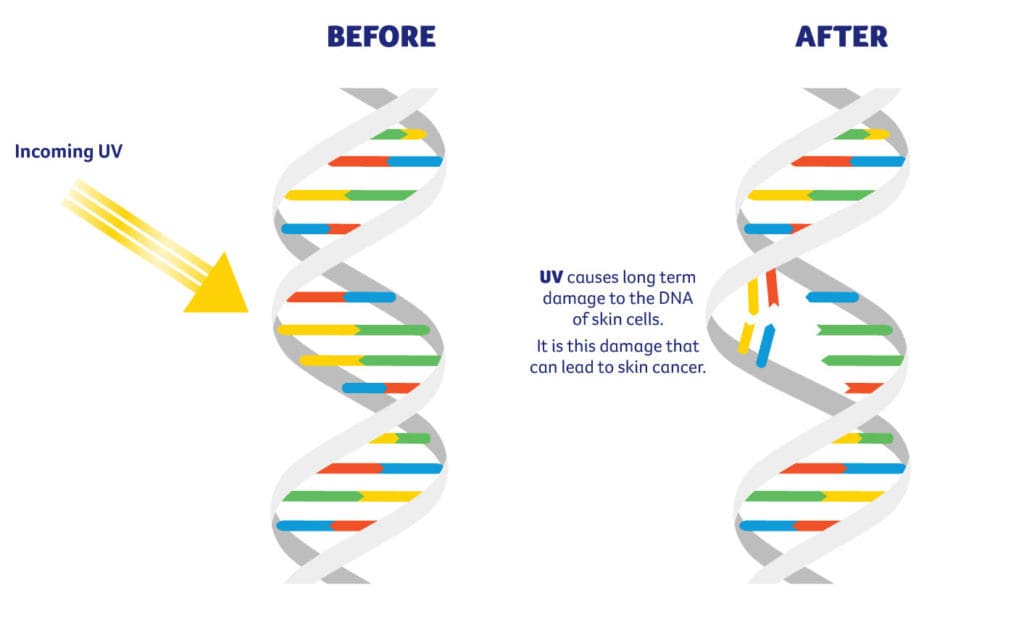
How is DNA damaged by UV light
Deteriorating effects of UV radiation on DNA include formation of various photoproducts, generation of free radicals and subsequent introduction of strand breaks [3]. In response to these threats, cells have evolved multiple mechanisms that counter the damage.
How does DNA get damaged
Endogenous sources of DNA damage include hydrolysis, oxidation, alkylation, and mismatch of DNA bases; sources for exogenous DNA damage include ionizing radiation (IR), ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and various chemicals agents.
How does UV light and other ionizing radiation damage DNA molecules
In fact, UV-A radiation commonly damages DNA in an oxygen-dependent manner that involves photosensitization. This leads to the production of a free radical that then interacts with and oxidizes DNA bases. These oxidized bases don't pair correctly during replication, resulting in mutations (Figure 1).
Is DNA susceptible to UV damage
Ultraviolet (UV) light kills cells by damaging their DNA. The light initiates a reaction between two molecules of thymine, one of the bases that make up DNA.
How does UV damage cells
Higher-energy UV rays are a form of ionizing radiation. This means they have enough energy to remove an electron from (ionize) an atom or molecule. Ionizing radiation can damage the DNA (genes) in cells, which in turn may lead to cancer.
How does UV light denature proteins
Specific amino acids, or protein building blocks, are able to absorb this UV light. Upon absorption, they can transfer an electron to nearby disulfide bonds formed between cysteine (Cys) amino acids, causing them to break.
How does UV cause mutations
Ultraviolet (UV) light induces specific mutations in the cellular and skin genome such as UV-signature and triplet mutations, the mechanism of which has been thought to involve translesion DNA synthesis (TLS) over UV-induced DNA base damage.
What causes oxidative DNA damage
Oxidative DNA damage is an inevitable consequence of cellular metabolism, with a propensity for increased levels following toxic insult. Although more than 20 base lesions have been identified, only a fraction of these have received appreciable study, most notably 8-oxo-2'deoxyguanosine.
Why does DNA fluoresce under UV light
Individual EtBr molecules can squeeze between neighboring base pairs in a DNA double helix in a process known as “intercalation”. When excited with UV light, any EtBr intercalated into the DNA fluoresces and produces a bright orange light. However, because EtBr is a potential mutagen, it must be handled with care.
What UV wavelength damages DNA
Our UV-vis spectroscopy of the genomic DNA showed a sharp cutoff in the ability of DNA to absorb UV at wavelengths 300–305 nm, with a 100-fold decrease in DNA absorption between wavelengths 290 and 305 nm, both before and after laser exposure (Fig.
How does UV light affect RNA
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation can cause several types of damage to RNA: photochemical modification, crosslinking, and oxidative damage. Much of the work describing UV damage to RNA has been carried out in vitro, with a few studies suggesting damage may also occur in vivo under physiologic conditions.
How does UV light affect cell growth
Following a low dose of UV radiation, DNA replication is inhibited and the cells undergo a transient arrest re-entering the cell cycle by 24 h. Instead, a high dose of UV damage leads to an initial replicative arrest followed by death of the cells by apoptosis.
How does UV damage proteins
The majority of UV-induced protein damage appears to be mediated by (1)O2, which reacts preferentially with Trp, His, Tyr, Met, Cys and cystine side chains. Direct photo-oxidation reactions (particularly with short-wavelength UV) and radicals can also be formed via triplet excited states of some of these side chains.
How does UV light affect proteins
The damage produced by UV-C radiation (100–280nm) in organisms and cells is a well known fact. The main reactions of proteins to UV-C radiation consist in the alteration of their secondary structures, exposure of hydrophobic residues, unfolding and aggregation.
Can UV light mutate DNA
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation causes various types of DNA damage, which leads to specific mutations and the emergence of skin cancer in humans, often decades after initial exposure. Different UV wavelengths cause the formation of prominent UV-induced DNA lesions.
How do oxygen radicals damage DNA
Much endogenous DNA damage arises from intermediates of oxygen reduction that either attack the bases or the deoxyribosyl backbone of DNA. Alternatively, oxygen radicals can attack other cellular components such as lipids to generate reactive intermediates that couple to DNA bases.
What causes most DNA damage in skin cells
Human skin is a stratified organ frequently exposed to sun-generated ultraviolet radiation (UVR), which is considered one of the major factors responsible for DNA damage.
Does UV light inhibit DNA replication
Exposure of eukaryotic cells to ultraviolet light results in a temporary inhibition of DNA replication as well as a temporary blockage of DNA fork progression.
What wavelength of UV light causes damage to DNA
Our UV-vis spectroscopy of the genomic DNA showed a sharp cutoff in the ability of DNA to absorb UV at wavelengths 300–305 nm, with a 100-fold decrease in DNA absorption between wavelengths 290 and 305 nm, both before and after laser exposure (Fig.
Does DNA absorb UV light
The purine and pyrimidine bases in DNA strongly absorb ultraviolet light. Double-stranded DNA absorbs less strongly than denatured DNA due to the stacking interactions between the bases.
Does UV light destroy cells
Instead, a high dose of UV damage leads to an initial replicative arrest followed by death of the cells by apoptosis.
How does UV radiation cause mutations
Ultraviolet (UV) light is a form of radiation that acts as a mutagen, an agent that causes mutations in DNA. Exposure to ultraviolet light causes chemical changes that alter the shape of your DNA, and the process that corrects DNA's shape can also cause changes to the DNA code.
How does UV cause damage to cells
Higher-energy UV rays are a form of ionizing radiation. This means they have enough energy to remove an electron from (ionize) an atom or molecule. Ionizing radiation can damage the DNA (genes) in cells, which in turn may lead to cancer.
How does UV damage RNA
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation can cause several types of damage to RNA: photochemical modification, crosslinking, and oxidative damage. Much of the work describing UV damage to RNA has been carried out in vitro, with a few studies suggesting damage may also occur in vivo under physiologic conditions.
How do radicals damage DNA
Endogenous and exogenous sources cause free radical-induced DNA damage in living organisms by a variety of mechanisms. The highly reactive hydroxyl radical reacts with the heterocyclic DNA bases and the sugar moiety near or at diffusion-controlled rates. Hydrated electron and H atom also add to the heterocyclic bases.


