What is the value of z value
A z-score equal to 0 represents an element equal to the mean. A z-score equal to 1 represents an element, which is 1 standard deviation greater than the mean; a z-score equal to 2 signifies 2 standard deviations greater than the mean; etc.
What is Z formula
z = (x – μ) / σ
For example, let's say you have a test score of 190. The test has a mean (μ) of 150 and a standard deviation (σ) of 25. Assuming a normal distribution, your z score would be: z = (x – μ) / σ
What is the z-score method
Z-score is a statistical measurement that describes a value's relationship to the mean of a group of values. Z-score is measured in terms of standard deviations from the mean. If a Z-score is 0, it indicates that the data point's score is identical to the mean score.
How do you find Z star
So if I do 1 minus point 96. That's going to give me a point or four but that's both tails combined. So if I take that and divide by 2 I get point O 2 so that would be in one tail.
What is Z in Z value
The z-score, also referred to as standard score, z-value, and normal score, among other things, is a dimensionless quantity that is used to indicate the signed, fractional, number of standard deviations by which an event is above the mean value being measured.
What is the Z in statistics
A z-score, or z-statistic, is a number representing how many standard deviations above or below the mean population the score derived from a z-test is. Essentially, it is a numerical measurement that describes a value's relationship to the mean of a group of values.
Why do we calculate z-scores
The standard score (more commonly referred to as a z-score) is a very useful statistic because it (a) allows us to calculate the probability of a score occurring within our normal distribution and (b) enables us to compare two scores that are from different normal distributions.
What is the easiest way to find the z-score
How do you find the z-score with mean and standard deviation If you know the mean and standard deviation, you can find the z-score using the formula z = (x – μ) / σ where x is your data point, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation.
What is the Z * in statistics
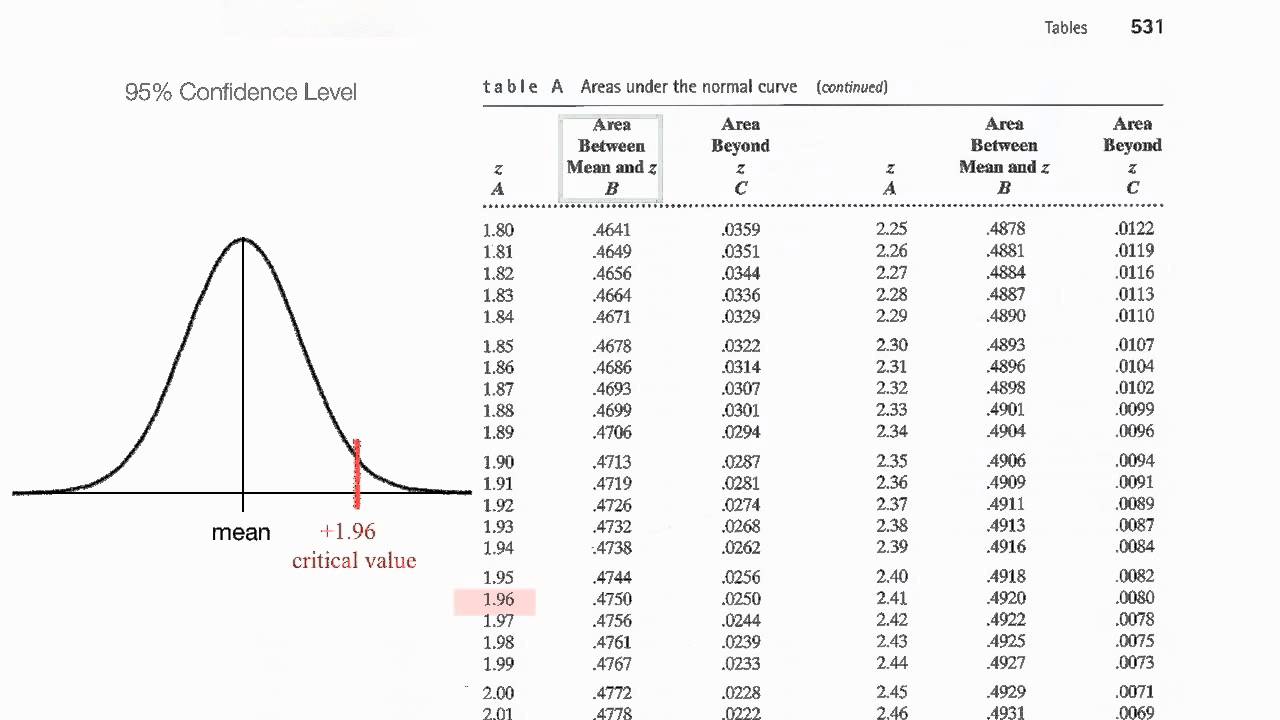
Z* represents the value of Z at different confidence interval. For a two-tailed test, the value of Z at 95% interval is +- 1.96.
How do you find the Z * for a confidence level
Number which is 0.06. So when you add those two 1.9 plus 0.06 that gives you the z-score of 1.96. So that's how you could find the z-score. Given the confidence. Level so if you know the confidence.
What is z-value examples
For example, the z-score of 0.54 can be located along a z-table, which illustrates what percentage is under the distribution curve at any given point. The z-score of 0.54 corresponds to 0.7054 on the z-table. This means that student A is taller than 70.54% of the class and am shorter than 29.46% of the class.
What is the value of Z * for a 95% confidence interval
1.96
The value of z* for a confidence level of 95% is 1.96. After putting the value of z*, the population standard deviation, and the sample size into the equation, a margin of error of 3.92 is found.
What is Z in statistics
A z-score, or z-statistic, is a number representing how many standard deviations above or below the mean population the score derived from a z-test is. Essentially, it is a numerical measurement that describes a value's relationship to the mean of a group of values.
What are the 4 steps to find the z-score
Below are steps you can use to find the Z-score of a data set:Determine the mean. The mean, or average, is a value that represents the average value within a data set.Choose a value for x.Find the standard deviation.Perform the calculation.
What is Z * maths
Integers
Integers. The letter (Z) is the symbol used to represent integers. An integer can be 0, a positive number to infinity, or a negative number to negative infinity.
What is Z * for 95% interval
1.96
The value of z* for a confidence level of 95% is 1.96. After putting the value of z*, the population standard deviation, and the sample size into the equation, a margin of error of 3.92 is found.
What is the Z * for a 99% confidence level
2.576
Step #5: Find the Z value for the selected confidence interval.
| Confidence Interval | Z |
|---|---|
| 90% | 1.645 |
| 95% | 1.960 |
| 99% | 2.576 |
| 99.5% | 2.807 |
What is the value of Z * for a 95 confidence interval
1.96
The value of z* for a confidence level of 95% is 1.96. After putting the value of z*, the population standard deviation, and the sample size into the equation, a margin of error of 3.92 is found.
What is the Z-value in z test
If the value of z is greater than 1.96 or less than -1.96, the null hypothesis is rejected. The value for z is calculated by subtracting the value of the average daily return selected for the test, or 1% in this case, from the observed average of the samples.
What is Z in Z-value
The z-score, also referred to as standard score, z-value, and normal score, among other things, is a dimensionless quantity that is used to indicate the signed, fractional, number of standard deviations by which an event is above the mean value being measured.
What is the Z * for a 90% confidence interval
1.645
Step #5: Find the Z value for the selected confidence interval.
| Confidence Interval | Z |
|---|---|
| 90% | 1.645 |
| 95% | 1.960 |
| 99% | 2.576 |
| 99.5% | 2.807 |
What is the value of Z * for a 90% confidence interval
Z-score for 90% confidence interval, or Z(0.90), equals 1.645.
How do you do the Z test step by step
The steps to calculate the z test statistic are as follows:Identify the type of test.Set up the hypotheses.Find the critical value at the given alpha level using the z table.Determine the z test statistic using the appropriate formula.Compare the critical value and test statistic to arrive at a conclusion.
What does Z * mean in statistics
Z* represents the value of Z at different confidence interval. For a two-tailed test, the value of Z at 95% interval is +- 1.96. For 95% confidence interval, the population mean will lie in the following range: Sample mean +- 1.96*StandardError.
What is Z * in number theory
Z denotes the set of integers; i.e. {…,−2,−1,0,1,2,…}. Q denotes the set of rational numbers (the set of all possible fractions, including the integers). R denotes the set of real numbers. C denotes the set of complex numbers. (This set will be introduced more formally later.)


