How much plastic waste in 2050
If these trends continue, by 2050 we'll have produced 26 billion metric tons of plastic waste, almost half of which will be dumped in landfills and the environment. Because plastic doesn't degrade easily, there will be zillions of tons of the material on our planet by the end of the millennium.
What is the expected plastic production in 2050
Plastic production forecast worldwide 2025-2050
Annual production volumes are expected to continue rising in the following decades, rising to approximately 590 million metric tons by 2050. this would be an increase of more than 30 percent compared with 2025.
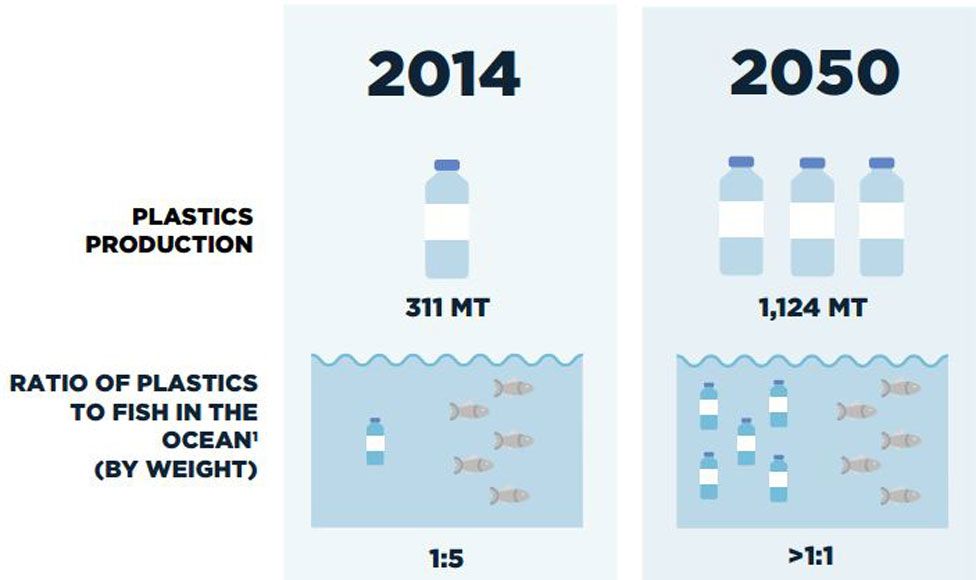
Is plastic more than fish in 2050
Plastic production will increase by 40% in the next 10 years. If we don't do anything about the plastic soup, oceans will carry more plastic than fish (by weight) by 2050. The United Nations warns that marine life will be irreparably destroyed. Coral reefs appear to be particularly vulnerable to plastic pollution.
Is plastic production expected to double by 2050
New research says current policies are not enough to bring about peak plastic consumption by 2050 in the world's 20 biggest economies, with plastic production predicted to reach 451 million tonnes (mt) by 2050.
What will oceans look like in 2050
Rivers of pollution flow into the ocean every day, with little sign of slowing down. Marine animals and birds now regularly eat plastic, and so do humans. It is estimated that by 2050 there could be more plastic in the sea than fish. As the plastic piles up, fish disappear.
Will plastic outweigh all the fish in the sea in 2050
If we keep producing (and failing to properly dispose of) plastics at predicted rates, plastics in the ocean will outweigh fish pound for pound in 2050, the nonprofit foundation said in a report Tuesday.
Can plastic last 1,000 years
It takes 1,000 years for a plastic bag to degrade in a landfill. Unfortunately, the bags don't break down completely but instead photo-degrade, becoming microplastics that absorb toxins and continue to pollute the environment.
Are we living in a plastic age
The plastic layers could be used to mark the beginning of the Anthropocene, the proposed geological epoch in which human activities dominate the planet, scientists suggest. According to them, the current period may become known as the plastic age after the bronze and iron ages.
Will plastic ever run out
However, even after we begin working with other types of waste, we won't run out of plastic in my lifetime. We just won't. There is more than 9 billion tons of plastic waste in the world. 91 percent of that is not recycled.
Is there a future without plastic
A future entirely without plastic is neither realistic nor desirable. But the world should aim for a future of drastically reduced plastic consumption and eliminated plastic pollution. This article explains the extent and nature of the plastic waste problem, and the political barriers to dealing with it.
What will the oceans look like in 100000 years
According to a simulation of planetary warming trends, failure to drastically cut greenhouse gas pollution within the next half century could choke Earth's oceans for the next 100,000 years. With warmer temperatures reducing its ability to absorb oxygen, much of the water would become barren and lifeless.
What will the ocean be like in 100 years
But in our best-case scenarios, oceans are on track to rise 2 to 3 feet (0.6 to 0.9 metres) by 2100. Even a sea-level rise below 3 feet (0.9 metres) could displace up to 4 million people. Oceans not only will have less ice at the poles, but they will also continue to acidify in the tropics.
What if ocean was full of plastic
Plastic on the ocean's surface can trap sunlight, making the surface warmer and reducing the amount of light and heat traveling to the depths of the ocean. If plastic litter were to cover the ocean's surface, it can have ripple effects on marine ecosystems and affect the planet's climate system, the scientists warn.
How long will plastic last in the ocean
If this waste isn't properly disposed of or managed, it can end up in the ocean. Unlike some other kinds of waste, plastic doesn't decompose. That means plastic can stick around indefinitely, wreaking havoc on marine ecosystems. Some plastics float once they enter the ocean, though not all do.
Did plastic exist in 1800
Since plastic was first developed in the 1800s, it has advanced to benefit every manufacturing sector including medicine, transportation, technology, packaging, construction, sport and leisure, agriculture, and manufacturing. Plastics have led to technological advances, design solutions, and financial savings.
Did plastic exist 100 years ago
Plastics: a story of more than 100 years of innovation
Finally, the wide range of completely synthetic materials that we would recognise as modern plastics started to be developed around 100 years ago: One of the earliest examples was invented by Alexander Parkes in 1855, who named his invention Parkesine.
Was there plastic 100 years ago
Finally, the wide range of completely synthetic materials that we would recognise as modern plastics started to be developed around 100 years ago: One of the earliest examples was invented by Alexander Parkes in 1855, who named his invention Parkesine. We know it today as celluloid.
How long until plastic is gone
20 to 500 years
While some plastics are reusable or recyclable, packaging and thicker plastic items are not. Plastic can take anywhere from 20 to 500 years to decompose, depending on the material's structure and environmental factors such as sunlight exposure.
How long will plastic last
20 to 500 years
Plastics can take anywhere from 20 to 500 years to decompose, depending on the material and structure. Additionally, how fast a plastic breaks down depends on sunlight exposure.
Will plastic ever go away
Aside from being incinerated, it is a problem that will almost never go away. Left to itself, plastic will get infinitely smaller, but never fully disappear. Lucy says, 'Microplastics are probably in every food we eat.
What did Earth look like 20,000 years ago
TO THE LAST 20,000 YEARS
Last Glacial Maximum- a time, around 20,000 years ago, when much of the Earth was covered in ice. The average global temperature may have been as much as 10 degrees Celsius colder than that of today. The Earth has a long history of cycles between warming and cooling.
What was Earth like 10 000 years ago
Roughly 10,000 years ago, Earth was experiencing a time of critical change. The planet was leaving the Ice Age, near the end of a much larger pattern of warming and cooling climate events. This led to major changes in the environments people were living in.
How hot will Earth get by 2100
3.6-7.2 degrees Fahrenheit
Since 1880, average global temperatures have increased by about 1 degrees Celsius (1.7° degrees Fahrenheit). Global temperature is projected to warm by about 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7° degrees Fahrenheit) by 2050 and 2-4 degrees Celsius (3.6-7.2 degrees Fahrenheit) by 2100.
How will Earth look in 2100
🌡🗓 Heatwaves will be 39 times more common than they were in the 19th Century. On average, the global temperature will be over 40°C around 7 days a year. 🌪 Extreme weather events such as cyclones, hurricanes and droughts would no longer be seen as "extreme", because of how often they would happen.
What will happen if we don’t stop using plastic
Plastic pollution can alter habitats and natural processes, reducing ecosystems' ability to adapt to climate change, directly affecting millions of people's livelihoods, food production capabilities and social well-being.


