidation, alkylation, and mismatch of DNA bases; sources for exogenous DNA damage include ionizing radiation (IR), ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and various chemicals agents.
Can UV cause DNA mutations
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation causes various types of DNA damage, which leads to specific mutations and the emergence of skin cancer in humans, often decades after initial exposure. Different UV wavelengths cause the formation of prominent UV-induced DNA lesions.
Does UV exposure trigger DNA replication
Upon UV irradiation, replication of DNA is inhibited (24) and the stalled replication forks are known to attract DNA damage sensor proteins which trigger the ATR/Chk1-dependent checkpoint signaling cascade that leads to activation of a variety of proteins including p53 (25-28).
Can DNA be destroyed by UV light
Both long and short wavelength UV light is damaging to DNA, but in different ways. Short wavelength UV-B and UV-C light can directly cause dimerization of pyrimidines, directly prevent replication of plasmid DNA, or induce mutations after faulty repair.
What type of damage does UV light cause in DNA
UV radiation causes two classes of DNA lesions: cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs, Figure 1) and 6-4 photoproducts (6-4 PPs, Figure 2). Both of these lesions distort DNA's structure, introducing bends or kinks and thereby impeding transcription and replication.
What UV light can DNA absorb
It is based on the principles that nucleic acids absorb ultraviolet (UV) light at a specific wavelength. For pure DNA samples, the maximum absorbance occurs over a broad peak at around 260 nm; at 280 nm it only absorbs about half as much UV light compared to 260 nm [2].
What happens if DNA is damaged
Damage to DNA can cause genetic alterations, and if genes that control cell growth are involved, these mutations can lead to the development of cancer.
Can radiation damage DNA
Ionizing radiation is a type of high-energy radiation that is able to release electrons from atoms and molecules generating ions which can break covalent bonds. Ionizing radiation directly affects DNA structure by inducing DNA breaks, particularly, DSBs.
Can DNA be heat killed
Direct heat exposure to cells causes protein degradation and DNA damage, which can lead to genetic alteration and cell death, but little is known about heat-induced effects on the surrounding tissue.
Does burning destroy DNA
In many forensic cases – particularly if the remains of the individual have been buried, exposed to the sun and elements, or burned in fire – the DNA molecule may be damaged. Standard forensic DNA analysis may be unable to recover usable DNA, preventing identification.
Which UV is responsible for DNA damage
UV-A and visible light energy (up to 670–700 nm) are able to generate singlet oxygen (1O2) that can damage DNA via indirect photosensitizing reactions [13].
How can a UV induced mutation affect DNA
UV radiation causes two classes of DNA lesions: cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs, Figure 1) and 6-4 photoproducts (6-4 PPs, Figure 2). Both of these lesions distort DNA's structure, introducing bends or kinks and thereby impeding transcription and replication.


