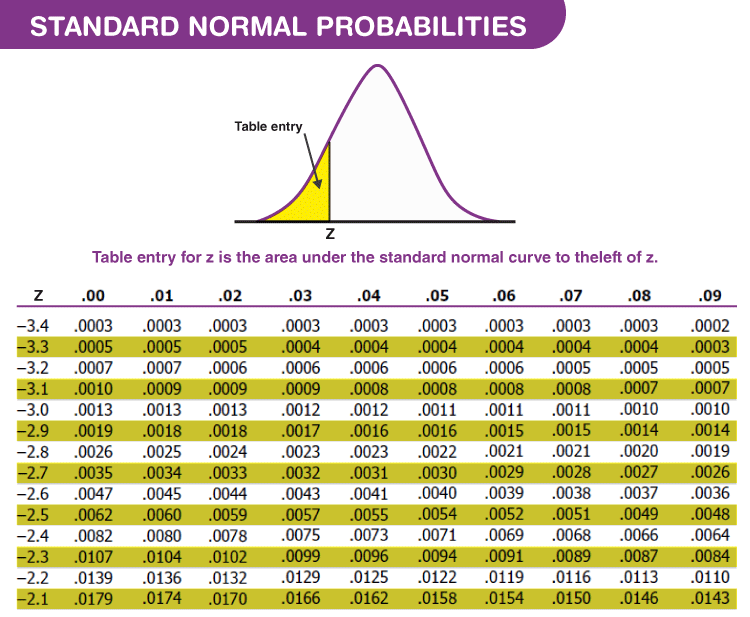
What is the value of Z
Z-score is measured in terms of standard deviations from the mean. If a Z-score is 0, it indicates that the data point's score is identical to the mean score. A Z-score of 1.0 would indicate a value that is one standard deviation from the mean.
What is Z value also known as
standard score
It is also known as standard score. It indicates how many standard deviations an entity is, from the mean. In order to use a z-score, the mean μ and also the population standard deviation σ should be known. A z score helps to calculate the probability of a score occurring within a standard normal distribution.
What is the Z in statistics
A z-score, or z-statistic, is a number representing how many standard deviations above or below the mean population the score derived from a z-test is. Essentially, it is a numerical measurement that describes a value's relationship to the mean of a group of values.
Is Z value same as sigma
As in the z-score, you still use the same normal-deviates from the z-table to approximate the area under the curve. The process sigma metric is essentially a Z equivalent.
What is Z in math
Integers. The letter (Z) is the symbol used to represent integers. An integer can be 0, a positive number to infinity, or a negative number to negative infinity.
What is Z of 1
A z-score of 1 is 1 standard deviation above the mean. A score of 2 is 2 standard deviations above the mean. A score of -1.8 is -1.8 standard deviations below the mean.
What is Z-value or p-value
p-value indicates how unlikely the statistic is. z-score indicates how far away from the mean it is.
How do you read Z-value
Z-scores are measured in standard deviation units.
A Z-score of 2.5 means your observed value is 2.5 standard deviations from the mean and so on. The closer your Z-score is to zero, the closer your value is to the mean. The further away your Z-score is from zero, the further away your value is from the mean.
What is Z in random variable
Definition: standard normal random variable
A standard normal random variable is a normally distributed random variable with mean μ=0 and standard deviation σ=1. It will always be denoted by the letter Z.
How do you interpret Z
Z-scores are measured in standard deviation units.
A Z-score of 2.5 means your observed value is 2.5 standard deviations from the mean and so on. The closer your Z-score is to zero, the closer your value is to the mean. The further away your Z-score is from zero, the further away your value is from the mean.
What is Z in Six Sigma
The Z score or value in process capability calculation is the mean distance from specification limits (USL and LSL) measured in standard deviation units. Z score tells the defects within the system. In other words, Z score tells the number of standard deviation existed between the mean and specification limit.
What is sigma level Z
What does a low Sigma or Z score mean for your process A low sigma (Z) score means that your process has a lot of defects. If we made a graph of this, a significant part of the tail of the distribution extends past the specification limit.
Does 0 belong to Z
Z+ is the set of all positive integers (1, 2, 3, …), while Z- is the set of all negative integers (…, -3, -2, -1). Zero is not included in either of these sets . Znonneg is the set of all positive integers including 0, while Znonpos is the set of all negative integers including 0.
What is Z in higher math
In the language of mathematics, the set of integers is often denoted by the boldface Z or blackboard bold .
What is the Z value of 2
0.47725
Z-table
| z | 0 | 0.02 |
|---|---|---|
| 1.9 | 0.47128 | 0.47257 |
| 2 | 0.47725 | 0.47831 |
| 2.1 | 0.48214 | 0.483 |
| 2.2 | 0.4861 | 0.48679 |
How do you calculate Z
There are three variables to consider when calculating a z-score: the raw score (x), the population mean (μ), and the population standard deviation (σ). To get the z-score, subtract the population mean from the raw score and divide the result by the population standard deviation.
Why do we use z-value
z-score is used when the data is normally distributed. The z-score will tell us how many standard deviations above or below the mean does a value lie.
What is Z-value examples
For example, the z-score of 0.54 can be located along a z-table, which illustrates what percentage is under the distribution curve at any given point. The z-score of 0.54 corresponds to 0.7054 on the z-table. This means that student A is taller than 70.54% of the class and am shorter than 29.46% of the class.
What is Z value in regression
The z value is the ratio of the estimated coefficient to its standard error. It measures the number of standard deviations that the estimated coefficient is away from zero. A higher absolute value of z value indicates that the estimated coefficient is more statistically significant.
What is Z in distribution
The standard normal distribution, also called the z-distribution, is a special normal distribution where the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1.
Why do we calculate Z value
The standard score (more commonly referred to as a z-score) is a very useful statistic because it (a) allows us to calculate the probability of a score occurring within our normal distribution and (b) enables us to compare two scores that are from different normal distributions.
What are the two values of Z
A positive z-value indicates that the point lies to the right of the mean, and a negative z-value indicates that the point lies left of the mean. There are a few different types of z-tables. The values in the table below represent the area between z = 0 and the given z-score.
What does Z tell you
Z scores (Z value) is the number of standard deviations a score or a value (x) is away from the mean. In other words, the Z-score measures the dispersion of data. Technically, a Z-score tells you how many standard deviations value (x) is below or above the population mean (µ).
What is Z from confidence level
Confidence Levels
| z-score (Standard Deviations) | p-value (Probability) | Confidence level |
|---|---|---|
| < -1.65 or > +1.65 | < 0.10 | 90% |
| < -1.96 or > +1.96 | < 0.05 | 95% |
| < -2.58 or > +2.58 | < 0.01 | 99% |
What is Z value in Six Sigma
Z scores (Z value) is the number of standard deviations a score or a value (x) is away from the mean. In other words, the Z-score measures the dispersion of data. Technically, a Z-score tells you how many standard deviations value (x) is below or above the population mean (µ).


