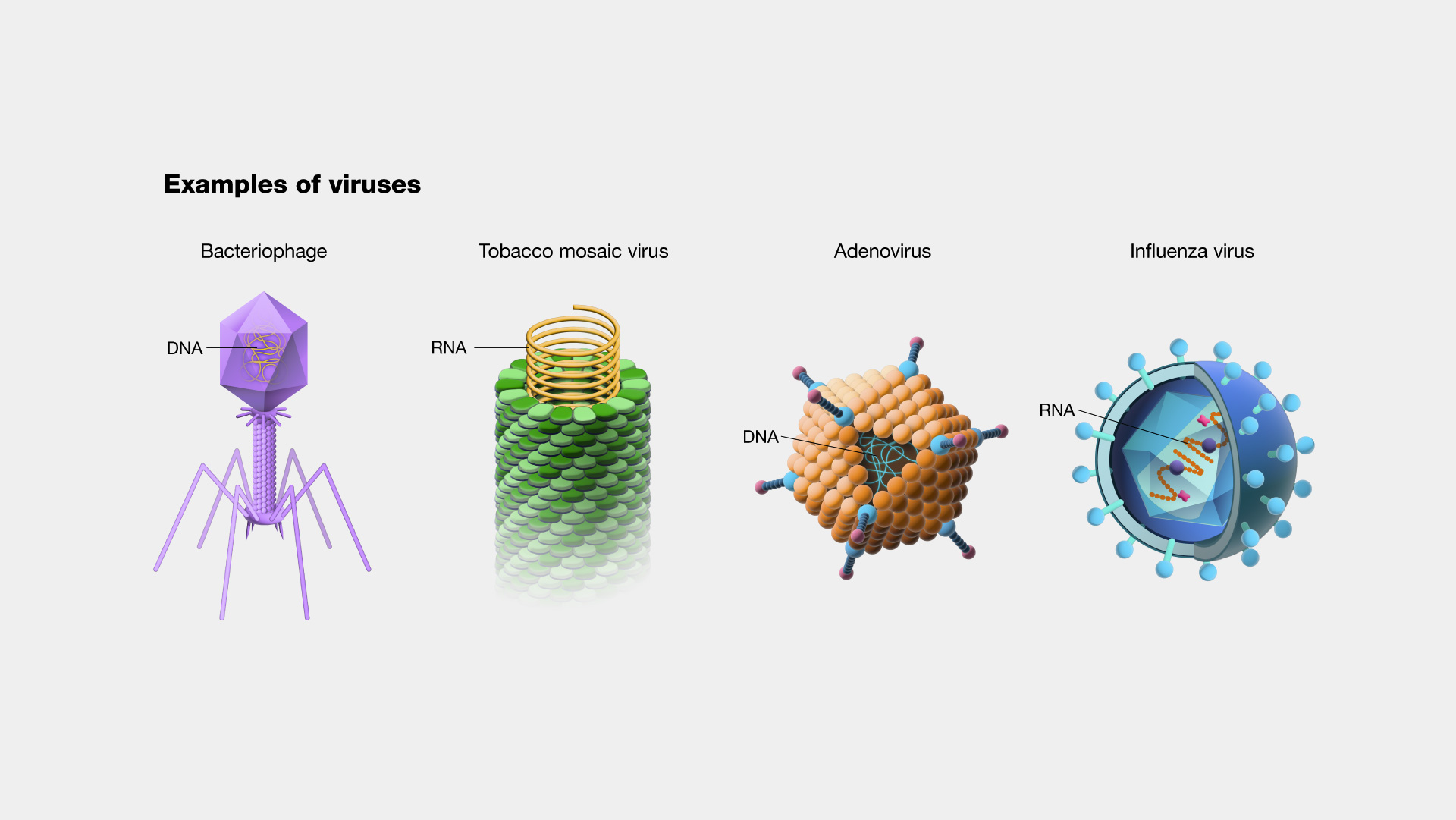
Are viruses DNA or RNA
Viral families are grouped based on their type of nucleic acid as genetic material, DNA or RNA 6. DNA viruses contain usually double‐stranded DNA (dsDNA) and rarely single‐stranded DNA (ssDNA). These viruses replicate using DNA‐dependent DNA polymerase. RNA viruses have typically ssRNA, but may also contain dsRNA.
Are there any viruses with DNA
DNA viruses comprise important pathogens such as herpesviruses, poxviruses, adenoviruses, and papillomaviruses, among others.
Where is virus DNA
cell nucleus
DNA viruses undertake their replication within the cell nucleus, and therefore they must first deliver their genome into the nucleus of their host cells. Thus, trafficking across the nuclear envelope is at the basis of DNA virus infections.
Why can’t viruses have both DNA and RNA
Answer and Explanation:
The genetic material in viruses is either RNA or DNA. It is not possible for a virus to contain both RNA and DNA. This is because (biologically speaking), there doesn't seem to be any need for it. As containing either of them gets the job done for a virus particle.
Do bacteria have DNA
Most bacteria have a haploid genome, a single chromosome consisting of a circular, double stranded DNA molecule.
Can viruses steal DNA
Scientists already know that viruses can steal DNA from their hosts. This is true for both viruses that infect eukaryotes — creatures with a nucleus in their cells — and those that infect bacteria. But viruses usually only have segments of DNA similar to their direct host.
Can viruses copy DNA
DNA viruses replicate their genomes using DNA polymerase enzymes and transcribe their mRNA using DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzymes.
Do viruses pass on DNA
When a type of virus known as a retrovirus infects a cell, it converts its RNA into DNA, which can then become part of a human chromosome. Once in a while, retroviruses infect sperm and egg cells and become "endogenous," meaning they are passed down from generation to generation.
Do viruses store DNA
Concept 25 Some viruses store genetic information in RNA.
So it came as a surprise when in 1971, it was discovered that some viruses shift their genetic information from RNA to DNA. Even so, these viruses ultimately make proteins in the same way as higher organisms.
Do all viruses only have RNA
Definition. A virus is an infectious microbe consisting of a segment of nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat.
Can viruses contain DNA but not RNA
Viruses are smaller and simpler in construction than unicellular microorganisms, and they contain only one type of nucleic acid—either DNA or RNA—never both.
Do fungi have DNA or RNA
Fungi are eukaryotes and have a complex cellular organization. As eukaryotes, fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus where the DNA is wrapped around histone proteins.
Do viruses have RNA
A virus is an infectious microbe consisting of a segment of nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat.
Can a virus destroy DNA
It is apparent, however, that many RNA viruses can also induce significant DNA damage, even in cases where viral replication takes place exclusively in the cytoplasm.
How much of our DNA is virus
Nearly one-tenth of the human genome contains snippets of viral DNA left over from ancient infections. These DNA fragments, called endogenous retroviruses (ERVs), have been passed along and modified over millions of years of evolution.
Do viruses convert DNA to RNA
During the replication of some DNA viruses, such as the hepadnaviruses or pararetroviruses, also carrying a RT, the DNA genome is transcribed to RNA that serves as a template to make new viral DNA strands.
Do viruses steal genes
Viruses are known to do this through a process called “cap-snatching,” in which they cut the end from one of the cell's own protein-encoding messages (a messenger RNA, or mRNA) and then extend that sequence with a copy of one of their own genes.
Why do viruses not have DNA
This is because viruses do not have the tools to replicate their genetic material themselves. More recently, scientists have discovered a new type of virus, called a mimivirus. These viruses do contain the tools for making a copy of its DNA.
Do all viruses contain both RNA and DNA
Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites, which by definition contain either a RNA or DNA genome surrounded by a protective, virus-coded protein coat. Viruses may be viewed as mobile genetic elements, most probably of cellular origin and characterized by a long co-evolution of virus and host.
Why do viruses not have both DNA and RNA
Answer and Explanation:
The genetic material in viruses is either RNA or DNA. It is not possible for a virus to contain both RNA and DNA. This is because (biologically speaking), there doesn't seem to be any need for it. As containing either of them gets the job done for a virus particle.
What virus has only RNA
1.1. RNA Viruses. Human diseases causing RNA viruses include Orthomyxoviruses, Hepatitis C Virus (HCV), Ebola disease, SARS, influenza, polio measles and retrovirus including adult Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Are all bacteria DNA or RNA
The genetic material of bacteria and plasmids is DNA. Bacterial viruses (bacteriophages or phages) have DNA or RNA as genetic material.
Is the coronavirus a DNA or RNA virus
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are positive-stranded RNA(+ssRNA) viruses with a crown-like appearance under an electron microscope (coronam is the Latin term for crown) due to the presence of spike glycoproteins on the envelope.
Are viruses living or nonliving
So were they ever alive Most biologists say no. Viruses are not made out of cells, they can't keep themselves in a stable state, they don't grow, and they can't make their own energy. Even though they definitely replicate and adapt to their environment, viruses are more like androids than real living organisms.
Is 8% of human DNA from virus
HERVs, or human endogenous retroviruses, make up around 8% of the human genome, left behind as a result of infections that humanity's primate ancestors suffered millions of years ago. They became part of the human genome due to how they replicate.


